Abstract
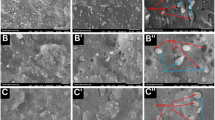
The effect of micron-sized hydrophobic calcium carbonate particles on the stabilization of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/polyisobutylene (PIB) immiscible model blends is investigated in this study. The analytical splitting of bulk and liquid–liquid interface contributions from the droplet bridging one is successfully performed due to the negligible contribution of hydrophobic microparticles to the bulk rheology of phases. The presence of particles at the fluid–fluid interface is supported by wetting parameter calculation and verified by optical microscopy observations. Moreover, direct visualizations shows that particles are able to form clusters of droplets by simultaneously adsorbing at two fluid–fluid interfaces and glue-dispersed droplets together, probably due to the patchy interactions induced by heterogeneous distribution of particles along the interface. Rheological studies show that the flow-induced coalescence is slowed down upon addition of particles and almost suppressed with the addition of 4 wt% particles. The linear viscoelastic response is modeled to estimate interfacial tension by considering the contribution of particle-induced droplet aggregation in addition to bulk and droplet deformation ones. From linear and nonlinear viscoelastic responses, the improved stability of filled polymer blends is attributed to the interfacial rheology and/or the bridged structure of droplets, even though the interfacial area is not fully covered by particles. Furthermore, Doi–Ohta scaling relations are investigated by employing stress growth response upon step-up of shear flow.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya H, Kuila T, Srivastava SK, Bhowmick AK (2008) Effect of layered silicate on EPDM/EVA blend nanocomposite: dynamic mechanical, thermal and swelling properties. Polym Compos 29:443–450
Akcora P, Liu H, Kumar SK, Moll J, Li Y, Benicewicz BC, Schadler LS, Acehan D, Panagiotopoulos AZ, Pryamitsyn V, Ganesan V, Ilavsky J, Thiyagarajan P, Colby RH, Douglas JF (2009) Anisotropic self-assembly of spherical polymer-grafted nanoparticles. Nature Mater 8:354–359
Ansari M, Haghtalab A, Semsarzadeh MA (2006) Effects of compatibilization on rheological properties of PS/PB blends and investigation of Doi–Ohta scaling relationship in double start-up of shear experiments. Rheol Acta 45:983–993
Arditty S, Whitby CP, Binks BP, Schmitt V, Leal-Calderon F (2003) Some general features of limited coalescence in solid-stabilized emulsions. Eur Phys J E 11:273–281
Aveyard R, Clint JH, Nees D, Paunov VN (2000) Compression and structure of monolayers of charged latex particles at air-water and octane-water interfaces. Langmuir 16:1969–1979
Beris AN, Stiakakis E, Vlassopoulos D (2008) A thermodynamically consistent model for the thixotropic behavior of concentrated star polymer suspensions. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 152:76–85
Binks BP (2002) Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7:21–41
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2000a) Influence of particle wettability on the type and stability of surfactant-free emulsions. Langmuir 16:8622–8631
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2000b) Catastrophic phase inversion of water-in-oil emulsions stabilised by hydrophobic silica. Langmuir 16:2539–2547
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2001) Pickering emulsions stabilized by monodisperse latex particles: effects of particle size. Langmuir 17:4540–4547
Binks BP, Whitby CP (2004) Silica particle-stabilized emulsions of silicone oil and water: aspects of emulsification. Langmuir 20:1130–1137
Boode K, Walstra P (1993) Partial coalescence in oil-in-water emulsions.1. Nature of the aggregation. Colloids Surf A 81:121–137
Boode K, Walstra P, Degrootmostert AEA (1993) Partial coalescence in oil-in-water emulsions. 2. Influence of the properties of the fat. Colloids Surf A 81:139–151
Bousmina M, Aouina M, Chaudhry B, Guénette R, Bretas RES (2001) Rheology of polymers blends: non-linear model for viscoelastic emulsions undergoing high deformation flows. Rheol Acta 40:538–551
Chaffey CE, Brenner H (1967) A second-order theory for shear deformation of drops. J Colloid Interface Sci 24:258–269
Chopra D, Vlassopoulos D, Hatzikiriakos SG (2000) Rheological response of phase separating polymer blends: poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride)/poly(methyl methacrylate). J Rheol 44:27–45
Coussot P, Leonov AI, Piau JM (1993) Rheology of concentrated dispersal systems in a low molecular weight matrix. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 46:94–114
Doi M, Ohta T (1991) Dynamics and rheology of complex interfaces. I. J Chem Phys 95:1242–1248
Elias L, Fenouillot F, Majeste JC, Cassagnau P (2007) Morphology and rheology of immiscible polymer blends filled with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 48:6029–6040
Elias L, Fenouillot F, Majeste JC, Alcouffe P, Cassagnau P (2008) Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer 49:4378–4385
Foudazi R, Nazockdast H (2010) Rheology of polypropylene/liquid crystalline polymer blends: effect of compatibilizer and silica. Appl Rheol 20:12218
Graebling D, Muller R, Palierne JF (1993a) Linear viscoelastic behavior of some incompatible polymer blends in the melt. Interpretation of data with a model of emulsion of viscoelastic liquids. Macromolecules 26:320–329
Graebling D, Muller R, Palierne JF (1993b) Linear viscoelasticity of incompatible polymer blends in the melt in relation with interfacial properties. J Phys IV(3):1525–1534
Gubbels F, Jerome R, Teyssie P, Vanlathem E, Deltour R, Calderone A, Parente V, Bredas JL (1994) Selective localization of carbon-black in immiscible polymer blends—a useful tool to design electrical conductive composites. Macromolecules 27:1972–1974
Gubbels F, Jerome R, Vanlathem E, Deltour R, Blacher S, Brouers F (1998) Kinetic and thermodynamic control of the selective localization of carbon black at the interface of immiscible polymer blends. Chem Mater 10:1227–1235
Hemelrijck EV, Puyvelde PV, Velankar S, Macosko CW, Moldenaers P (2004) Interfacial elasticity and coalescence suppression in compatibilized polymer blends. J Rheol 48:143–158
Horozov TS, Binks BP (2006) Particle-stabilized emulsions: a bilayer or a bridging monolayer. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:773–776
Iza M, Bousmina M (2000) Nonlinear rheology of immiscible polymer blends: step strain experiments. J Rheol 44:1363–1384
Iza M, Bousmina M, Jérôme R (2001) Rheology of compatibilized immiscible viscoelastic polymer blends. Rheol Acta 40:10–22
Jacobs U, Fahrlander M, Winterhalter J, Friedrich C (1999) Analysis of Palierne’s emulsion model in the case of viscoelastic interfacial properties. J Rheol 43:1495–1509
Kaelble DH (1970) Dispersion-polar surface tension properties of organic solids. J Adhes 2:66–81
Lee MN, Chan HK, Mohraz A (2012) Characteristics of Pickering emulsion gels formed by droplet bridging. Langmuir 28:3085–3091
Leonov AI (1990) On the rheology of filled polymers. J Rheol 34:1039–1068
Masalova I, Malkin AYa, Foudazi R (2008) Yield stress as measured in steady shearing and in oscillations. Appl Rheol 18:44790
Minale M, Moldenaers P, Mewis J (1997) Effect of shear history on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends. Macromolecules 30:5470–5475
Nagarkar SP, Velankar SS (2012) Morphology and rheology of ternary fluid/fluid/solid systems. Soft Matter 8:8464–8477
Okamoto K, Takahashi M, Yamane H, Kashihara H, Watanabe H, Masuda T (1999) Shape recovery of a dispersed droplet phase and stress relaxation after application of step shear strains in a polystyrene/polycarbonate blend melt. J Rheol 43:951–965
Onuki A (1987) Viscosity enhancement by domains in phase-separating fluids near the critical point: proposal of critical rheology. Phys Rev A 35:5149–5155
Owens DK, Wendt RC (1969) Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 13:1741–1747
Palierne JF (1990) Linear rheology of viscoelastic emulsions with interfacial tension. Rheol Acta 29:204–214
Pickering SU (1908) Emulsions. J Chem Soc Abstr 91–92:2001–2021
Ramsden W (1903) Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and suspensions (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation)—preliminary account. Proc R Soc Lond A 72:156–164
Reynaert S, Moldenaers P, Vermant J (2006) Control over colloidal aggregation in monolayers of latex particles at the oil water interface. Langmuir 22:4936–4945
Reynaert S, Moldenaers P, Vermant J (2007) Interfacial rheology of stable and weakly aggregated two-dimensional suspensions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:6463–6475
Sacanna S, Kegel WK, Philipse AP (2007) Thermodynamically stable Pickering emulsions. Phys Rev Lett 98:158301
Sigillo IL, Di Santo, Guido S, Grizzuti N (1997) Comparative measurements of interfacial tension in a model polymer blend. Polym Eng Sci 37:1540–1549
Stancik EJ, Kouhkan M, Fuller GG (2004) Coalescence of particle-laden fluid interfaces. Langmuir 20:90–94
Sumita M, Sakata K, Asai S, Miyasaka K, Nakagawa H (1991) Dispersion of fillers and the electrical conductivity of polymer blends. Polym Bull 25:265–271
Takahashi Y, Noda I (1995) Immiscible polymer blends under shear flow. In: Nakatani AI, Dadmun MD (eds) Flow-induced structure in polymers. American Chemical Society, Washington DC
Takahashi Y, Kurashima N, Noda I, Doi M (1994a) Experimental tests of the scaling relation for textured materials in mixtures of two immiscible fluids. J Rheol 38:699–712
Takahashi Y, Kitade S, Kurashima N, Noda I (1994b) Viscoelastic properties of immiscible polymer blends under steady and transient shear flows. Polym J 26:1206–1212
Tambe DE, Sharma MM (1994) The effect of colloidal particles on fluid-fluid interfacial properties and emulsion stability. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 52:1–63
Thareja P (2008) Study of particles at fluid/fluid interfaces. PhD Thesis, Chemical Engineering, University of Pittsburgh , Pittsburgh
Thareja P, Velankar SS (2007) Particle-induced bridging in immiscible polymer blends. Rheol Acta 46:405–412
Thareja P, Velankar S (2008) Rheology of immiscible blends with particle-induced drop clusters. Rheol Acta 47:189–200
Thareja P, Moritz K, Velankar SS (2010) Interfacially active particles in droplet/matrix blends of model immiscible homopolymers: particles can increase or decrease drop size. Rheol Acta 49:285–298
Vandebril S, Vermant J, Moldenaers P (2010) Efficiently suppressing coalescence in polymer blends using nanoparticles: role of interfacial rheology. Soft Matter 6:3353–3362
Vermant J, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P, Mewis J, Fuller GG (1998) Anisotropy and orientation of the microstructure in viscous emulsions during shear flow. Langmuir 14:1612– 1617
Vermant J, Cioccolo G, Nair KG, Moldenaers P (2004) Coalescence suppression in model immiscible polymer blends by nano-sized colloidal particles. Rheol Acta 43:529–538
Vermant J, Vandebril S, Dewitte C, Moldenaers P (2008) Particle-stabilized polymer blends. Rheol Acta 47:835–839
Vignati E, Piazza R (2003) Pickering emulsions: interfacial tension, colloidal layer morphology, and trapped-particle motion. Langmuir 19:6650–6656
Vinckier I, Moldenaers P, Mewis J (1996) Relationship between rheology and morphology of model blends in steady shear flow. J Rheol 40:613–631
Wagner M, Wolf BA (1993) Interfacial tension between poly (isobutylene) and poly(dimethylsiloxane): influence of chain length, temperature, and solvents. Macromolecules 26:6498– 6502
Xu H, Lask M, Kirkwood J, Fuller GG (2007) Particle bridging between oil and water interfaces. Langmuir 4:4837–4841
Yamane H, Takahashi M, Hayashi R, Okamoto K, Kashihara H, Masuda T (1998) Observation of deformation and recovery of poly (isobutylene) droplet in a poly(isobutylene)/poly(dimethylsiloxane) blend after application of step shear strain. J Rheol 42:567– 580
Yeganeh JK, Goharpey F, Foudazi R (2010) Rheology and morphology of dynamically asymmetric LCST blends: polystyrene/poly (vinyl methyl ether). Macromolecules 43:8670–8685
Yeganeh JK, Goharpey F, Foudazi R (2012) Can only rheology be used to determine the phase separation mechanism in dynamically asymmetric polymer blends (PS/PVME)?RSC Advances 2:8116–8127
Zhang Z, Glotzer SC (2004) Morphology and rheology of ternary fluid–fluid–solid systems. Nano Lett 4:1407–1413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghimi, E., Goharpey, F. & Foudazi, R. Role of droplet bridging on the stability of particle-containing immiscible polymer blends. Rheol Acta 53, 165–180 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0752-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0752-0