Abstract
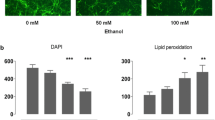
Cerebellar hypoplasia in experimental fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is associated with impaired insulin-stimulated survival signaling. In vitro studies demonstrated that ethanol inhibition of neuronal survival is mediated by apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction. Since insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) regulate energy metabolism, and ethanol can exert its toxic effects by causing oxidative damage to DNA and proteins, we further characterized the effects of chronic gestational exposure to ethanol on mitochondrial gene expression, and the degree to which ethanol inhibition of mitochondrial function is mediated by impaired insulin/IGF responsiveness. Pregnant Long-Evans rats were fed isocaloric liquid diets containing 0, 2, 4.5, 6.5, or 9.25% v/v ethanol from gestation day 6 through delivery. Cerebella harvested on postnatal day 1 were examined for indices of oxidative stress, and mRNA levels of mitochondrial, pro-oxidant, and pro-apoptosis gene expression. Rat primary cerebellar neuron cultures were used to characterize the effects of ethanol (50 mM for 96 h) on insulin and IGF stimulated mitochondrial function and ATP production. Ethanol-exposed cerebella had significantly reduced mRNA levels of mitochondrial genes encoding Complexes II-A, IV, and V, increased expression of p53 and NADPH oxidase (NOX) 1 and 3, and increased immunoreactivity for 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal (HNE) and 8-OHdG in cerebellar granule cells. The activations of p53 and NOX genes were highest in cerebella from pups exposed to the 6.5 or 9.25% ethanol containing diet, whereas the impairments in mitochondrial Complex IV and V expression were similar at low and high levels of ethanol exposure. In vitro experiments confirmed that ethanol treatment reduces neuronal expression of mitochondrial genes encoding Complexes IV and V, impairs mitochondrial function and ATP production, and increases HNE and 8-OHdG immunoreactivity, but they also showed that these effects were not insulin- or IGF-dependent. Together, the results suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and DNA damage in FAS may be largely due to the toxic effects of ethanol rather than specific impairments in insulin or IGF signaling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballinger SW, Patterson C, Yan CN, Doan R, Burow DL, Young CG, Yakes FM, Van Houten B, Ballinger CA, Freeman BA, Runge MS (2000) Hydrogen peroxide- and peroxynitrite-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 86:960–966
Baumber J, Ball BA, Gravance CG, Medina V, Davies-Morel MC (2000) The effect of reactive oxygen species on equine sperm motility, viability, acrosomal integrity, mitochondrial membrane potential, and membrane lipid peroxidation. J Androl 21:895–902
Burd L, Klug MG, Martsolf JT, Kerbeshian J (2003) Fetal alcohol syndrome: neuropsychiatric phenomics. Neurotoxicol Teratol 25:697–705
Camandola S, Poli G, Mattson MP (2000) The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal increases AP-1- binding activity through caspase activation in neurons. J Neurochem 74:159–168
Chen GJ, Xu J, Lahousse SA, Caggiano NL, de la Monte SM (2003) Transient hypoxia causes Alzheimer-type molecular and biochemical abnormalities in cortical neurons: potential strategies for neuroprotection. J Alzheimers Dis 5:209–228
Chinopoulos C, Tretter L, Adam-Vizi V (1999) Depolarization of in situ mitochondria due to hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in nerve terminals: inhibition of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. J Neurochem 73:220–228
Clarren SK, Alvord EJ, Sumi SM, Streissguth AP, Smith DW (1978) Brain malformations related to prenatal exposure to ethanol. J Pediatr 92:64–67
da Silva AM, Payao SL, Borsatto B, Bertolucci PH, Smith MA (2000) Quantitative evaluation of the rRNA in Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 120:57–64
de la Monte S, Wands J (2005) Review of insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression, signaling, and malfunction in the central nervous system: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 7:45–61
de la Monte SM, Ganju N, Banerjee K, Brown NV, Luong T, Wands JR (2000) Partial rescue of ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by growth factor activation of phosphoinositol-3-kinase. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:716–726
de la Monte SM, Ganju N, Wands JR (1999) Microtiter immunocytochemical ELISA assay: a novel and highly sensitive method of quantifying immunoreactivity. Biotecniques 26:1073–1076
de la Monte SM, Neely TR, Cannon J, Wands JR (2001) Ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated mitochondrial function in cerebellar granule neurons. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:1950–1960
de la Monte SM, Wands JR (2001) Mitochondrial DNA damage and impaired mitochondrial function contribute to apoptosis of insulin-stimulated ethanol-exposed neuronal cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:898–906
de la Monte SM, Wands JR (2002) Chronic gestational exposure to ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated survival and mitochondrial function in cerebellar neurons. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci 59:882–893
de la Monte SM, Xu XJ, Wands JR (2005) Ethanol inhibits insulin expression and actions in the developing brain. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:1131–1145
Gao HM, Liu B, Hong JS (2003) Critical role for microglial NADPH oxidase in rotenone-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 23:6181–6187
Hallak H, Seiler AE, Green JS, Henderson A, Ross BN, Rubin R (2001) Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I signaling by ethanol in neuronal cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1058–1064
Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:425–479
Hong-Brown LQ, Frost RA, Lang CH (2001) Alcohol impairs protein synthesis and degradation in cultured skeletal muscle cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1373–1382
Ikonomidou C, Bittigau P, Ishimaru MJ, Wozniak DF, Koch C, Genz K, Price MT, Stefovska V, Horster F, Tenkova T, Dikranian K, Olney JW (2000) Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science 287:1056–1060
Karl PI, Fisher SE (1993) Ethanol alters hormone production in cultured human placental trophoblasts. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 17:816–821
Lam YA, Pickart CM, Alban A, Landon M, Jamieson C, Ramage R, Mayer RJ, Layfield R (2000) Inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9902–9906
Lee RD, An SM, Kim SS, Rhee GS, Kwack SJ, Seok JH, Chae SY, Park CH, Choi YW, Kim HS, Cho HY, Lee BM, Park KL (2005) Neurotoxic effects of alcohol and acetaldehyde during embryonic development. J Toxicol Environ Health A 68:2147–2162
Lewis PD (1985) Neuropathological effects of alcohol on the developing nervous system. Alcohol Alcohol 20:195–200
Liesi P (1997) Ethanol-exposed central neurons fail to migrate and undergo apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 48:439–448
Maier SE, Cramer JA, West JR, Sohrabji F (1999) Alcohol exposure during the first two trimesters equivalent alters granule cell number and neurotrophin expression in the developing rat olfactory bulb. J Neurobiol 41:414–423
Maier SE, Miller JA, Blackwell JM, West JR (1999) Fetal alcohol exposure and temporal vulnerability: regional differences in cell loss as a function of the timing of binge-like alcohol exposure during brain development. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:726–734
Maier SE, West JR (2001) Regional differences in cell loss associated with binge-like alcohol exposure during the first two trimesters equivalent in the rat. Alcohol 23:49–57
Mander P, Brown GC (2005) Activation of microglial NADPH oxidase is synergistic with glial iNOS expression in inducing neuronal death: a dual-key mechanism of inflammatory neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation 2:20
Mattson SN, Schoenfeld AM, Riley EP (2001) Teratogenic effects of alcohol on brain and behavior. Alcohol Res Health 25:185–191
Minana R, Climent E, Barettino D, Segui JM, Renau-Piqueras J, Guerri C (2000) Alcohol exposure alters the expression pattern of neural cell adhesion molecules during brain development. J Neurochem 75:954–964
Munzel T, Daiber A, Mulsch A (2005) Explaining the phenomenon of nitrate tolerance. Circ Res 97:618–628
Nikolic M, Dudek H, Kwon YT, Ramos YF, Tsai LH (1996) The cdk5/p35 kinase is essential for neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev 10:816–825
O’Malley KD, Nanson J (2002) Clinical implications of a link between fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Can J Psychiatry 47:349–354
Olney JW, Ishimaru MJ, Bittigau P, Ikonomidou C (2000) Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Apoptosis 5:515–521
Ramachandran V, Perez A, Chen J, Senthil D, Schenker S, Henderson GI (2001) In utero ethanol exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction, which can result in apoptotic cell death in fetal brain: a potential role for 4-hydroxynonenal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:862–871
Soscia SJ, Tong M, Xu XJ, Cohen AC, Chu J, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2006) Chronic gestational exposure to ethanol causes insulin and IGF resistance and impairs acetylcholine homeostasis in the brain. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2039–2056
Swanson DJ, King MA, Walker DW, Heaton MB (1995) Chronic prenatal ethanol exposure alters the normal ontogeny of choline acetyltransferase activity in the rat septohippocampal system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:1252–1260
Volk B (1984) Cerebellar histogenesis and synaptic maturation following pre- and postnatal alcohol administration. An electron-microscopic investigation of the rat cerebellar cortex. Acta Neuropathol 63:57–65
Xu J, Yeon JE, Chang H, Tison G, Chen GJ, Wands J, de la Monte S (2003) Ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated neuronal survival in the developing brain: role of PTEN phosphatase. J Biol Chem 278:26929–26937
Yanni PA, Lindsley TA (2000) Ethanol inhibits development of dendrites and synapses in rat hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 120:233–243
Zhang FX, Rubin R, Rooney TA (1998) Ethanol induces apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons by inhibiting insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling. J Neurochem 71:196–204
Acknowledgments
Supported by grants AA02666, AA-02169, AA-11431, AA12908, and K24 AA-16126 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, J., Tong, M. & de la Monte, S.M. Chronic ethanol exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in immature central nervous system neurons. Acta Neuropathol 113, 659–673 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0199-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0199-4