Abstract
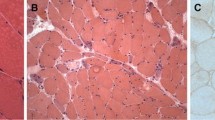
Different immune effector mechanisms have been characterised in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM): in polymyositis (PM) and sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM), T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity targets nonnecrotic muscle fibres, whereas in dermatomyositis (DM) the complement-mediated immune response is directed against the microvasculature. As nitric oxide (NO) has an important function in cell signalling and in the cytotoxicity displayed by activated macrophages, it is potentially involved in the immunopathogenesis of IIM. Using immunohistochemical, in situ hybridisation and Western blotting techniques, we visualised the three isoforms of NO synthase (NOS) in muscle tissues from normal controls and from patients diagnosed with IIM. The levels of both constitutive isoforms of NOS (endothelial, i.e., eNOS, and neuronal, i.e., nNOS) were unchanged in IIM as compared with normal muscle. Both protein and mRNA of the inducible form (iNOS) were detected in half of the control biopsies. Constant and increased iNOS protein expression was found in endomysial infiltrates of PM and sIBM, whereas perimysial inflammatory cells in DM were largely negative. We developed a quantitative Western blotting protocol which confirmed the constitutive nature of nNOS and eNOS and the significant induction of iNOS in PM. Our results appoint iNOS with a dual function: a limited and transient role in normal muscle physiology and an active cytotoxic role in PM and sIBM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anneser JMH, Cookson MR, Ince PG, Shaw PJ, Borasio GD (2001) Glial cells of the spinal cord and subcortical white matter up-regulate neuronal nitric oxide synthase in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 171:418–421
Balligand JL, Ungureanu-Longrois D, Simmons WW, Kobzik L, Lowenstain CJ, Lomas S, Kelly RA, Smith RA, Smith TW, Michel T (1995) Induction of NO synthase in rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells by IL-1beta and IFN-gamma. Am J Physiol 268:H1293–1303
Bagasra O, Michaels FH, Zheng YM, Bobroski LE, Spitsin SV, Fang Fu Z, Tawadros R, Koprowski H (1995) Activation of the inducible form of nitric oxide synthase in the brains of patients with multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:12041–12045
Barnes PJ (1995) Nitric oxide and airway disease. Ann Med 27:389–393
Brenman JE, Chao DS, Xia H, Aldape K, Bredt DS (1995) Nitric oxide synthase complexed with dystrophin and absent from skeletal muscle sarcolemma in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell 82:743–752
Chao DS, Gorospe JFM, Brenman JE, Rafael JA, Peters MF, Froehner SC, Hoffman EP, Chamberlain JS, Bredt DS (1996) Selective loss of sarcolemmal nitric oxide synthase in Becker muscular dystrophy. J Exp Med 184:609–618
Dalakas MC (1991) Polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and inclusion body myositis. N Engl J Med 325:1487–1498
De Bleecker JL, Meire VI, Declercq W, Van Aken EH (1999) Immunolocalization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its receptors in inflammatory myopathies. Neuromusc Dis 9:239–246
De Bleecker JL, De Paepe B, Vanwalleghem IE, Schröder JM (2002) Differential expression of chemokines in inflammatory myopathies. Neurology 58:1779–1785
De Paepe B, Verstraeten VLRM, De Potter CR, Bullock GR (2002) Increased angiotensin II type-2 receptor density in hyperplasia, DCIS and invasive carcinoma of the breast is paralleled with increased iNOS expression. Histochem Cell Biol 117:13–19
Förstermann U, Closs EI, Pollock JS, Nakane M, Schwarz P, Gath I, Kleinert H (1994) Nitric oxide synthase isozymes: characterization, purification, molecular cloning, and functions. Hypertension 23:1121–1131
German Z, Chambliss KL, Pace MC, Arnet UA, Lowenstein CJ, Shaul PW (2000) Molecular basis of cell-specific endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression in airway epithelium. J Biol Chem 275:8183–8189
Gradini R, Realacci M, Ginepri A, Naso G, Santangelo C, Cela O, Sale P, Berardi A, Petrangeli E, Gallucci M, Silverio F di, Russo MA (1999) Nitric oxide synthases in normal and benign hyperplastic human prostate: immunohistochemistry and molecular biology. J Pathol 189:224–229
Jungi TW, Adler H, Adler B, Thony M, Krampa M, Peterhans E (1996) Inducible nitric oxide synthase of macrophages. Present knowledge and evidence for species-specific regulation. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 54:323–330
Kawamoto H, Takumida M, Takedo S, Watanabe H, Fukushima N, Yajin K (1998) Localization of nitric oxide synthase in human nasal mucosa with nasal allergy. Acta Otolaryngol (Suppl) 539:65–70
Liu JSH, Zhao ML, Brosnan CF, Lee SC (2001) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine in multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Pathol 158:2057–2066
Lundberg I, Brengman JM, Engel AG (1995) Analysis of cytokine expression in muscle in inflammatory myopathy, Duchenne dystrophy, and non-weak controls. J Neuroimmunol 63:9–16
Koh E, Noh SH, Lee YD, Lee HY, Han JW, Lee HW, Hong S (1999) Differential expression of nitric oxide synthase in human stomach cancer. Cancer Lett 146:173–180
Sakurai H, Kohsaka H, Liu MF, Higashiyama H, Hirata Y, Kanno K, Saito I (1995) Nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in inflammatory arthritides. J Clin Invest 96:2357–2363
Sasaki S, Shibata N, Iwata M (2001) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 101:351–357
Singh VK, Mehrotra S, Narayan P, Pandey CM, Agarwal SS (2000) Modulation of autoimmune diseases by nitric oxide. Immunol Res 22:1–19
Tews DS, Goebel HH (1998) Cell death and oxidative damage in inflammatory myopathies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 87:240–247
Tseng L, Zhang J, Peresleni TY, Golgorsky MS (1996) Cyclic expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the epithelial glands of human endometrium. J Soc Gynecol Invest 3:33–38
Wei C, Jiang S, Lust JA, Daly RC, McGregor CG (1996) Genetic expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human atrial myocardium. Mayo Clinic Proc 71:346–350
Yao A, Kohmoto O, Serizawa T, Takahashi T (1997) Transcriptional regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 81:911–921
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Ghent Flemish University Research Fund for Bilateral Collaboration, the Flemish Fund for Scientific Research, the Belgian Association against Neuromuscular Disorders (ABMM) and “KidAuQuai”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Paepe, B., Racz, G.Z., Schröder, J.M. et al. Expression and distribution of the nitric oxide synthases in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Acta Neuropathol 108, 37–42 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0859-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0859-6