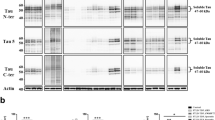
Abstract
Some cases of familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD) leading to frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) are caused by mutations in tau on chromosome 17 (FTDP-17). Certain mutations alter the ratio between four (4R tau) and three (3R tau) repeat tau isoforms whereas cases with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD) mainly have 4R tau brain pathology. We assessed tau mRNA and protein levels in frontal cortex from 15 sporadic FTLD, 21 PSP, 5 CBD, 15 Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and 16 control brains. Moreover, we investigated the disease association and possible tau splicing effects of the tau H1 haplotype. Cases with FTLD and PSP had lower tau mRNA levels than control brains. When analyzing 4R tau and 3R tau mRNA separately, control subjects displayed a 4R tau/3R tau ratio of 0.48. Surprisingly, FTLD brains displayed a more elevated ratio (1.32) than PSP brains (1.12). Also, several FTLD and PSP cases had higher 4R tau/3R tau mRNA than FTDP-17 cases, included as reference tissues, and the ratio increase was seen regardless of underlying histopathology, i.e. both for tau-positive and tau-negative FTLD cases. Furthermore, total tau protein levels were slightly decreased in both FTLD and AD as compared to control subjects. Finally, we confirmed the association of tau H1 with PSP, but could not find any haplotype-related effect on tau exon 10 splicing. In conclusion, we demonstrated increased but largely variable 4R tau/3R tau mRNA ratios in FTLD and PSP cases, suggesting heterogeneous pathophysiological processes within these disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador-Ortiz C, Lin WL, Ahmed Z, Personett D, Davies P, Duara R, Graff-Radford NR, Hutton ML, Dickson DW (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 61:435–445
Andorfer C, Kress Y, Espinoza M, de Silva R, Tucker KL, Barde YA, Duff K, Davies P (2003) Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J Neurochem 86:582–590
Baker M, Litvan I, Houlden H, Adamson J, Dickson D, Perez-Tur J, Hardy J, Lynch T, Bigio E, Hutton M (1999) Association of an extended haplotype in the tau gene with progressive supranuclear palsy. Hum Mol Genet 8:711–715
Bergeron C, Pollanen MS, Weyer L, Lang AE (1997) Cortical degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. A comparison with cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:726–734
Buée L, Delacourte A (1999) Comparative biochemstry of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, FTDP-17 and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:681–693
Chambers CB, Lee JM, Troncoso JC, Reich S, Muma NA (1999) Overexpression of four-repeat tau mRNA isoforms in progressive supranuclear palsy but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 46:325–332
Conrad C, Andreadis A, Trojanowski JQ, Dickson DW, Kang D, Chen X, Wiederholt W, Hansen L, Masliah E, Thal LJ, Katzman R, Xia Y, Saitoh T (1997) Genetic evidence for the involvement of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 41:277–281
de Silva R, Lashley T, Strand C, Shiarli AM, Shi J, Tian J, Bailey KL, Davies P, Bigio EH, Arima K, Iseki E, Murayama S, Kretzschmar H, Neumann M, Lippa C, Halliday G, Mackenzie J, Ravid R, Dickson D, Wszolek Z, Iwatsubo T, Pickering-Brown SM, Holton J, Lees A, Revesz T, Mann DM (2006) An immunohistochemical study of cases of sporadic and inherited frontotemporal lobar degeneration using 3R- and 4R-specific tau monoclonal antibodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:329–340
DeTure M, Ko LW, Yen S, Nacharaju P, Easson C, Lewis J, van Slegtenhorst M, Hutton M, Yen SH (2000) Missense tau mutations identified in FTDP-17 have a small effect on tau-microtubule interactions. Brain Res 853:5–14
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Foster NL, Wilhelmsen K, Sima AAF, Jones MZ, D’Amato CJ, Gilman S (1997) Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17: a consensus conference. Ann Neurol 41:706–715
Goedert M, Jakes R (2005) Mutations causing neurodegenerative tauopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739:240–250
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA (1989) Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 3:519–526
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Potier MC, Ulrich J, Crowther RA (1989) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J 8:393–399
Hauw JJ, Daniel SE, Dickson D, Horoupian DS, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, McKee A, Tabaton M, Litvan I (1994) Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 44:2015–2019
Houlden H, Baker M, Morris HR, MacDonald N, Pickering-Brown S, Adamson J, Lees AJ, Rossor MN, Quinn NP, Kertesz A, Khan MN, Hardy J, Lantos PL, St George-Hyslop P, Munoz DG, Mann D, Lang AE, Bergeron C, Bigio EH, Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Dickson D, Wood NW, Hutton M (2001) Corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy share a common tau haplotype. Neurology 56:1702–1706
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Hyman B, Trojanowski J (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer disease from the National Institute on Aging and the Reagan Institute Working Group on diagnostic criteria for the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 56:1095–1097
Ingelsson M, Fabre S, Lilius L, Andersen C, Viitanen M, Almkvist O, Wahlund L, Lannfelt L (2001) Increased risk for frontotemporal dementia through interaction between tau polymorphisms and apolipoprotein E epsilon4. Neuroreport 12:905–909
Ingelsson M, Ramasamy K, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Skoglund L, Matsui T, Orne J, Kowa H, Augustinack JC, de Silva R, Lees AJ, Lannfelt L, Vanderburg CR, Growdon JH, Frosch MP, Standaert DG, Irizarry MC, Hyman BT (2006) No alteration in tau exon 10 alternative splicing in tangle-bearing neurons of the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol 112:439–449
Leverenz JB, Yu CE, Montine TJ, Steinbart E, Bekris LM, Zabetian C, Kwong LK, Lee VM, Schellenberg GD, Bird TD (2007) A novel progranulin mutation associated with variable clinical presentation and tau, TDP43 and alpha-synuclein pathology. Brain 130:1360–1374
Lilius L, Froelich Fabre S, Basun H, Forsell C, Axelman K, Mattila K, Andreadis A, Viitanen M, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L, Lannfelt L (1999) Tau gene polymorphisms and apolipoprotein E may interact to increase risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 277:29–32
Mackenzie IR, Shi J, Shaw CL, Duplessis D, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2006) Dementia lacking distinctive histology (DLDH) revisited. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:551–559
Mandelkow E-M, Stamer K, Vogel R, Thies E, Mandelkow E (2003) Clogging of axons by tau, inhibition of axonal traffic and starvation of synapses. Neurobiol Aging 24:1079–1085
McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick’s Disease. Arch Neurol 58:1803–1809
Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D (1991) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 41:479–486
Myers AJ, Kaleem M, Marlowe L, Pittman AM, Lees AJ, Fung HC, Duckworth J, Leung D, Gibson A, Morris CM, de Silva R, Hardy J (2005) The H1c haplotype at the MAPT locus is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 14:2399–2404
Nagiec EW, Sampson KE, Abraham I (2001) Mutated tau binds less avidly to microtubules than wildtype tau in living cells. J Neurosci Res 63:268–275
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Pittman A, Myers A, Duckworth J, Bryden L, Hanson M, Abou-Sleiman P, Wood N, Hardy J, Lees A, de Silva R (2004) The structure of the tau haplotype in controls and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Hum Mol Genet 13:1267–1274
Pittman AM, Myers AJ, Abou-Sleiman P, Fung HC, Kaleem M, Marlowe L, Duckworth J, Leung D, Williams D, Kilford L, Thomas N, Morris CM, Dickson DW, Wood NW, Hardy J, Lees AJ, de Silva R (2005) Linkage disequilibrium fine-mapping and haplotype association analysis of the tau gene in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. J Med Genet 42:837–846
Sahara N, Tomiyama T, Mori H (2000) Missense point mutations of tau to segregate with FTDP-17 exhibit site-specific effects on microtubule structure in COS cells: a novel action of R406W mutation. J Neurosci Res 60:380–387
SantaCruz K, Lewis J, Spires T, Paulson J, Kotilinek L, Ingelsson M, Guimaraes A, DeTure M, Ramsden M, McGowan E, Forster C, Yu M, Orne J, Janus C, Mariash A, Kuskowski M, Hyman BT, Hutton M, Ashe KH (2005) Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function. Science 309:476–481
Taniguchi S, McDonagh AM, Pickering-Brown SM, Umeda Y, Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M, Mann DM (2004) The neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with respect to the cytological and biochemical characteristics of tau protein. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:1–18
Vandermeeren M, Mercken M, Vanmechelen E, Six J, van de Voorde A, Martin J-J, Cras P (1993) Detection of tau proteins in normal and Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid with a sensitive sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Neurochem 61:1828–1834
Varani L, Hasegawa M, Spillantini MG, Smith MJ, Murrell JR, Ghetti B, Klug A, Goedert M, Varani G (1999) Structure of tau exon 10 splicing regulatory element RNA and destabilization by mutations of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8229–8234
Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Van Deerlin VM, Bruce J, Shuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, Arnold SE, Masliah E, Galasko D, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2001) Loss of brain tau defines novel sporadic and familial tauopathies with frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 49:165–175
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support from NIH (P50 AG05134, PHS P30 AG10133 and AG08487), the Angel Fund, the Rubenstein Foundation, the Emory ADC, the American Federation of Aging Research Beeson Award (M.C.I.) and the J.D. French Alzheimer Foundation (M.C.I). M.I. was supported by the Swedish Research Council. The brain tissues used in this study were provided by The Massachusetts Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center (MADRC) neuropathology core and The Harvard Brain Bank (supported in part by PHS grant number R24-MH 068855). Karlotta Fitch is acknowledged for technical assistance and Vilmantas Giedraitis for statistical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingelsson, M., Ramasamy, K., Russ, C. et al. Increase in the relative expression of tau with four microtubule binding repeat regions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy brains. Acta Neuropathol 114, 471–479 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0280-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0280-z