Abstract
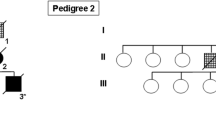
We report a familial disorder occurring in three patients that presented as frontotemporal dementia (FTD). A neuropathological study was performed in a 58-year-old patient, who developed FTD 2 years prior to the onset of motor neuron disease (MND), and died at age 62. Lesions indicative of associated MND were observed: neuronal loss in the anterior horns of the spinal cord, Bunina bodies, axonal spheroids, degeneration of the pyramidal tracts, and of FTD: decreased neuronal density and laminar microvacuolation of layers II and III in the frontal and temporal cortex. Ubiquitin-only-immunoreactive changes were found in the spinal cord and medulla, but were absent from the temporal and frontal cortex. There were also widespread deposits of various neuronal and glial inclusions containing abnormally phosphorylated tau protein, the Western blotting pattern of which was characterized by two major bands of 64 and 69 kDa. There were no abnormalities of the entire coding sequences of microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) and copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD 1 ) genes. Our results suggest that FTD associated with MND can be caused by a larger spectrum of neuropathological lesions than commonly accepted.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basak M, Erturk M, Oflazoglu B, Ozel A, Yildiz GB, Forta H (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 105:395–399
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL, World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases (2000) El Escorial revisited. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:293–299
Brown J, Ashworth A, Gydesen S, Sorensen A, Hardy J, Collinge J (1995) Familial non-specific dementias maps to chromosome 3. Hum Mol Genet 45:1625–1628
Buée L, Delacourte A (1999) Comparative biochemistry of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, FTDP-17 and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:681–693
Dickson DW (ed) (2003) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, p 414
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Dumanchin C, Camuzat A, Campion D, Verpillat P, Hannequin D, Dubois B, Saugier-Veber P, Martin C, Penet C, Charbonnier F, Agid Y, Frebourg T, Brice A (1998) Segregation of a missense mutation in the microtubule-associated protein tau gene with familial frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism. Hum Mol Genet 7:1825–1829
Ghetti B, Hutton M, Wszolek ZK (2003) Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 associated with tau gene mutations (FTDP-17) In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 86–102
Gunnarsson LG, Dahlbom K, Strandman E (1991) Motor neuron disease and dementia reported among 13 members of a single family. Acta Neurol Scand 84:429–433
Hauw JJ, Daniel SE, Dickson D, Horoupian DS, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, McKee A, Tabaton M, Litvan I (1994) Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy) Neurology 44:2015–2019
Heutink P (2000) Untangling tau-related dementia. Hum Mol Genet 9:979–986
Hosler BA, Siddique T, Sapp PC, Sailor W, Huang MC, Hossain A, Daube JR, Nance M, Fan C, Kaplan J, Hung WY, McKenna-Yasek D, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Horvitz RH, Horvitz RHB Jr (2000) Linkage of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia to chromosome 9q21-q22. JAMA 284:1664–1669
Houlden H, Baker M, Adamson J, Grover A, Waring S, Dickson D, Lynch T, Boeve B, Petersen RC, Pickering-Brown S, Owen F, Neary D, Craufurd D, Snowden J, Mann D, Hutton M (1999) Frequency of tau mutations in three series of non-Alzheimer’s degenerative dementia. Ann Neurol 46:243–248
Hudson AJ (1981) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its association with dementia, parkinsonism, and other neurological disorders : a review. Brain 104:217–247
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, et al (1998) Association of missense and 5’-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Komori T, Arai N, Oda M, Nakayama H, Mori H, Yagishita S, Takahashi T, Amano N, Murayama S, Murakami S, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Sasaki S, Iwata M (1998) Astrocytic plaques and tufts of abnormal fibers do not coexist in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 96:401–408
Litvan I, Hauw JJ, Bartko JJ, Lantos PL, Daniel SE, Horoupian DS, McKee A, Dickson D, Bancher C, Tabaton M, Jellinger K, Anderson DW (1996) Validity and reliability of the preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy and related disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:97–105
Lowe J, Rossor M (2003) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 342–348
Lynch T, Sano M, Marder KS, Bell KL, Foster NL, Defendini RF, Sima AAF, Keohane C, Nygaard TG, Fahn S, Mayeux R, Rowland LP, Wilhelmsen KC (1994) Clinical characteristics of a family with chromosome 17-linked disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophy complex. Neurology 44:1878–1884
Mawal-Dewan M, Schmidt ML, Balin B, Perl DP, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1996) Identification of phosphorylation sites in PHF-TAU from patients with Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1051–1059
Mitsuyama Y (1993) Presenile dementia with motor neuron disease. Dementia 4:137–142
Nakano I (2000) Frontotemporal dementia with motor neuron disease (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia) Neuropathology 20:68–75
Neary D (1995) Neuropsychological aspects of frontotemporal degeneration. Ann NY Acad Sci 769:15–22
Neary D (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. A consensus on clinical diagnosis criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2000) Cognitive change in motor neuron disease/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (MND/ALS) J Neurol Sci 180:15–20
Niizato K, Tsuchiya K, Tominaga I, Kato Y, Ikeda K (1997) Pick’s disease with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): report of two autopsy cases and literature review. J Neurol Sci 148:107–112
Paviour DC, Lees AJ, Josephs KA, Ozawa T, Ganguly M, Strand C, Godbolt A, Howard RS, Revesz T, Holton JL (2004) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-only-immunoreactive neuronal changes: broadening the clinical picture to include progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 127:2441–2451
Pinsky L, Finlayson MH, Libman I, Scott BH (1975) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia: a second Canadian family. Clin Gen 7:186–191
Siddique T, Nijhawan D, Hentati A (1996) Molecular genetic basis of familial ALS. Neurology 47 (Suppl 2):S27–S35
Wilhelmsen KC (1998) Chromosome 17-linked dementias. Cell Mol Life Sci 54:920–924
Wilhelmsen KC, Forman MS, Rosen HJ, Alving LI, Goldman J, Feiger J, Lee JV, Segall SK, Kramer JH, Lomen-Hoerth C, Rankin KP, Johnson J, Feiler HS, Weiner MW, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Miller BL (2004) 17q-linked frontotemporal dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis without tau mutations with tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions. Arch Neurol 61:398–406
Zhang L, Ulug AM, Zimmerman RD, Lin MT, Rubin M, Beal MF (2003) The diagnostic utility of FLAIR imaging in clinically verified amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:521–527
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Richard Medeiros, Rouen University Hospital Medical Editor, for his valuable advice in editing the manuscript, and to Siegfried Le Roy for the iconography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinaud, O., Laquerrière, A., Guyant-Maréchal, L. et al. Frontotemporal dementia, motor neuron disease and tauopathy: clinical and neuropathological study in a family. Acta Neuropathol 110, 84–92 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-1028-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-1028-2