Abstract
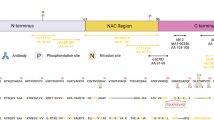
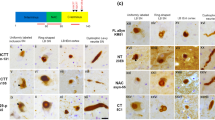
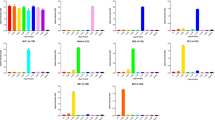
Immunohistochemical detection of protein components of pathological inclusions is widely used for neuropathological diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders. However, different antibodies and antigen unmasking methods may account for variability between research studies and thus may affect diagnostic accuracy. Using two different antibodies raised against either a segment (184–200 aa) or the full length of human recombinant brain-specific tubulin polymerization promoting protein TPPP/p25, we immunohistochemically screened neurodegenerative disorders, both with and without pathological α-synuclein structures. We tested three different epitope unmasking methods, we applied laser confocal microscopy to evaluate double immunolabelling, and we compared the amount of structures exhibiting TPPP/p25 and α-synuclein immunoreactivity. We demonstrate that there are a variety of staining patterns depending on the epitope retrieval method and antibody used. The antibody raised against aa 184–200 segment of TPPP/p25 is better in immunolabelling the majority of α-synuclein immunopositive neuronal and glial pathological profiles detectable in Parkinson’s disease, diffuse Lewy-body disease, and multiple system atrophy, in addition to immunostaining some extracellular huntingtin immunoreactive structures, lipofuscin, and neuromelanin particles. In contrast, the one raised against the full-length human recombinant TPPP/p25 is more suitable to immunodetect normal oligodendrocytes. Exposition of the segment aa 184–200 of TPPP/p25 in the aggregates of pathological inclusions renders this antibody a reliable marker of all types of α-synucleinopathies and suggests a role for TPPP/p25 in the aggregation process of some neurodegenerative conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alafuzoff I, Pikkarainen M, Al-Sarraj S, Arzberger T, Bell J, Bodi I, Bogdanovic N, Budka H, Bugiani O, Ferrer I, Gelpi E, Giaccone G, Graeber MB, Hauw JJ, Kamphorst W, King A, Kopp N, Korkolopoulou P, Kovacs GG, Meyronet D, Parchi P, Patsouris E, Preusser M, Ravid R, Roggendorf W, Seilhean D, Streichenberger N, Thal DR, Kretzschmar H (2006) Interlaboratory comparison of assessments of Alzheimer disease-related lesions: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:740–757
Baker KG, Huang Y, McCann H, Gai WP, Jensen PH, Halliday GM (2006) P25alpha immunoreactive but alpha-synuclein immunonegative neuronal inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:193–195
Campbell BC, McLean CA, Culvenor JG, Gai WP, Blumbergs PC, Jakala P, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Li QX (2001) The solubility of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy differs from that of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 76:87–96
Charles V, Mezey E, Reddy PH, Dehejia A, Young TA, Polymeropoulos MH, Brownstein MJ, Tagle DA (2000) Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity of huntingtin polyglutamine aggregates in striatum and cortex of Huntington’s disease patients and transgenic mouse models. Neurosci Lett 289:29–32
Croisier E, MRes DE, Deprez M, Goldring K, Dexter DT, Pearce RK, Graeber MB, Roncaroli F (2006) Comparative study of commercially available anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:351–356
Dickson DW (2005) Required techniques and useful molecular markers in the neuropathologic diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 109:14–24
Fasano M, Giraudo S, Coha S, Bergamasco B, Lopiano L (2003) Residual substantia nigra neuromelanin in Parkinson’s disease is cross-linked to alpha-synuclein. Neurochem Int 42:603–606
Halliday GM, Cullen KM, Kril JJ, Harding AJ, Harasty J (1996) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunohistochemistry in human cortex: a quantitative study using different antisera. Neurosci Lett 209:29–32
Hlavanda E, Kovacs J, Olah J, Orosz F, Medzihradszky KF, Ovadi J (2002) Brain-specific p25 protein binds to tubulin and microtubules and induces aberrant microtubule assemblies at substoichiometric concentrations. Biochemistry 41:8657–8664
Jellinger KA (2006) P25alpha immunoreactivity in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:112
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Kovacs GG, Head MW, Hegyi I, Bunn TJ, Flicker H, Hainfellner JA, McCardle L, Laszlo L, Jarius C, Ironside JW, Budka H (2002) Immunohistochemistry for the prion protein: comparison of different monoclonal antibodies in human prion disease subtypes. Brain Pathol 12:1–11
Kovacs GG, Flicker H, Budka H (2003) Immunostaining for ubiquitin: efficient pretreatment. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29:174–177
Kovacs GG, Laszlo L, Kovacs J, Jensen PH, Lindersson E, Botond G, Molnar T, Perczel A, Hudecz F, Mezo G, Erdei A, Tirian L, Lehotzky A, Gelpi E, Budka H, Ovadi J (2004) Natively unfolded tubulin polymerization promoting protein TPPP/p25 is a common marker of alpha-synucleinopathies. Neurobiol Dis 17:155–162
Lindersson E, Lundvig D, Petersen C, Madsen P, Nyengaard JR, Hojrup P, Moos T, Otzen D, Gai WP, Blumbergs PC, Jensen PH (2005) p25alpha Stimulates alpha-synuclein aggregation and is co-localized with aggregated alpha-synuclein in alpha-synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 280:5703–5715
Martin CP, Vazquez J, Avila J, Moreno FJ (2002) P24, a glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK 3) inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1586:113–122
Mori F, Tanji K, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2002) Demonstration of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in neuronal and glial cytoplasm in normal human brain tissue using proteinase K and formic acid pretreatment. Exp Neurol 176:98–104
Nishie M, Mori F, Houzen H, Yamaguchi J, Jensen PH, Wakabayashi K (2006) Oligodendrocytes within astrocytes (“emperipolesis”) in the cerebral white matter in hepatic and hypoglycemic encephalopathy. Neuropathology 26:62–65
Olah J, Tokesi N, Vincze O, Horvath I, Lehotzky A, Erdei A, Szajli E, Medzihradszky KF, Orosz F, Kovacs GG, Ovadi J (2006) Interaction of TPPP/p25 protein with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and their co-localization in Lewy bodies. FEBS Lett 580:5807–5814
Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S, Dikkes P, Tsai LH (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402:615–622
Preusser M, Lehotzky A, Budka H, Ovádi J, Kovács GG (2006) TPPP/p25 in brain tumours: expression in non-neoplastic oligodendrocytes but not oligodendroglioma cells. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) (in press)
Prusiner SB (2001) Shattuck lecture–neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N Engl J Med 344:1516–1526
Skjoerringe T, Lundvig DM, Jensen PH, Moos T (2006) P25alpha/Tubulin polymerization promoting protein expression by myelinating oligodendrocytes of the developing rat brain. J Neurochem 99:333–342
Takahashi M, Tomizawa K, Ishiguro K, Sato K, Omori A, Sato S, Shiratsuchi A, Uchida T, Imahori K (1991) A novel brain-specific 25 kDa protein (p25) is phosphorylated by a Ser/Thr-Pro kinase (TPK II) from tau protein kinase fractions. FEBS Lett 289:37–43
Takahashi M, Tomizawa K, Fujita SC, Sato K, Uchida T, Imahori K (1993) A brain-specific protein p25 is localized and associated with oligodendrocytes, neuropil, and fiber-like structures of the CA3 hippocampal region in the rat brain. J Neurochem 60:228–235
Tirian L, Hlavanda E, Olah J, Horvath I, Orosz F, Szabo B, Kovacs J, Szabad J, Ovadi J (2003) TPPP/p25 promotes tubulin assemblies and blocks mitotic spindle formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13976–13981
Tribl F, Marcus K, Meyer HE, Bringmann G, Gerlach M, Riederer P (2006) Subcellular proteomics reveals neuromelanin granules to be a lysosome-related organelle. J Neural Transm 113:741–749
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to Gerda Ricken and Helga Flicker for their technical assistance. This work was supported in part by EU Grant FP6, BNEII No LSHM-CT-2004-503039, by the Austrian-Hungarian Intergovernmental Cooperation (A14/04), by FP6-2003-LIFESCIHEALTH-I: Bio-Sim, by NKFP-MediChem2 1/A/005/2004, and by OTKA T-046071 to JO.GGK receives Bolyai fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovács, G.G., Gelpi, E., Lehotzky, A. et al. The brain-specific protein TPPP/p25 in pathological protein deposits of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol 113, 153–161 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0167-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0167-4