Abstract
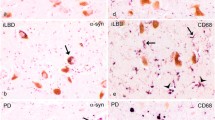
Dementia is a frequent complication of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and usually occurs late in the protracted course of the illness. We have already reported numerous MHC class II-positive microglia in the hippocampus in PD patients, and that this phenomenon may be responsible for functional changes in the neurons and the cognitive decline in PD patients. In this study, we have investigated the distribution of activated microglia and the immunohistochemical and the mRNA expression of several cytokines and neurotrophic factors of the hippocampus in PD and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). The brains from five cases of PD and five cases of DLB that were clinically and neuropathologically diagnosed, and those from four normal controls (NC) were evaluated by immunohistochemistry using anti-HLA-DP, -DQ, -DR (CR3/43), anti-α-synuclein, anti-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein antibodies. In addition, the mRNA expressions of cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, TGF-β) and neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF, NGF, NT-3) of these brains were evaluated by the reverse transcription-PCR method. MHC class II-positive microglia were distributed diffusely in the hippocampus of PD and DLB brains. Although the cytoplasm of pyramidal and granular cells of the hippocampus in NC brains was strongly stained by anti-BDNF antibodies, it was only weakly stained in PD and DLB brains. The mRNA expression of IL-6 was significantly increased in the hippocampus of PD and DLB brains, and that of BDNF was significantly decreased in the hippocampus of DLB brains. The increased number of activated microglia and the production of neurotrophic cytokines such as IL-6, together with the decreased expression of the neurotrophic factors of neurons in the hippocampus of PD and DLB brains, may be related to functional cellular changes associated with dementia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland D, Tandberg E, Larsen JP, Cummings JL (1996) Frequency of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 53:538–542
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Nielsen H, Kragh-Sφrensen P (2001) Risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. A community-based, prospective study. Neurology 56:730–736
Alderson RF, Alterman AL, Barde Y-A, Lindsay RM (1990) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron 5:297–306
Barger SW, Horster D, Furukawa K, Goodman Y, Krieglstein J, Mattson MP (1995) Tumor necrosis factors α and β protect neurons against amyloid β-peptide toxicity: evidence for involvement of a kB-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 92:9328–9332
Batchelor PE, Liberatore GT, Wong JYF, Porritt MJ, Frerichs F, Donnan GA, Howells DW (1999) Activated macrophages and microglia induce dopaminergic sprouting in the injured striatum and express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci 19:1708–1716
Benisty S, Boissiere F, Faucheux B, Agid Y, Hirsch C (1998) trkB messenger RNA expression in normal human brain and in the substantia nigra of parkinsonian patients: an in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience 86:813–826
Braak H, Tredici KD, Rüb U, Vos RAI, Steur ENHJ, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Cassarino DS, Fall CP, Swerdlow RH, Smith TS, Halvorsen EM, Miller SW, Parks JP, Parker WD Jr, Bennett JP Jr (1997) Elevated reactive oxygen species and antioxidant enzyme activities in animal and cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1362:77–86
Chao CC, Hu S, Molitor TW, Shaskan EG, Peterson PK (1992) Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a nitric oxide mechanism. J Immunol 149:2736–2741
Cheng B, Christakos S, Mattson MP (1994) Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron 12:139–153
Churchyard A, Lees AJ (1997) The relationship between dementia and direct involvement of the hippocampus and amygdala in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 49:1570–1576
Conner JM, Lauterborn JC, Yan Q, Gall CH, Varon S (1997) Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport. J Neurosci 17:2295–2313
Cordato NJ, Halliday GM, Harding AJ, Hely MA, Morris JGL (2000) Regional brain atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy and Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 47:718–728
Dickson DW, Ruan D, Crystal H, Mark MH, Davies P, Kress Y, Yen S-H (1991) Hippocampal degeneration differentiates diffuse Lewy body disease (DLBD) from Alzheimer’s disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of CA2–3 neurites specific to DLBD. Neurology 41:1402–1409
Dickson DW, Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Zhao M-L, Yen S-H, Trojanowski JQ (1994) Immunoreactivity profile of hippocampal CA2/3 neurites in diffuse Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 87:269–276
Galvin JE, Uryu K, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (1999) Axon pathology in Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia hippocampus contains α-, β-, and γ-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13450–13455
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 56:33–39
Green J, McDonald WM, Vitek JL, Evatt M, Freeman A, Haber M, Bakay RAE, Triche S, Sirockman B, DeLong MR (2002) Cognitive impairment in advanced PD without dementia. Neurology 59:1320–1324
Hama T, Kushima Y, Miyamoto M, Kubota M, Takei N, Hatanaka H (1991) Interleukin-6 improves the survival of mesencephalic catecholaminergic and septal cholinergic neurons from postnatal, two-week-old rats in cultures. Neuroscience 40:445–452
Harding AJ, Halliday GM (2001) Cortical Lewy body pathology in the diagnosis of dementia. Acta Neuropathol 102:355–363
Harding AJ, Lakay B, Halliday GM (2002) Selective hippocampal neuron loss in dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann Neurol 51:125–128
Hartmann A, Hunot S, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Vyas S, Faucheux BA, Mouatt-Prignot A, Turmel H, Srinivasan A, Ruberg M, Evan GL, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (2000) Caspase-3: a vulnerability factor and a final effector in the apoptotic cell death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2875–2880
Hartmann A, Troadec JD, Hunot S, Kikly K, Faucheux BA, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (2001) Caspase-8 is an effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease, but pathway inhibition results in neuronal necrosis. J Neurosci 21:2247–2255
Hickey WF, Kimura H (1988) Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science 239:290–292
Hofer M, Pagliusi SR, Hohn A, Leibrock J, Barde Y-A (1990) Regional distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult mouse brain. EMBO J 9:2459–2464
Hunot S, Boissiere F, Faucheux B, Brugg B, Mouatt-Prigent A, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (1996) Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 72:355-363
Hurting HI, Trojanowski JQ, Galvin J, Ewbank D, Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Clark CM, Glosser G, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Arnold SE (2000) Alpha-synuclein cortical Lewy bodies correlate with dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54:1916–1921
Hyman C, Hofer M, Barde Y-A, Juhasz M, Yancopoulos GD, Squinto SP, Lindsay RM (1991) BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature 350:230–232
Imamura K, Ito M, Suzumura A, Asai J, Takahashi A (1990) Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against rat microglia and ontogenic distribution of positive cells. Lab Invest 63:853–861
Imamura K, Hishikawa N, Sawada M, Nagatsu T, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y (2003) Distribution of MHC class II-positive microglia and cytokine profile of Parkinson’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 106:518–526
Ip NY, Li Y, Yancopoulos GD, Lindsay RM (1993) Cultured hippocampal neurons show responses to BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4, but not NGF. J Neurosci 13:3394-3405
Jellinger KA (2000) Cell death mechanism in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 107:1-29
Kawamoto Y, Nakamura S, Nakano S, Oka N, Akiguchi I, Kimura J (1996) Immunohistochemical localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult rat brain. Neuroscience 74:1209–1226
Kim H, Gearing M, Mirra SS (1995) Ubiquitin-positive CA2/3 neurites in hippocampus coexist with cortical Lewy bodies. Neurology 45:1768–1770
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Knüsel B, Winslow JW, Rosenthal A, Burton LE, Seid DP, Nikolics K, Hefti F (1991) Promotion of central cholinergic and dopaminergic neuron differentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not neurotrophin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:961–965
Koutsilieri E, Scheller C, Grünblatt E, Nara K, Li J, Pederer P (2002) Free radicals in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249 (Suppl 2):II/1–II/5
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Laakso MP, Partanen K, Riekkinen P, Lehtovirta M, Helkala E-L, Hallikainen M, Hänninen T, Vainio P, Soininen H (1996) Hippocampal volumes in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, and in vascular dementia: an MRI study. Neurology 46:678–681
Liu B, Du L, Hong JS (2000) Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:607–617
Mackenzie IRA (2000) Activated microglia in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 55:132–134
Mattila PM, Röyttä M, Lönnberg P, Marjamäki P, Helenius H, Rinne JO (2001) Choline acetyltransferase activity and striatal dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s disease in relation to cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol 102:160–166
Mayeux R, Chen J, Mirabello E, Marder K, Bell K, Dooneief G, Cote L, Stern Y (1990) An estimate of the incidence of dementia in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 40:1513–1517
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Tago H, McGeer EG (1988) Expression of the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol 76:550–557
McGeer PL, Kawamata T, Walker DG, Akiyama H, Tooyama I, McGeer EG (1993) Microglia in degenerative neurological disease. Glia 7:84–925
McGuire SO, Ling ZD, Lipton JW, Sortwell CE, Collier TJ, Carvey PM (2001) Tumor necrosis factor alpha is toxic to embryonic mesencephalic dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol 169:219–230
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, Salmon, DP, Lowe J, Mirra SS, Byrne EJ, Lennox G, Quinn NP, Edwardson JA, Ince PG, Bergeron C, Burns A, Miller BL, Lovestone S, Collerton D, Jansen ENH, Ballard C, Vos RA de, Wilcock GK, Jellinger KA, Perry RH (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathological diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47:1113–1124
Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T (2000) The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammation process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 95:425–432
Mogi M, Hamada M, Kondo T, Roederer P, Inagaki H, Minami M, Nagatsu T (1994) Interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-α are elevated in the brain from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci Lett 180:147–150
Mogi M, Togari A, Kondo T, Mizuno Y, Komure O, Kuno S, Ichinose H, Nagatsu T (1999) Brain-derived growth factor and nerve growth factor concentrations are decreased in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 270:45–48
Nagata K, Nakajima K, Kohsaka K (1993) Plasminogen promotes the development of rat mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in vitro. Dev Brain Res 75:31–37
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A, Riederor P (1999) Cytokines in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroSci News 2:88–90
Nagatsu T (2002) Parkinson’s disease: changes in apoptosis-related factors suggesting possible gene therapy. J Neural Transm 109:731–745
Neumann H, Misgeld T, Matsumuro K, Wekerle H (1998) Neurotrophins inhibit major histocompatibility class II inducibility of microglia: involvement of the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5779–5784
Parain K, Murer MG, Yan Q, Faucheux B, Agid Y, Hirsch E, Raisman-Vozari R (1999) Reduced expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in Parkinson’s disease substantia nigra. Neuroreport 10:557–561
Perry VH, Hume DA, Gordon S (1985) Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience 15:313–326
Phillips HS, Hains JM, Laramee GR, Rosenthal A, Winslow JW (1990) Widespread expression of BDNF but not NT3 by target areas of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Science 250:290–294
Phillips HS, Hains JM, Armanini M, Laramee GR, Johonson SA, Winslow JW (1991) BDNF mRNA is decreased in the hippocampus of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 7:695–702
Satoh T, Nakamura S, Taga T, Matsuda T, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Kaziro Y (1988) Induction of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells by B-cell stimulatory factor 2/interleukin 6. Mol Cell Biol 8:3546–3549
Sauer H, Wong V, Björklund (1995) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-4/5 modify neurotransmitter-related gene expression in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat striatum. Neuroscience 65:927–933
Sawada M, Suzumura A, Marunouchi T (1995) Cytokine network in the central nervous system and its roles in growth and differentiation of glial and neuronal cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 13:253–264
Schmidt-Kastner R, Wetmore C, Olson L (1996) Comparative study of brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA and protein at the cellular level suggests multiple roles in hippocampus, striatum and cortex. Neuroscience 74:161–183
Siegel GJ, Chauhan NB (2000) Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease brain. Brain Res Rev 33:199–22
Spina MB, Squinto SP, Miller J, Lindsay RM, Hyman C (1992) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects dopamine neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine and N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion toxicity: involvement of the glutathione system. J Neurochem 59:99–106
Wetmore C, Ernfors P, Persson H, Olson L (1990) Localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA to neurons in the brain by in situ hybridization. Exp Neurol 109:141–152
Yurek DM, Lu W, Hipkens S, Wiegand SJ (1996) BDNF enhances the functional reinnervation of the striatum by grafted fetal dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol 137:105–118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imamura, K., Hishikawa, N., Ono, K. et al. Cytokine production of activated microglia and decrease in neurotrophic factors of neurons in the hippocampus of Lewy body disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 109, 141–150 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0919-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0919-y