Abstract
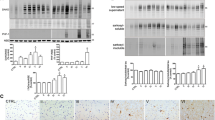
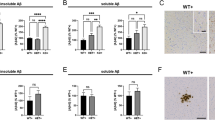
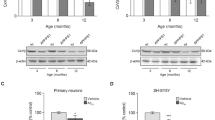
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the intracellular accumulation of highly phosphorylated tau protein, the extracellular formation of amyloid plaques and a significant loss of neurons. Recent evidence suggests that neuronal death in AD involves an aborted attempt of cells to re-enter the cell cycle. To study the effect of amyloid deposits on cell cycle related events in vivo, the expression of cell cycle markers was examined by immunohistochemistry in amyloid precursor protein (APP) transgenic mice (APP23 mice, Swedish double mutation). Aβ deposition in APP23 mice is associated with prominent gliosis that is characterized by an astrocytic expression of cyclins D1, E and B1 as well as the nuclear translocation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 4. However, amyloid plaque formation is not accompanied by significant changes in the neuronal expression of cyclins or cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. It is concluded, therefore, that in contrast to AD, amyloid pathology in APP23 mice is not associated with changes in the expression of cell cycle markers in neurons. The results support the assumption that the neuronal re-expression of cell cycle components in AD is not a consequence of Aβ formation and deposition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt T, Rödel L, Gärtner U, Holzer M (1996) Expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 7:3047–3049
Arendt T, Holzer M, Gärtner U (1998) Neuronal expression of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors of the INK4 family in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 105:949–960
Arendt T, Holzer M, Gärtner U, Brückner MK (1998) Aberrancies in signal transduction and cell cycle related events in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 54:147–158
Arendt T, Holzer M, Stöbe A, Gärtner U, Lüth HJ, Brückner MK, Ueberham U (2000) Activated mitogenic signaling induces a process of dedifferentiation in Alzheimer's disease that eventually results in cell death. Ann NY Acad Sci 920:249–255
Bach JH, Chae HS, Rah JC, Lee MW, Park CH, Choi SH, Choi JK, Lee SH, Kim YS, Kim KY, Lee WB, Suh YH, Kim SS (2001) C-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein induces astrocytosis. J Neurochem 78:109–120
Bondolfi L, Calhoun M, Ermini F, Kuhn HG, Wiederhold KH, Walker L, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M (2002) Amyloid-associated neuron loss and gliogenesis in the neocortex of amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J Neurosci 22:515–522
Bornemann KD, Staufenbiel M (2000) Transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 908:260–266
Bornemann KD, Wiederhold KH, Pauli C, Ermini F, Stalder M, Schnell L, Sommer B, Jucker M, Staufenbiel M (2001) Abeta-induced inflammatory processes in microglia cells of APP23 transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 158:63–73
Busciglio J, Yeh J, Yankner BA (1993) Beta-Amyloid neurotoxicity in human cortical culture is not mediated by excitotoxins. J Neurochem 61:1565–1568
Calhoun ME, Wiederhold KH, Abramowski D, Phinney AL, Probst A, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Sommer B, Jucker M (1998) Neuron loss in APP transgenic mice. Nature 395:755–756
Copani A, Condorelli F, Caruso A, Vancheri C, Sala A, Giuffrida Stella AM, Canonico PL, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA (1999) Mitotic signaling by beta-amyloid causes neuronal death. FASEB J 13:2225–2234
Fischer SJ, McDonald ES, Gross L, Windebank AJ (2001) Alterations in cell cycle regulation underlie cisplatin induced apoptosis of dorsal root ganglion neurons in vivo. Neurobiol Dis 8:1027–1035
Freeman RS, Estus S, Johnson EM Jr (1994) Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: selective induction of cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron 12:343–355
Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, et al (1995) Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature 373:523–527
Geula C, Wu CK, Saroff D, Lorenzo A, Yuan M, Yankner BA (1998) Aging renders the brain vulnerable to amyloid beta-protein neurotoxicity. Nat Med 4:827–831
Hsiao K (1998) Transgenic mice expressing Alzheimer amyloid precursor proteins. Exp Gerontol 33:883–889
Hu J, Akama KT, Krafft GA, Chromy BA, Van Eldik LJ (1998) Amyloid-beta peptide activates cultured astrocytes: morphological alterations, cytokine induction and nitric oxide release. Brain Res 785:195–206
Husseman JW, Nochlin D, Vincent I (2000) Mitotic activation: a convergent mechanism for a cohort of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging 21:815–828
Ino H, Chiba T (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and cyclin D1 are required for excitotoxin-induced neuronal cell death in vivo. J Neurosci 21:6086–6094
Jin K, Nagayama T, Chen J, Stetler AR, Kawaguchi K, Simon RP, Graham SH (1999) Molecular cloning of a cell cycle regulation gene cyclin H from ischemic rat brain: expression in neurons after global cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 73:1598–1608
Katchanov J, Harms C, Gertz K, Hauck L, Waeber C, Hirt L, Priller J, von Harsdorf R, Bruck W, Hortnagl H, Dirnagl U, Bhide PG, Endres M (2001) Mild cerebral ischemia induces loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and activation of cell cycle machinery before delayed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 21:5045–5053
Kaya SS, Mahmood A, Li Y, Yavuz E, Chopp M (1999) Expression of cell cycle proteins (cyclin D1 and cdk4) after controlled cortical impact in rat brain. J Neurotrauma 16:1187–1196
Lamb BT, Bardel KA, Kulnane LS, Anderson JJ, Holtz G, Wagner SL, Sisodia SS, Hoeger EJ (1999) Amyloid production and deposition in mutant amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1 yeast artificial chromosome transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci 2:695–697
Legrier ME, Ducray A, Propper A, Kastner A (2001) Region-specific expression of cell cycle inhibitors in the adult brain. Neuroreport 12:3127–3131
Li J, Meyer AN, Donoghue DJ (1997) Nuclear localization of cyclin B1 mediates its biological activity and is regulated by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:502–507
Li V, Kelly K, Schrot R, Langan TJ (1996) Cell cycle kinetics and commitment in newborn, adult, and tumoral astrocytes. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 96:138–147
Li Y, Chopp M, Powers C (1997) Granule cell apoptosis and protein expression in hippocampal dentate gyrus after forebrain ischemia in the rat. J Neurol Sci 150:93–102
Liu DX, Greene LA (2001) Neuronal apoptosis at the G1/S cell cycle checkpoint. Cell Tissue Res 305:217–228
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7951–7955
Lüth HJ, Holzer M, Gärtner U, Staufenbiel M, Arendt T (2001) Expression of endothelial and inducible NOS-isoforms is increased in Alzheimer's disease, in APP23 transgenic mice and after experimental brain lesion in rat: evidence for an induction by amyloid pathology. Brain Res 913:57–67
Malchiodi-Albedi F, Domenici MR, Paradisi S, Bernardo A, Ajmone-Cat MA, Minghetti L (2001) Astrocytes contribute to neuronal impairment in beta A toxicity increasing apoptosis in rat hippocampal neurons. Glia 34:68–72
Matsunaga Y (2000) Expression of cyclin E in postmitotic cells in the central nervous system. Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi 67:169–181
Mattson MP, Cheng B, Davis D, Bryant K, Lieberburg I, Rydel RE (1992) Beta-Amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 12:376–389
McShea A, Harris PL, Webster, Wahl AF, Smith MA (1997) Abnormal expression of the cell cycle regulators P16 and CDK4 in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 150:1933–1939
Milton NG (2002) The amyloid-beta peptide binds to cyclin B1 and increases human cyclin-dependent kinase-1 activity. Neurosci Lett 322:131–133
Miyajima M, Nornes HO, Neuman T (1995) Cyclin E is expressed in neurons and forms complexes with cdk5. Neuroreport 6:1130–1132
Miyazawa K, Himi T, Garcia V, Yamagishi H, Sato S, Ishizaki Y (2000) A role for p27/Kip1 in the control of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation. J Neurosci 20:5756–5763
Nagahama H, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K, Nagata M, Tomita K, Nakayama K (2001) Spatial and temporal expression patterns of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 during mouse development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 203:77–87
Nagy Z, Esiri MM, Cato AM, Smith AD (1997) Cell cycle markers in the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 94:6–15
Oka T, Kubo T, Enokido Y, Hatanaka H (1996) Expression of cyclin A decreases during neuronal apoptosis in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 97:96-106
Pike CJ, Cummings BJ, Monzavi R, Cotman CW (1994) Beta-amyloid-induced changes in cultured astrocytes parallel reactive astrocytosis associated with senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 63:517–531
Pines J, Hunter T (1991) Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport. J Cell Biol 115:1–17
Postigo JA, Werf YD van der, Korf HJ, Krugers HJ (1998) Altered expression of the cell cycle regulatory protein cyclin D1 in the rat dentate gyrus after adrenalectomy-induced granular cell loss. Neurosci Lett 241:107–110
Prosperi E, Stivala LA, Scovassi AI, Bianchi L (1997) Cyclins: relevance of subcellular localization in cell cycle control. Eur J Histochem 41:161–168
Richter JD (2001) Think globally, translate locally: what mitotic spindles and neuronal synapses have in common. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7069–7071
Sgambato A, Cittadini A, Faraglia B, Weinstein IB (2000) Multiple functions of p27(Kip1) and its alterations in tumor cells: a review. J Cell Physiol 183:18–27
Shambaugh GE 3rd, Haines GK 3rd, Koch A, Lee EJ, Zhou J, Pestell R (2000) Immunohistochemical examination of the INK4 and Cip inhibitors in the rat neonatal cerebellum: cellular localization and the impact of protein calorie malnutrition. Brain Res 855:11–22
Sherr C J (1995) D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci 20:187–190
Shirvan A, Ziv I, Machlin T, Zilkha-Falb R, Melamed E, Barzilai A (1997) Two waves of cyclin B and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression during dopamine-triggered neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 69:539–549
Shirvan A, Ziv I, Zilkha-Falb R, Machlyn T, Barzilai A, Melamed E (1998) Expression of cell cycle-related genes during neuronal apoptosis: is there a distinct pattern? Neurochem Res 23:767–777
Small DL, Monette R, Comas T, Fournier M, Morley P (1999) Loss of cyclin D1 in necrotic and apoptotic models of cortical neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 842:376–383
Small DL, Monette R, Fournier MC, Zurakowski B, Fiander H, Morley P (2001) Characterization of cyclin D1 expression in a rat global model of cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 900:26–37
Sommer B, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Abramowski D, Wiederhold KH, Calhoun M, Jucker M, Kelly P, Staufenbiel M (2000) Transgenic approaches to model Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci 11:47–51
Stalder M, Phinney A, Probst A, Sommer B, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M (1999) Association of microglia with amyloid plaques in brains of APP23 transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 154:1673–1684
Stalder M, Deller T, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M (2001) 3D-Reconstruction of microglia and amyloid in APP23 transgenic mice: no evidence of intracellular amyloid. Neurobiol Aging 22:427–434
Sturchler-Pierrat C, Abramowski D, Duke M, Wiederhold KH, Mistl C, Rothacher S, Ledermann B, Burki K, Frey P, Paganetti PA, Waridel C, Calhoun ME, Jucker M, Probst A, Staufenbiel M, Sommer B (1997) Two amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse models with Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13287–13292
Tamaru T, Trigun SK, Okada M, Nakagawa H (1993) Identification of cells expressing a D type G1 cyclin in matured brain: implication for its role in neuronal function. Neurosci Lett 153:169–172
Thatcher JD, McBride B, Katula KS (1995) Promoter binding factors regulating cyclin B transcription in the sea urchin embryo. DNA Cell Biol 14:869–881
Timsit S, Rivera S, Ouaghi P, Guischard F, Tremblay E, Ben-Ari Y, Khrestchatisk M (1999). Increased cyclin D1 in vulnerable neurons in the hippocampus after ischaemia and epilepsy: a modulator of in vivo programmed cell death? Eur J Neurosci 11:263–278
Van Lookeren Campagne M, Gill R (1998) Cell cycle-related gene expression in the adult rat brain: selective induction of cyclin G1 and p21Waf1/Cip1 in neurons following focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 84:1097–1112
Vincent I, Jicha G, Rosado M, Dickson DW (1997) Aberrant expression of mitotic cdc2/cyclin B1 kinase in degenerating neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurosci 17:3588–3598
Watanabe G, Pena P, Shambaugh GE 3rd, Haines GK 3rd, Pestell RG (1998) Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor proteins during neonatal cerebellar development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 108:77–87
Wiessner C, Brink I, Lorenz P, Neumann-Haefelin T, Vogel P, Yamashita K (1996) Cyclin D1 messenger RNA is induced in microglia rather than neurons following transient forebrain ischaemia. Neuroscience 72:947–958
Wu Q, Combs C, Cannady SB, Geldmacher DS, Herrup K (2000) Beta-amyloid activated microglia induce cell cycling and cell death in cultured cortical neurons. Neurobiol Aging 21:797–806
Yang J, Kornbluth S (1999) All aboard the cyclin train: subcellular trafficking of cyclins and their CDK partners. Trends Cell Biol 9:207–210
Yankner BA, Dawes LR, Fisher S, Villa-Komaroff L, Oster-Granite ML, Neve RL (1989) Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's disease. Science 245:417–420
Yankner BA, Duffy LK, Kirschner DA (1990) Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250:279–282
Zindy F, Soares H, Herzog KH, Morgan J, Sherr CJ, Roussel MF (1997) Expression of INK4 inhibitors of cyclin D-dependent kinases during mouse brain development. Cell Growth Differ 8:1139–1150
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from the Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung (IZKF) at the University of Leipzig (01KS9504, Project C1); the European Commission (QLK6-CT-1999-02112) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gärtner, U., Brückner, M.K., Krug, S. et al. Amyloid deposition in APP23 mice is associated with the expression of cyclins in astrocytes but not in neurons. Acta Neuropathol 106, 535–544 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0760-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0760-8