Abstract.
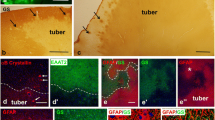
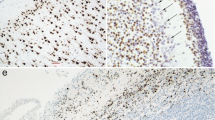
Cerebral cortical lesions of tuberous sclerosis (TSC) and focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) show disturbances in laminar architecture and cellular differentiation. We immunohistochemically studied the expression of doublecortin, a fetal neuronal protein that regulates neuronal migration, in the surgical specimens of five TSC and eight FCD patients. In both TSC and FCD, bizarre giant cells showed a variable degree of doublecortin immunoreactivity. Both cytomegalic neurons and balloon cells were positive. The staining tended to be more intense in TSC than in FCD, although there were exceptional cases in both groups. Doublecortin immunoreactivity of normal-sized neural cells was restricted to a small number of astrocytes, and comparable to that in control patients. The persistent expression of doublecortin by giant cells in the postnatal cerebrum is additional evidence of abnormal differentiation, which may be relevant to the pathogenesis of cortical disarray in TSC and FCD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuguchi, M., Yamanouchi, H., Becker, L.E. et al. Doublecortin immunoreactivity in giant cells of tuberous sclerosis and focal cortical dysplasia. Acta Neuropathol 104, 418–424 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-002-0575-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-002-0575-z