Abstract
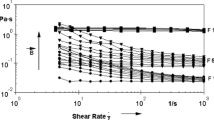
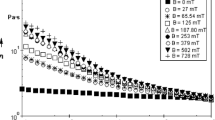
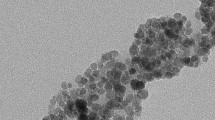
A new magnetorheological cell is implemented to perform measurements of temperature-controlled flows and determine viscoelastic properties in magnetic complex fluids under applied continuous magnetic fields. The flow properties of water-based and oil-based ferrofluids with volume fractions up to 10 % are investigated here in various situations of interparticle interaction, leading also to various microstructures already known from previous works. Shear flow behaviors under magnetic fields resulting in a competition between magnetic and hydrodynamic forces are directly related to the microscopic structure of the probed magnetic fluids.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias JL, Gallardo V, Gomez-Lopera S, Delgado A (2005) Loading of 5-fluorouracil to poly(ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles with a magnetic core. J Biomed Nanotech 1:214–223
Avdeev MV, Dubois E, Mériguet G, Wandersman E, Garamus VM, Feoktystov AV, Perzynski R (2009) Small-angle neutron scattering analysis of a water-based magnetic fluid with charge stabilization: contrast variation and scattering of polarized neutrons. J Appl Cryst 42:1009–1019
Bacri JC, Perzynski R, Salin D, Servais J (1987) Magnetic transient birefringence of ferrofluids: particle size determination. J Phys France 48:1385–1391
Bacri JC, Perzynski R, Salin D, Cabuil V, Massart R (1989) Phase diagram of an ionic magnetic colloid: experimental study of the effect of ionic strength. J Colloid Interface Sci 132:43–53
Bacri JC, Perzynski R, Salin D, Cabuil V, Massart R (1990) Ionic ferrofluids: a crossing of chemistry and physics. J Magn Magn Mater 85:27–32
Bee A, Massart R, Neveu S (1995) Synthesis of very fine maghemite particles. J of Magn Magn Mater 149:6–9
Berkovski B (1996) ed., Magnetic fluids and applications, Handbook Begell House Inc. Publ. New York
Borin D, Odenbach S (2009) Magnetic measurements on frozen ferrofluids as a method for estimating the magnetoviscous effect. J Phys Condens Matter 21:246002 (5pp)
Cousin F, Cabuil V, Levitz P (2002) Magnetic colloidal particles as probes for the determination of the structure of laponite suspensions. Langmuir 18:1466–1473
Cousin F, Dubois E, Cabuil V (2003) Tuning the interactions of a magnetic colloidal suspension. Phys Rev E 68:021405-1–021405-9
Cruz CD, Sandre O, Cabuil V (2005) Phase behavior of nanoparticles in a thermotropic liquid crystal. J Phys Chem B 109:14292–14299
Dubois E, Cabuil V, Boué F, Perzynski R (1999) Structural analogy between aqueous and oily magnetic fluids. J Chem Phys 111:7147–7160
Dubois E, Perzynski R, Boué F, Cabuil V (2000) Liquid-gas transitions in charged colloidal dispersions: small-angle neutron scattering coupled with phase diagrams of magnetic fluids. Langmuir 16:5617–5625
Duran J, Arias J, Gallardo V, Delgado A (2008) Magnetic colloids as drug vehicles. J Pharm Sci 97:2948–2983
Frka-Petesic B (2010) Ph.D. thesis, UPMC-Paris 6
Frka-Petesic B, Dubois E, Almasy L, Dupuis V, Cousin F, Perzynski R (2013) Structural probing of clusters and gels of self-aggregated magnetic nanoparticles. Magnetohydrodynamics 49:328–338
Galicia A, Cousin F, Dubois E, Sandre O, Cabuil V, Perzynski R (2009) Static and dynamic structural probing of swollen polyacrylamide ferrogels. Soft Matter 5:2614–2624
Galindo-Gonzalez C, de Vicente J, Ramos-Tejada M, Lopez-Lopez M, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Duran J (2005) Preparation and sedimentation behavior in magnetic fields of magnetite-covered clay particles. Langmuir 21:4410–4419
Galindo-Gonzalez C, Lopez-Lopez M, Duran J (2012) J Applied Physics 112:043917-1–043917-11
Gazeau F, Dubois E, Bacri JC, Boué F, Cebers A, Perzynski R (2002) Anisotropy of the structure factor of magnetic fluids under a field probed by small-angle neutron scattering. Phys Rev E 65:031403-1–031403-15
Gazeau F, Boué F, Dubois E, Perzynski R (2003) Static and quasi-elastic small angle neutron scattering on biocompatible ionic ferrofluids: magnetic and hydrodynamic interactions. J Phys Condens Matter 15:S1305–S1334
Gomez-Lopera S, Arias J, Gallardo V, Delgado A (2006) Colloidal stability of magnetite/poly(lactic acid) core/shell nanoparticles. Langmuir 22:2816–2821
Gomez-Ramirez A, Lopez-Lopez M, Duran J (2011) Steady shear flow of magnetic fiber suspensions: theory and comparison with experiments. J Rheol 55:43–68
Hasmonay E, Bée A, Bacri JC, Perzynski R (1999) pH Effect on an ionic ferrofluid: evidence of a thixotropic magnetic phase. J Phys Chem B 103:6421–6428
Hong R, Ren Z, Han Y, Zheng HLY, Ding J (2007) Rheological properties of water-based Fe3O4 ferrofluids. Chem Eng Sci 62:5912–5924
Hong R, Li J, Zhang S, Li H, Zheng Y, Ding J, Wei D (2009) Preparation and characterization of silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as precursor of ferrofluids. Appl Surf Sci 255:3485–3492
Huang JP, Wang ZW, Holm C (2005) Computer simulations of the structure of colloidal ferrofluids. Phys Rev E 71:061203-1–061203-11
Itri R, Depeyrot J, Tourinho F, Sousa M (2001) Nanoparticle chain-like formation in electrical double-layered magnetic fluids evidenced by small-angle X-ray scattering. Eur Phys J E 4:201–208
Kroell M, Pridoehl M, Zimmermann L, Pop S, Odenbach S (2005) Magnetic and rheological characterization of novel ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater 289:21–24
Kuzhir P, Gomez-Ramirez A, Lopez-Lopez M, Bossis G, Zubarev A (2011) J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 166
Larson RG (1999) The structure and rheology of complex fluids, Oxford Univ. Press Inc., N.Y
Lopez-Lopez M, Zugaldia A, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Duran J (2006) Sedimentation and redispersion phenomena in iron-based magnetorheological fluids. J Rheol 50:543–560
Lopez-Lopez M, Zugaldia A, Gomez-Ramirez A, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Duran J (2008) Effect of particle aggregation on the magnetic and magnetorheological properties of magnetic suspensions. J Rheol 52:901–912
Massart R (1980) Preparation of aqueous ferrofluids without using surfactant—behavior as a function of the pH and the counterions. CR Acad Sci Paris Ser C 291:1–3
Massart R (1981) Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans Magn MAG-17:1247–1248
Mériguet G, Dubois E, Perzynski R (2003) Liquid-liquid phase-transfer of magnetic nanoparticles in organic solvents. J Colloid Interface Sci 267:78–85
Mériguet G, Cousin F, Dubois E, Boué F, Cebers A, Farago B, Perzynski R (2006) What tunes the structural anisotropy of magnetic fluids under a magnetic field. J Phys Chem B 110:4378–4386
Mériguet G, Wandersman E, Dubois E, Cebers A, de Andrade GJ, Demouchy G, Depeyrot J, Robert A, Perzynski R (2012) Magnetohydrodynamics 48:415–426
Mertelj A, Cmok L, Copic M (2009) Anomalous diffusion in ferrofluids. Phys Rev E 79:041402-1–041402-8
Odenbach S, Stork H (1998) Shear dependence of field-induced contributions to the viscosity of magnetic fluids at low shear rates. J Magn Magn Mater 183:188–194
Odenbach S, Rylewicz T, Heyen M (1999) A rheometer dedicated for the investigation of viscoelastic effects in commercial magnetic fluids. J Magn Magn Mater 201:155–158
Park B, Fang F, Choi H (2010) Magnetorheology: materials and application. Soft Matter 6:5246–5253
Patel R (2011) Mechanism of chain formation in nanofluid based MR fluids. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1360–1363
Ponton A, Bée A, Hasmonay E, Perzynski R, Talbot D (2002) Dynamic probing of thixotropic magnetic gels. J Magn Magnc Mater 252:232–234
Ponton A, Bée A, Talbot D, Perzynski R (2005) Regeneration of thixotropic magnetic gels studied by mechanical spectroscopy: the effect of the pH. J Phys Condens Matter 17:821–836
Ramos J, Hidalgo-Alvarez R, de Vicente J (2011) Steady shear magnetorheology of inverse ferrofluids. J Rheol 55:127–152
Ren Z, Han Y, Hong R, Ding J, Li H (2008) On the viscosity of magnetic fluid with low and moderate solid fraction. Particuology 6:191–198
Rodriguez-Arco L, Lopez-Lopez M, Duran J, Zubarev A, Chirikov D (2011) Stability and magnetorheological behaviour of magnetic fluids based on ionic liquids. J Phys Condens Matter 23:455101 (15pp)
Sandre O, Browaeys J, Perzynski R, Bacri JC, Cabuil V, Rosensweig RE (1999) Assembly of microscopic highly magnetic droplets: magnetic alignment versus viscous drag. Phys Rev E 59:1736–1746
Santiago-Quinones DI, Raj K, Rinaldi C (2013) A comparison of the magnetorheology of two ferrofluids with different magnetic field-dependent chaining behavior. Rheol Acta 52:719–726
Shah K, Upadhyay RV, Aswal VK (2012) Influence of large size magnetic particles on the magneto-viscous properties of ferrofluid. Smart Mater Struct 21:075005 (12pp)
Shahnazian H, Odenbach S (2007) Int J Mod Phys B 21:4806–4812
Shahnazian H, Odenbach S (2008a) New driving unit for the direct measurement of yield stress with a stress controlled rheometer. Appl Rheol 18:54974 (7pp)
Shahnazian H, Odenbach S (2008b) Rheological investigations of ferrofluids with a shear stress controlled rheometer. J Phys Condens Matter 20:204137 (4pp)
Shahnazian H, Graf D, Borin D, Odenbach S (2009) Rheology of a ferrofluid based on nanodisc cobalt particles. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:205004 (6pp)
Shima PD, Philip J (2011) Tuning of thermal conductivity and rheology of nanofluids using an external stimulus. J Phys Chem C 115:20097–20104
Shliomis MI (1972) Effective viscosity of magnetic suspensions. Zh Eksp Teor Fiz 61:2411–2418 [Sov Phys JETP 34: 1291-1294]
Soto-Aquino D, Rinaldi C (2010) Magnetoviscosity in dilute ferrofluids from rotational Brownian dynamics simulations. Phys Rev E 82:046310-1–046310-10
Tourinho FA, Franck R, Massart R (1990) Aqueous ferrofluids based on manganese and cobalt ferrites. J Mater Sci 25:3249–3254
Vereda F, de Vicente J, Segovia-Gutierrez J, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Average particle magnetization as an experimental scaling parameter for the yield stress of dilute magnetorheological fluids. J Phys D Appl Phys 44:425002 (6pp)
Vicente JD, Klingenberg D, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Magnetorheological fluids: a review. Soft Matter 7:3701–3710
Volkova O, Bossis G, Guyot G, Bashtovoi V, Reks A (2000) Magnetorheology of magnetic holes compared to magnetic particles. J Rheol 44:91–104
Wandersman E, Dubois E, Cousin F, Dupuis V, Mériguet G, Perzynski R, Cebers A (2009a) Relaxation of the field-induced structural anisotropy in a rotating magnetic fluid. EPL 86:10005 (6pp)
Wandersman E, Dupuis V, Dubois E, Perzynski R (2009b) Rotational dynamics and aging in a magnetic colloidal glass. Phys Rev E 80:041504-1–041504-12
Zubarev A, Odenbach S, Fleischer J (2002) Rheological properties of dense ferrofluids. Effect of chain-like aggregates. J Magn Magn Mater 252:241–243
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by E. U. under grant no. 235673 from Intra European Fellowship Seventh Framework Program (Marie Curie Actions) and by the program Thermelec which enabled the rheometer modifications and the magnetorheological cell development. The authors are grateful to Dr. Sophie Neveu for the synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Servais and D. Charalampous are also acknowledged for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galindo-Gonzalez, C., Ponton, A., Bee, A. et al. Investigation of water-based and oil-based ferrofluids with a new magnetorheological cell: effect of the microstructure. Rheol Acta 55, 67–81 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-015-0892-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-015-0892-5