Abstract
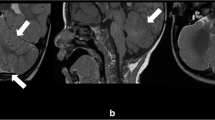
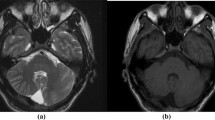
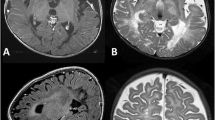
Lissencephaly with agenesis of the corpus callosum and rudimentary dysplastic cerebellum may represent a subset of lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia (LCH) of unknown etiology, one that is distinct from other types of LCH. We present a detailed neuropathological description of an autopsy brain from a 7-day-old neonate born at 38-gestational weeks, presenting with this malformation. The brain was severely hydrocephalic and totally agyric. The corpus callosum was absent and deep gray matter structures indistinct. A rudimentary dysplastic cerebellum, dysplastic olivary nuclei and nearly complete absence of corticospinal tracts were also noted. Microscopic examination revealed various types of dysplastic and malformative features throughout the brain in addition to the classic four-layered neocortical structure characteristic of type I lissencephaly. Unique features in the present case were (1) bilateral periventricular undulating cortical ribbon-like structures mimicking fused gyri and sulci, associated with aberrant reelin expression, (2) large dysplastic neocortical neurons positive for phosphorylated neurofilament, calbindin-D28K, tuberin, hamartin, doublecortin, LIS1, reelin and Dab1, (3) derangement of radial glial fibers, and (4) disorganized cerebellar cortex and heterotopic gray matter composed exclusively of granule cells in the cerebellar deep white matter. The clinicopathological features in the present case are suggestive of a distinct category of lissencephaly with cerebellar involvement. We suggest a possible classification of this unique case among the LCH syndromes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attia-Sobol J, Encha-Razavi F, Hermier M, Vitrey D, Verloes A, Plauchu H (2001) Lissencephaly type III, stippled epiphyses and loose, thick skin: a new recessively inherited syndrome. Am J Med Genet 99:14–20
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2001) Classification system for malformations of cortical development: update 2001. Neurology 57:2168–2178
Bonneau D, Toutain A, Laquerriere A, Marret S, Saugier-Veber P, Barthez MA, Radi S, Biran-Mucignat V, Rodriguez D, Gelot A (2002) X-linked lissencephaly with absent corpus callosum and ambiguous genitalia (XLAG): clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and neuropathological findings. Ann Neurol 51:340–349
Cahana A, Escamez T, Nowakowski RS, Hayes NL, Giacobini M, Holst A von, Shmueli O, Sapir T, McConnell SK, Wurst W, Martinez S, Reiner O (2001) Targeted mutagenesis of Lis1 disrupts cortical development and LIS1 homodimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6429–6434
Cepeda C, Hurst RS, Flores-Hernández J, Hernández-Echeagaray E, Klapstein GJ, Boylan MK, Calvert CR, Jocoy EL, Nguyen OK, André VM, Vinters HV, Ariano MA, Levine MS, Mathern GW (2003) Morphological and electrophysiological characterization of abnormal cell types in pediatric cortical dysplasia. J Neurosci Res 72:472–486
Clark GD, Mizuguchi M, Antalffy B, Barnes J, Armstrong D (1997) Predominant localization of the LIS family of gene products to Cajal-Retzius cells and ventricular neuroepithelium in the developing human cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:1044–1052
Crino PB, Miyata H, Vinters HV (2002) Neurodevelopmental disorders as a cause of seizures: Neuropathologic, genetic, and mechanistic considerations. Brain Pathol 12:212–33
Dahmane N, Ruiz-i-Altaba A (1999) Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 126:3089–3100
Des Portes V, Pinard JM, Billuart P, Vinet MC, Koulakoff A, Carrie A, Gelot A, Dupuis E, Motte J, Berwald-Netter Y, Catala M, Kahn A, Beldjord C, Chelly J (1998) A novel CNS gene required for neuronal migration and involved in X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly syndrome. Cell 92:51–61
Dobyns WB, Berry-Kravis E, Havernick NJ, Holden KR, Viskochil D (1999) X-linked lissencephaly with absent corpus callosum and ambiguous genitalia. Am J Med Genet 86:331–337
Farah S, Sabry MA, Khuraibet A, Khaffagi S, Rudwan M, Hassan M, Haseeb N, Abulhassan S, Abdel-Rasool MA, Elgamal S, Qasrawi B, Al-Busairi W, Farag TI (1997) Lissencephaly associated with cerebellar hypoplasia and myoclonic epilepsy in a Bedouin kindred: a new syndrome? Clin Genet 51:326–330
Förster E, Tielsch A, Saum B, Weiss KH, Johanssen C, Graus-Porta D, Müller U, Frotscher M (2002) Reelin, Disabled 1, and beta 1 integrins are required for the formation of the radial glial scaffold in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13178–13183
Friede RL (1973) Dating the development of human cerebellum. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 23:48–58
Friede RL (1989) Developmental neuropathology, 2nd rev. and expanded edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Gleeson JG, Allen KM, Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Cooper EC, Dobyns WB, Minnerath SR, Ross ME, Walsh CA (1998) Doublecortin, a brain-specific gene mutated in human X-linked lissencephaly and double cortex syndrome, encodes a putative signaling protein. Cell 92:63–72
Gleeson JG, Minnerath SR, Fox JW, Allen KM, Luo RF, Hong SE, Berg MJ, Kuzniecky R, Reitnauer PJ, Borgatti R, Mira AP, Guerrini R, Holmes GL, Rooney CM, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Cooper EC, Ricci S, Cusmai R, Crawford TO, Leroy R, Andermann E, Wheless JW, Dobyns WB, Ross ME, Walsh CA (1999) Characterization of mutations in the gene doublecortin in patients with double cortex syndrome. Ann Neurol 45:146–153
Guihard-Costa AM, Ménez F, Delezoide AL (2002) Organ weights in human fetuses after formalin fixation: standards by gestational age and body weight. Pediatr Dev Pathol 5:559–578
Harding BN, Copp AJ (2002) Malformations. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology, 7th edn, Vol I. Arnold, London, pp 357–483
Hong SE, Shugart YY, Huang DT, Shahwan SA, Grant PE, Hourihane JO, Martin ND, Walsh CA (2000) Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations. Nat Genet 26:93–96
Hori A, Matsushita M, Murofushi K, Iizuka R (1974) Heterotopien im Kleinhirnmark. No To Hattatsu 6:404–408
Hunter-Schaedle KE (1997) Radial glial cell development and transformation are disturbed in reeler forebrain. J Neurobiol 33:459–472
Johnson MW, Emelin JK, Park SH, Vinters HV (1999) Co-localization of TSC1 and TSC2 gene products in tubers of patients with tuberous sclerosis. Brain Pathol 9:45–54
Johnson MW, Kerfoot C, Bushnell T, Li M, Vinters HV (2001) Hamartin and tuberin expression in human tissues. Mod Pathol 14:202–210
Kerner B, Graham JM Jr, Golden JA, Pepkowitz SH, Dobyns WB (1999) Familial lissencephaly with cleft palate and severe cerebellar hypoplasia. Am J Med Genet 87:440–445
King JAC, Gardner V, Chen H, Blackburn W (1995) Neu-Laxova syndrome: pathological evaluation of a fetus and review of the literature. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med 15:57–79
Kobayashi K, Nakahori Y, Miyake M, Matsumura K, Kondo-Iida E, Nomura Y, Segawa M, Yoshioka M, Saito K, Osawa M, Hamano K, Sakakihara Y, Nonaka I, Nakagome Y, Kanazawa I, Nakamura Y, Tokunaga K, Toda T (1998) An ancient retrotransposal insertion causes Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature 394:388–392
Kroon AA, Smit BJ, Barth PG, Hennekam RC (1996) Lissencephaly with extreme cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia. A magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuropediatrics 27:273–276
Landrieu P, Husson B, Pariente D, Lacroix C (1998) MRI-neuropathological correlations in type 1 lissencephaly. Neuroradiology 40:173–176
Letinic K, Zoncu R, Rakic P (2002) Origin of GABAergic neurons in the human neocortex. Nature 417:645–649
Lund JS, Lewis DA (1993) Local circuit neurons of developing and mature macaque prefrontal cortex: Golgi and immunocytochemical characteristics. J Comp Neurol 328:282–312
Marín-Padilla M (1998) Cajal-Retzius cells and the development of the neocortex. Trends Neurosci 21:64–71
Miyata M, Miyata H, Mikoshiba K, Ohama E (1999) Development of Purkinje cells in humans: an immunohistochemical study using a monoclonal antibody against the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate type 1 receptor (IP3R1). Acta Neuropathol 98:226–232
Miyata T, Nakajima K, Aruga J, Takahashi S, Ikenaka K, Mikoshiba K, Ogawa M (1996) Distribution of a reeler gene-related antigen in the developing cerebellum: an immunohistochemical study with an allogeneic antibody CR-50 on normal and reeler mice. J Comp Neurol 372:215–228
Norman MG (1996) Malformations of the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:133–143
Norman MG, McGillivray BC, Kalousek DK, Hill A, Poskitt KJ (1995) Congenital malformations of the brain: pathological, embryological, clinical, radiological and genetic aspects. Oxford University Press, New York
Ogata T, Matsuo N, Hiraoka N, Hata JI (2000) X-linked lissencephaly with ambiguous genitalia: delineation of further case. Am J Med Genet 94:174–176
Ostrovskaya TI, Lazjuk GI (1988) Cerebral abnormalities in the Neu-Laxova syndrome. Am J Med Genet 30:747–756
Park SH, Pepkowitz SH, Kerfoot C, De Rosa MJ, Poukens V, Wienecke R, DeClue JE, Vinters HV (1997) Tuberous sclerosis in a 20-week gestation fetus: immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 94:180–186
Patel S, Barkovich AJ (2002) Analysis and classification of cerebellar malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1074–1087
Qin J, Mizuguchi M, Itoh M, Takashima S (2000) Immunohistochemical expression of doublecortin in the human cerebrum: comparison of normal development and neuronal migration disorders. Brain Res 863:225–232
Reiner O, Carrozzo R, Shen Y, Wehnert M, Faustinella F, Dobyns WB, Caskey CT, Ledbetter DH (1993) Isolation of a Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene containing G protein beta-subunit-like repeats. Nature 364:717–721
Reiner O, Albrecht U, Gordon M, Chianese KA, Wong C, Gal-Gerber O, Sapir T, Siracusa LD, Buchberg AM, Caskey CT, Eichele G (1995) Lissencephaly gene (LIS1) expression in the CNS suggests a role in neuronal migration. J Neurosci 15:3730–3738
Reynolds GP, Beasley CL (2001) GABAergic neuronal subtypes in the human frontal cortex—development and deficits in schizophrenia. J Chem Neuroanat 22:95–100
Ross ME, Swanson K, Dobyns WB (2001) Lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia (LCH): a heterogeneous group of cortical malformations. Neuropediatrics 32:256–263
Takada K, Nakamura H, Suzumori K, Ishikawa T, Sugiyama N (1987) Cortical dysplasia in a 23-week fetus with Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:300–306
Trommsdorff M, Gotthardt M, Hiesberger T, Shelton J, Stockinger W, Nimpf J, Hammer RE, Richardson JA, Herz J (1999) Reeler/Disabled-like disruption of neuronal migration in knockout mice lacking the VLDL receptor and ApoE receptor 2. Cell 97:689–701
Wallace VA (1999) Purkinje-cell-derived Sonic hedgehog regulates granule neuron precursor cell proliferation in the developing mouse cerebellum. Curr Biol 9:445–448
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP (1999) Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog. Neuron 22:103–114
Yoshida A, Kobayashi K, Manya H, Taniguchi K, Kano H, Mizuno M, Inazu T, Mitsuhashi H, Takahashi S, Takeuchi M, Herrmann R, Straub V, Talim B, Voit T, Topaloglu H, Toda T, Endo T (2001) Muscular dystrophy and neuronal migration disorder caused by mutations in a glycosyltransferase, POMGnT1. Dev Cell 1:717–724
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Alexander Blooks and Beth Johnson (Section of Neuropathology, UCLA Medical Center) for invaluable technical assistance. H.M. is supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyata, H., Chute, D.J., Fink, J. et al. Lissencephaly with agenesis of corpus callosum and rudimentary dysplastic cerebellum: a subtype of lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia. Acta Neuropathol 107, 69–81 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0776-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0776-0