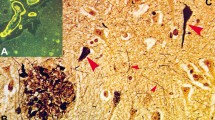
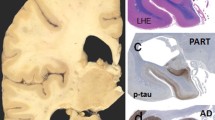
Abstract
Neurofibrillary tangle predominant dementia (NFTPD) is a subset of late onset dementia, clinically different from traditional “plaque and tangle” Alzheimer disease (AD): later onset, shorter duration, less severe cognitive impairment, and almost absence of ApoE ε4. Neuropathology reveals abundant allocortical neurofibrillary pathology with no or few isocortical tau lesions, absence of neuritic plaques, absence or scarcity of amyloid deposits, but neurofibrillary changes comprising both 3 and 4 repeat (3R and 4R) tau immunohistochemistry are not significantly different from those in classical AD. Comparing 51 autopsy cases of NFTPD with 244 classical AD subjects, the nosology of NFTPD and its differences from AD are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano N, Mizutani T, Otani T, Kase A, Saitoh A, Matsushita M, Yagishita S (1994) Clinicopathological investigations of atypical senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuropathology 14:127–136
Arai T, Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Tsuchiya K, Iritani S, Ishiguro K, Yagishita S, Oda T, Odawara T, Iseki E (2003) Different immunoreactivities of the microtubule-binding region of tau and its molecular basis in brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Pick’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 105:489–498
Attems A, Quass M, Jellinger KA (2006) Tau and alpha-synuclein brainstem pathology in Alzheimer disease. Relations with extrapyramidal signs. Acta Neuropathol DOI 10.1007/s00401-006-0146-9
Attems J, Jellinger KA (2006) Tau and alpha-synuclein brainstem pathology in Alzheimer disease (abstract). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33:2–3
Attems J, Jellinger KA (2006) Hippocampal sclerosis in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. Neurology 66:775
Bales KR, Verina T, Dodel RC, Du Y, Altstiel L, Bender M, Hyslop P, Johnstone EM, Little SP, Cummins DJ, Piccardo P, Ghetti B, Paul SM (1997) Lack of apolipoprotein E dramatically reduces amyloid beta-peptide deposition. Nat Genet 17:263–264
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 477:90–99
Bancher C, Jellinger KA (1994) Neurofibrillary tangle predominant form of senile dementia of Alzheimer type: a rare subtype in very old subjects. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:565–570
Bancher C, Egensperger R, Kosel S, Jellinger K, Graeber MB (1997) Low prevalence of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele in the neurofibrillary tangle predominant form of senile dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 94:403–409
Beach TG, Sue L, Scott S, Layne K, Newell A, Walker D, Baker M, Sahara N, Yen SH, Hutton M, Caselli R, Adler C, Connor D, Sabbagh M (2003) Hippocampal sclerosis dementia with tauopathy. Brain Pathol 13:263–278
Berg L, McKeel DW Jr, Miller JP, Baty J, Morris JC (1993) Neuropathological indexes of Alzheimer’s disease in demented and nondemented persons aged 80 years and older. Arch Neurol 50:349–358
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 82:239–259
Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T, Kretzschmar H, Del Tredici K (2006) Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:389–404
Buee L, Delacourte A (1999) Comparative biochemistry of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, FTDP-17 and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:681–693
Cairns NJ, Grinber LT, Liscic RM, Tu P, Morris JC (2006) Expanding the neuropathological spectrum of frontotemporal lobar degenerations: review of 833 prospectively assessed dementia cases (abstract). J Neural Transm 113:VII
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Risch NJ, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC Jr, Rimmler JB, Locke PA, Conneally PM, Schmader KE et al (1994) Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 7:180–184
Corder EH, Lannfelt L, Viitanen M, Corder LS, Manton KG, Winblad B, Basun H (1996) Apolipoprotein E genotype determines survival in the oldest old (85 years or older) who have good cognition. Arch Neurol 53:418–422
de Silva R, Lashley T, Gibb G, Hanger D, Hope A, Reid A, Bandopadhyay R, Utton M, Strand C, Jowett T, Khan N, Anderton B, Wood N, Holton J, Revesz T, Lees A (2003) Pathological inclusion bodies in tauopathies contain distinct complements of tau with three or four microtubule-binding repeat domains as demonstrated by new specific monoclonal antibodies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29:288–302
de Silva R, Lashley T, Strand C, Shiarli AM, Shi J, Tian J, Bailey KL, Davies P, Bigio EH, Arima K, Iseki E, Murayama S, Kretzschmar H, Neumann M, Lippa C, Halliday G, Mackenzie J, Ravid R, Dickson D, Wszolek Z, Iwatsubo T, Pickering-Brown SM, Holton J, Lees A, Revesz T, Mann DM (2006) An immunohistochemical study of cases of sporadic and inherited frontotemporal lobar degeneration using 3R- and 4R-specific tau monoclonal antibodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:329–340
Delacourte A, Buee L (2000) Tau pathology: a marker of neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 13:371–376
Delacourte A (2005) Alzheimer’s disease: a true tauopathy fueled by amyloid precursor protein dysfunction. In: Hanin I, Cacabelos R, Fisher A (eds) Progress in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 301–307
Delaere P, Duyckaerts C, He Y, Piette F, Hauw JJ (1991) Subtypes and differential laminar distributions of beta A4 deposits in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship with the intellectual status of 26 cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 81:328–335
Delaere P, He Y, Fayet G, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ (1993) Beta A4 deposits are constant in the brain of the oldest old: an immunocytochemical study of 20 French centenarians. Neurobiol Aging 14:191–194
Dickson DE (2001) Progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. In: Hof RR, Mobbs LCK (eds) Functional neurobiology of aging. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 155–171
Dickson DW, Davies P, Bevona C, Van Hoeven KH, Factor SM, Grober E, Aronson MK, Crystal HA (1994) Hippocampal sclerosis: a common pathological feature of dementia in very old (> or =80 years of age) humans. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:212–221
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Dickson DW (2004) Sporadic tauopathies: Pick’s disease, corticobasal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy and argyrophilic grain disease. In: Esiri MM, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (eds) The neuropathology of dementia, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 227–256
Dickson DW (2005) Required techniques and useful molecular markers in the neuropathologic diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 109:14–24
Dickson DW (2006) Differential diagnosis of the sporadic tauopathies (abstract). Brain Pathol 16(suppl 1):S5
Ding ZT, Wang Y, Jiang YP, Yoshida M, Mimuro M, Inagaki T, Iwase T, Hashizume Y (2006) Argyrophilic grain disease: frequency and neuropathology in centenarians. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:320–328
Duyckaerts C (2005) Atypical parkinsonian disorders. In: Litvan I (eds) Current clinical neurology: atypical parkinsonian disorders. Humana Press. Totowa, pp 111–138
Enstice KM, Hladik CL, Stark JM, Bigio EH, White CL (2006) Preferential 3-repeat tau staining of extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in tangle predominant senile dementia (abstract). Brain Pathol 16(suppl 1):S49
Feany MB, Dickson DW (1995) Widespread cytoskeletal pathology characterizes corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 146:1388–1396
Feany MB, Dickson DW (1996) Neurodegenerative disorders with extensive tau pathology: a comparative study and review. Ann Neurol 40:139–148
Feany MB, Mattiace LA, Dickson DW (1996) Neuropathologic overlap of progressive supranuclear palsy, Pick’s disease and corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:53–67
Fujino Y, Wang DS, Thomas N, Espinoza M, Davies P, Dickson DW (2005) Increased frequency of argyrophilic grain disease in Alzheimer disease with 4R tau-specific immunohistochemistry. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:209–214
Giannakopoulos P, Hof PR, Surini M, Michel JP, Bouras C (1993) Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in the cerebral cortex of nonagenarians and centenarians. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 85:602–610
Greenberg SM, Vonsattel JP, Segal AZ, Chiu RI, Clatworthy AE, Liao A, Hyman BT, Rebeck GW (1998) Association of apolipoprotein E epsilon2 and vasculopathy in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 50:961–965
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Iijima M, Tabira T, Goedert M (1999) FTDP-17 mutations N279K and S305N in tau produce increased splicing of exon 10. FEBS Lett 443:93–96
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D, Goate A, Morris JC, Wilhelmsen KC, Schellenberg GD, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1998) Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science 282:1914–1917
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Hyman BT, Augustinack JC, Ingelsson M (2005) Transcriptional and conformational changes of the tau molecule in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739:150–157
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Haga C, Tanno E, Tokuda T, Ikeda S (1995) Thorn-shaped astrocytes: possibly secondarily induced tau-positive glial fibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 90:620–625
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Arai T, Sahara N, Mori H, Usami M, Sakata M, Mizutani T, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (1997) A subset of senile dementia with high incidence of the apolipoprotein E epsilon2 allele. Ann Neurol 41:693–695
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Sahara N, Mori H, Usami M, Sakata M, Mizutani T, Wakabayashi K, Takahasi H (1997) Senile dementia with abundant neurofibrillary tangles without accompanying senile plaques: a subset of senile dementia with high incidence of the ApoE epsilon2 allele. In: Iqbal K, Winblad B, Nishimura T, Takeda M, Wisniewski HM (eds) Alzheimer’s disease: biology, diagnosis and therapeutics. Wiley, New York, pp 257–265
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Arai T, Oda T, Kato M, Iseki E, Kosaka K, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (1999) Clinical aspects of ‘senile dementia of the tangle type’: a subset of dementia in the senium separable from late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10:6–11
Ingelsson M, Ramasamy K, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Skoglund L, Matsui T, Orne J, Kowa H, Raju S, Vanderburg CR, Augustinack JC, de Silva R, Lees AJ, Lannfelt L, Growdon JH, Frosch MP, Standaert DG, Irizarry MC, Hyman BT (2006) No alteration in tau exon 10 alternative splicing in tangle-bearing neurons of the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 112:439–449
Iseki E, Togo T, Suzuki K, Katsuse O, Marui W, de Silva R, Lees A, Yamamoto T, Kosaka K (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies from the perspective of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 105:265–270
Iseki E, Yamamoto R, Minegishi M, Togo T, Katsuse O, Kosaka K, Akiyama H, Tsuchiya K, de Silva R, Andrew L, Arai H (2006) Immunohistochemical investigation of neurofibrillary tangles and their tau informs in brains of limbic neurofibrillary tangle formation. Neurosci Lett 405:29–33
Ishizawa T, Ko LW, Cookson N, Davias P, Espinoza M, Dickson DW (2002) Selective neurofibrillary degeneration of the hippocampal CA2 sector is associated with four-repeat tauopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:1040–1047
Itoh Y, Yamada M, Suematsu N, Matsushita M, Otomo E (1998) An immunohistochemical study of centenarian brains: a comparison. J Neurol Sci 157:73–81
Jellinger KA, Bancher C (1998) Senile dementia with tangles (tangle predominant form of senile dementia). Brain Pathol 8:367–376
Jellinger KA (2003) Plaque-predominant and tangle-predominant variants of Alzheimer’s disease. In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 66–68
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2003) Incidence of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer disease: a postmortem study. Acta Neuropathol 105:14–17
Jellinger KA (2005) Neuropathology and tau. In: Hanin I, Cacabelos R, Fisher A (eds) Recent progress in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Taylor & Francis, New York, pp 317–327
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2005) Alzheimer pathology in the olfactory bulb. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31:203
Jellinger KA (2006) A view on early diagnosis of dementias from neuropathology. In: Herholz K, Morris C, Perani D (eds) Early diagnosis of dementias. Taylor & Francis, New York, pp 311–428
Kitamura T, Sugimori K, Sudou S, Shimazaki M, Uotani C, Kobayashi K, Koshino Y (2006) Relationship between microtubule-binding repeats and morphology of neurofibrillary tangle in Alzheimer’s disease (abstract). Neuropathology 26:A8
Knopman DS (2003) Alzheimer type dementia. In: Dickson erani D (eds) Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 24–39
Komori T, Arai N, Oda M, Nakayama H, Mori H, Yagishita S, Takahashi T, Amano N, Murayama S, Murakami S, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Sasaki S, Iwata M (1998) Astrocytic plaques and tufts of abnormal fibers do not coexist in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 96:401–408
Kosaka K, Iseki E, Odawara T, Hino H, Kanai A, Kato M (1997) Limbic neurofibrillary tangle dementia (LNTD) (abstract). Brain Pathol 7:1114
LaDu MJ, Lukens JR, Reardon CA, Getz GS (1997) Association of human, rat, and rabbit apolipoprotein E with beta-amyloid. J Neurosci Res 49:9–18
Lee VM, Kenyon TK, Trojanowski JQ (2005) Transgenic animal models of tauopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739:251–259
Ma J, Yee A, Brewer HB Jr, Das S, Potter H (1994) Amyloid-associated proteins alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and apolipoprotein E promote assembly of Alzheimer beta-protein into filaments. Nature 372:92–94
Matsumoto S, Udaka F, Kameyama M, Kusaka H, Ito H, Imai T (1996) Subcortical neurofibrillary tangles, neuropil threads, and argentophilic glial inclusions in corticobasal degeneration. Clin Neuropathol 15:209–214
Mirra SS, Gearing M, McKeel DW Jr, Crain BJ, Hughes JP, van Belle G, Heyman A (1994) Interlaboratory comparison of neuropathology assessments in Alzheimer’s disease: a study of the consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s disease (CERAD). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 53:303–315
Mirra SS, Hyman BT (2002) Aging and dementia. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s Neuropathology, 7th edn. E. Arnold, London, pp 195–271
Mizutani T, Shimada H (1992) Neuropathological background of twenty-seven centenarian brains. J Neurol Sci 108:168–177
Nicoll JA, Burnett C, Love S, Graham DI, Dewar D, Ironside JW, Stewart J, Vinters HV (1997) High frequency of apolipoprotein E epsilon 2 allele in hemorrhage due to cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Ann Neurol 41:716–721
Nishimura M, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Akiguchi I, Kimura J (1995) Immunocytochemical characterization of glial fibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol 146:1052–1058
Noda K, Sasaki K, Fujimi K, Wakisaki Y, Tanizaki Y, Wakugawa Y, Iida M, Iwaki T (2006) Neuropathological study on senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type (tangle-only dementia) in general population: the Hisayama study (abstract). Neuropathology 26:A9
Rebeck GW, Reiter JS, Strickland DK, Hyman BT (1993) Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron 11:575–580
Reed LA, Grabowski TJ, Schmidt ML, Morris JC, Goate A, Solodkin A, Van Hoesen GW, Schelper RL, Talbot CJ, Wragg MA, Trojanowski JQ (1997) Autosomal dominant dementia with widespread neurofibrillary tangles. Ann Neurol 42:564–572
Sergeant N, David JP, Goedert M, Jakes R, Vermersch P, Buee L, Lefranc D, Wattez A, Delacourte A (1997) Two-dimensional characterization of paired helical filament-tau from Alzheimer’s disease: demonstration of an additional 74-kDa component and age-related biochemical modifications. J Neurochem 69:834–844
Spires TL, Orne JD, SantaCruz K, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Ashe KH, Hyman BT (2006) Region-specific dissociation of neuronal loss and neurofibrillary pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Am J Pathol 168:1598–1607
Takahashi T, Amano N, Hanihara T, Nagatomo H, Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Yamaoka K, Toda H, Tanabe T (1996) Corticobasal degeneration: widespread argentophilic threads and glia in addition to neurofibrillary tangles: similarities of cytoskeletal abnormalities in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Sci 138:66–77
Thal DR, Braak H (2005) Post-mortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Pathologe 26:201–213
Tiraboschi P, Yaari R, Hansen LA, Ho G, Thal LJ, Salmon D, Corey-Bloom J (2006) Neurofibrillary tangle-predominant dementia (abstract). Neurology 66(suppl 2):A379
Togo T, Sahara N, Yen SH, Cookson N, Ishizawa T, Hutton M, de Silva R, Lees A, Dickson DW (2002) Argyrophilic grain disease is a sporadic 4-repeat tauopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:547–556
Togo T, Akiyama H, Iseki E, Uchikado H, Kondo H, Ikeda K, Tsuchiya K, de Silva R, Lees A, Kosaka K (2004) Immunohistochemical study of tau accumulation in early stages of Alzheimer-type neurofibrillary lesions. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 107:504–508
Tolnay M, Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Ulrich J, Langui D, Probst A (1997) Argyrophilic grain disease: widespread hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in limbic neurons. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 93:477–484
Tolnay M, Sergeant N, Ghestem A, Chalbot S, De Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Probst A, Delacourte A (2002) Argyrophilic grain disease and Alzheimer’s disease are distinguished by their different distribution of tau protein isoforms. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 104:425–434
Tolnay M, Villoz N, Probst A, Miserez AR (2003) Apolipoprotein E genotype in senile dementia with tangles differs from Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29:80–84
Tolnay M, Clavaguera F (2004) Argyrophilic grain disease: a late-onset dementia with distinctive features among tauopathies. Neuropathology 24:269–283
Tsuboi Y, Josephs KA, Cookson N, Dickson DW (2003) ApoE E4 is a determinant for Alzheimer type pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 60:240–245
Ulrich J, Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Dukas L, Staehelin HB (1992) Abundant neurofibrillary tangles without senile plaques in a subset of patients with senile dementia. Neurodegeneration 1:257–284
Yamada M, Itoh Y, Otomo E, Suematsu N, Matsushita M (1996) Dementia of the Alzheimer type and related dementias in the aged: DAT subgroups and senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type. Neuropathology 16:89–98
Yamada M, Itoh Y, Sodeyama N, Suematsu N, Otomo E, Matsushita M, Mizusawa H (2001) Senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 12:117–126
Yamada M (2002) Risk factors for cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly. Ann N Y Acad Sci 977:37–44
Yamada M (2003) Senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type (tangle-only dementia): neuropathological criteria and clinical guidelines for diagnosis. Neuropathology 23:311–317
Yamazaki M, Hashimoto T, Nagasao J, Mori O, Tsuchiya K, Katayama Y, Oyanagi K (2006) Coexistence of both 3- and 4-repeat tau isoforms in glia among tauopathies (abstract). Brain Pathol 16(suppl 1):S48
Zhukareva V, Shah K, Uryu K, Braak H, Del Tredici K, Sundarraj S, Clark C, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Biochemical analysis of tau proteins in argyrophilic grain disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Pick’s disease: a comparative study. Am J Pathol 161:1135–1141
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Mrs. V. Rappelsberger for excellent laboratory work, Mr. E. Mitter-Ferstl, PhD, for secretarial and computer work, and Mr. D.W. Dickson, MD, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, USA, for valuable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellinger, K.A., Attems, J. Neurofibrillary tangle-predominant dementia: comparison with classical Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol 113, 107–117 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0156-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0156-7