Abstract
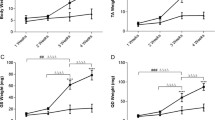
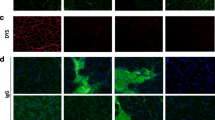
In dystrophinopathies, disease severity is generally related to the extent of muscle fibrosis. To determine whether a decrease in matrix degradation contributes to the severe fibrosis seen in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), we quantified RNA transcript numbers for the fibrolytic matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-1 and −2 and their natural tissue inhibitors (TIMP)-1 and −2 in DMD muscle as well as in pathological and normal controls. In addition, we investigated gelatinase (MMP-2) enzyme activity by zymography. We found an up-regulation of TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and MMP-2 RNA in DMD muscle. Zymography revealed an increase in MMP-2 activity in DMD muscle homogenates, which was absent in pathological and normal controls. Therefore, besides enhanced fibrogenesis, a disturbance of matrix degradation may play a significant role in muscle fibrosis in DMD. TIMP-1 should be investigated further as a promising target for pharmacological intervention to prevent muscle fibrosis in DMD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez K, Fadic R, Brandan E (2002) Augmented synthesis and differential localization of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Cell Biochem 85:703–713
Bernasconi P, Torchiana E, Confalonieri P, Brugnoni R, Barresi R, Mora M, Cornelio F, Morandi L, Mantegazza R (1995) Expression of the transforming factor-β1 in dystrophic patient muscles correlates with fibrosis. J Clin Invest 96:1137–1144
Chang C, Werb Z (2001) The many faces of metalloproteinases: cell growth, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol 11:37–43
Choi YC, Dalakas MC (2000) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in the muscle of patients with inflammatory myopathies. Neurology 54:65–71
D’Amore PA, Brown RH, KU PT, Hoffman EP, Watanabe H, Arahata K (1994) Elevated basic fibroblast growth factor in the serum of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol 35:362–365
Docherty AP, Lyons A, Smith BJ, Wright EM, Stephens PE, Harris TJR (1985) Sequence of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and its identity to erythroid-potentiating activity. Nature 318:66–69
Duance VC, Stephens HR, Dunn M, Bailey AJ, Dubowitz V (1980) A role of collagen in the pathogenesis of muscular dystrophy. Nature 284:470–472
Emery AEH (1991) Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases—a world survey. Neuromuscul Disord 1:19–29
Engel AG, Yamamoto M, Fischbeck KH (1994) Dystrophinopathies. In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1133–1187
Gaschen FP, Hoffman EP, Gorospe JRM, Uhl EW, Senior DF, Cardinet GH Pearce LK (1992) Dystrophin deficiency causes lethal muscle hypertrophy. J Neurol Sci 110:149–159
Gianelli G, Falk-Marzillier J, Schiraldi O, Stetler-Stevenson, WG, Quaranta V (1999) Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloproteinase-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science 277:225–228
Gorospe JRM, Tharp MD, Hinckley J, Kornegay JN, Hoffman EP (1994) A role of mast cells in the progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy? J Neurol Sci 122:44–56
Gulberg D, Velling T, Sjöberg G, Salmivirta K, Gaggero B, Tiger CF, Edström L, Sejersen T (1997) Tenascin-C expression correlates with macrophage invasion in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and in myositis. Neuromuscul Disord 7:39–54
Günther U, Schuppan D, Bauer M, Matthes H, Stallmach A, Schmitt-Gräff A, Riecken EO, Herbst H (1999) Fibrogenesis and fibrolysis in collagenous colitis: patterns of procollagen types I and IV, matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and −13, and TIMP-1 gene expression. Am J Pathol 155:493–503
Haslett JN, Sanoudou D, Kho AT, Han M, Bennett RR, Kohane IS, Beggs AH, Kunkel LM (2003) Gene expression profiling of Duchenne muscular dystrophy skeletal muscle. Neurogenetics 4:163–171
Herbst H, Milani S, Schuppan D, Stein H (1991) Temporal and spatial patterns of proto-oncogene expression at early stages of toxic liver injury in the rat. Lab Invest 65:324–333
Herbst H, Wege T, Milani S, Pellegrini G, Orzechowski HD, Bechstein WO, Neuhaus P, Gressner AM, Schuppan D (1997) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and −2 RNA expression in rat and human liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol 150:1647–1659
Huhtala P, Chow LT, Tryggvason K (1990) Structure of human type IV collagenase gene. J Biol Chem 265:11077–11082
Ionasescu V, Ionanescu R (1982) Increased collagen synthesis by Duchenne myogenic clones. J Neurol Sci 54:79–87
Iredale JP (1997) Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in liver fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29:43–54
Jong L de, Wolterman RA, Hillarius SM, Bolhius PA (1987) Collagen synthesis in cultured myoblasts and myotubes from patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 82:271–280
Kieseier BC, Schneider C, Clements JM, Gearing AJH, Gold R, Toyka KV, Hartung HP (2001) Expression of specific matrix metalloproteinases in inflammatory myopathies. Brain 124:341–351
Kolkenbrock H, Orgel D, Hecker-Kia A, Noack W, Ulbrich N (1991) The complex between a tissue unhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2) and 72 kDa progelatinase is a metalloproteinase. Eur J Biochem 198:775–781
Lichtenhagen R, Breitenstein K, Arndt B, Kühbacher T, Böker KHW (1998) Comparison of matrix metalloproteinase expression in normal and cirrhotic human liver. Virchows Arch 432:153–158
Livak KJ, Flood JA, Marmaro J, Giusti W, Deetz K (1995) Oligonucleotides with fluorescent dyes at opposite ends provide a quenched probe system useful for detecting PCR product and nucleic acid hybridization. PCR Methods Appl 4:357–362
McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases: they are not just for matrix anymore. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:534–540
Messent AJ, Tuckwell DS, Knauper V, Humphries MJ, Murphy G, Gavrilovic J (1998) Effects of collagenase-cleavage of type I collagen on α2β1 integrin mediated cell adhesion. J Cell Sci 111:1127–1135
Milani S, Herbst H, Schuppan D, Hahn EG, Stein H (1989) In situ hybridisation for procollagen types I, III, and IV mRNA in normal and fibrotic rat liver: evidence for predominant expression in non-parenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 10:84–92
Moers A von, Möller P, Herbst H, Schuppan D, Stoltenburg-Didinger G (1996) Expression of mRNA of procollagen type I and procollagen type IV and its cellular localisation in spinal muscular atrophy and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 6:S34
Olson MW, Gervasi DC, Mobashery S, Fridman R (1997) Kinetic analysis of the binding of human matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −9 to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2. J Biol Chem 272:29975–29983
Pastoret C, Sebille A (1995) Mdx mice show progressive weakness and muscle deterioration with age. J Neurol Sci 129:97–105
Peters CA, Freeman MR, Frenandez CA, Shepard J, Wiederschain DG, Moses MA (1997) Dysregulated proteolytic balance as the basis of excess extracellular matrix in fibrotic disease. Am J Physiol 272:R1960–1965
Porter JD, Merriam AP, Leahy P, Gong B, Feuermann J, Cheng G, Khanna S (2004) Temporal gene expression profiling of dystrophin-deficient (mdx) mouse diaphragm identifies conserved and muscle group-specific mechanisms in the pathogenesis of muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 13:257–269
Sharma AK, Mauer SM, Kim Y, Michael AF (1995) Altered expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 in obstructive nephropahty. J Lab Clin Med 125:754–761
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Brown PD, Onisto M, Levy AT, Liotta LA (1990) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) mRNA expression in tumor cell lines and human tissues. J Biol Chem 265:13933–13938
Swiderski RE, Dencoff JE, Floerchinger CS, Shapiro SD, Hunninghake GW (1998) Differential expression of extracellular matrix remodeling genes in a murine model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 152:821–828
Valentine BA, Cooper BJ, De La Hunta A, O’Quinn R, Blue JT (1988) Canine X-linked muscular dystrophy; an animal model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 88:69–81
Whitham SE, Murphy G, Angel P, Rahmsdorf HJ, Smith BJ, Lyons A, Harris T, Reynolds JJ, Herrlich P, Docherty AJ (1986) Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J 240:913–916
Woessner JF, Nagase H (eds) (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 72–135
Yamazaki M, Minota S, Sakurai H, Miyazono K, Yamada A, Kanazawa I, Kawai M (1994) Expression of transforming growth factor- beta 1 and its relation to endomysial fibrosis in progressive muscular dystrophy. Am J Pathol 144:221–226
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Sanitätsrat Dr. Emil Alexander Huebner und Gemahlin-Stiftung (TS 114/61/96) and the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Muskelkranke (DGM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Moers, A., Zwirner, A., Reinhold, A. et al. Increased mRNA expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 and -2 in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Acta Neuropathol 109, 285–293 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0941-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0941-0