Abstract
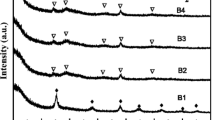
A low-cost electrorheological (ER) material made of micro/nano-structured montmorillonite/titania particles was prepared by a one-pot solvothermal method. The micro/nano-structured particles were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectra, and scanning electron microscopy. It was found that the nanorod-like titania assembled on the surface of montmorillonite, the diameters of the nanorods were about 30 nm, and the lengths were about 300 nm. The electrorheological property of the micro/nano-structured particles in silicone oil was measured under dc electric fields. It was found that the micro/nano-structured montmorillonite/titania ER fluid exhibited much stronger electrorheological effect compared to pure montmorillonite and pure titania nanorod ER fluids, while its leaking current density was significantly lower than that of montmorillonite ER fluid. The stronger electrorheological effect might be attributed to the larger interfacial polarization and interparticle friction, which originated from the unique structure and morphology of micro/nano-structured particles, compared to pure montmorillonite and pure titania nanorods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartl MH, Boettcher SW, Frindell KL et al (2005) 3-D molecular assembly of function in titania-based composite material systems. Acc Chem Res 38:263–271
Block H, Kelly JP (1988) Electro-rheology. J Phys D: Appl Phys 21:1661–1677
Cho MS, Choi HJ, To K (1998) Effect of ionic pendent groups on a polyaniline-based electrorheological fluid. Macromol Rapid Commun 19:271–273
Cho MS, Choi HJ, Ahn WS (2004) Enhanced electrorheology of conducting polyaniline confined in MCM-41 channels. Langmuir 20(1):202–207
Cho MS, Cho YH, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2003) Synthesis and electrorheological characteristics of polyaniline-coated poly(methyl methacrylate) microsphere: size effect. Langmuir 19(14):5875–5881
Cho MS, Kim JW, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2005) Polyaniline and its modification for electroresponsive material under applied electric fields. Polym Adv Technol 6:352–356
Choi HJ, Cho MS, Jhon MS (1998) Electrorheological properties of poly(acene quinone) radical suspensions. Polym Adv Technol 8:697–700
Choi HJ, Lee YH, Kim CA, John MS (2000) Microencapsulated polyaniline particles for electrorheological materials. J Mater Sci Lett 19:533–535
Choi HJ, Cho MS, Kim JW, Kim CA, Jhon MS (2001) A yield stress scaling function for electrorheological fluids. Appl Phys Lett 78:3806–3808
Couter SP, Weiss KD, Carlson JD (1993) Engineering applications of electrorheological materials. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 4:248–259
Dong YC, Feng SS (2005) Nanoparticles of montmorillonite (MMT)/poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 26:6068–6076
Fang FF, Choi HJ, Joo J (2008) Conducting polymer/clay nanocomposites and their applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8(4):1559–1581
Foulc JN, Atten P, Boissy C (1996) Correlation between electrical and rheological properties of electrorheological fluids. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 17:579–582
Gast P, Zukoski CF (1989) Electrorheological fluids as colloidal suspensions. Adv Colloid Interfacial Sci 30:153–202
Halsey TC (1992) Electrorheological fluids. Science 258:761–766
Han ZH, Zhu HY, Ratinac KR, Ringerc SP, Shi J, Liu JW (2008) Nanocomposites of layered clays and cadmium sulfide: similarities and differences in formation, structure and properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 108:168–182
Hao T (1997) The role of the dielectric loss of dispersed material in the electrorheological effect. Appl Phys Lett 70:1956–1958
Hao T, Kawai A, Ikazaki F (1998) Mechanism of the electrorheological effect: evidence from the conductive, dielectric, and surface characteristics of water-free electrorheological fluids. Langmuir 14:1256–1262
Huang JP (2004) Force acting on the microparticles in electrorheological solids under the application of a nonuniform ac electric field. Chem Phys Lett 390:380–383
Ikazaki F, Kawai A, Uchida K, Kawakami T, Edmura K, Sakurai K, Anzai H, Asako Y (1998) Mechanisms of electrorheology: the effect of the dielectric property. J Phys D: Appl Phys 31:336–347
Jang WH, Kim JW, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2001) Synthesis and electrorheology of camphorsulfonic acid doped polyaniline suspensions. Colloid Polym Sci 279:823–827
Kim JW, Kim SG, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (1999) Synthesis and electrorheological properties of polyaniline-Na + -montmorillonite suspensions. Macromol Rapid Commun 20:450–452
Kim SG, Lim JY, Sung JH, Choi HJ, Seo Y (2007) Emulsion polymerized polyaniline synthesized with dodecylbenzene-sulfonic acid and its electrorheological characteristics: temperature effect. Polymer 48:6622–6631
Klingenberg DJ, Swol F, Zukoski CF (1991) The small shear rate response of electrorheological suspensions: I. Simulation in the point–dipole limit. J Chem Phys 94:6160–6163
Lim YT, Park JH, Park OO (2002) Improved electrorheological effect in polyaniline nanocomposite suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 245:198–203
López-López MT, Kuzhir P, Bossis G, Mingalyov P (2008) Preparation of well-dispersed magnetorheological fluids and effect of dispersion on their magnetorheological properties. Rheol Acta 47:787–796
López-López MT, Kuzhir P, Bossis G (2009) Magnetorheology of fiber suspensions: I. Experimental. J Rheol 53:115–126
Lu J, Zhao XP (2002) Electrorheological properties of suspensions based on polyaniline-montmorillonite clay nanocomposite. J Mater Res 15:2258–2265
Lu J, Zhao XP (2004) A new approach of enhancing the shear stress of electrorheological fluids of montmorillonite nanocomposite by emulsion intercalation of poly-N-methaniline. J Colloid Interface Sci 273:651–657
Manikandana D, Divakara D, Valentine RA, Revathia S, Esther Leena Preethia M, Sivakumar T (2007) Synthesis of platinum nanoparticles in montmorillonite and their catalytic behaviour. Appl Clay Sci 37:193–200
O’Dwyer C, Navas D, Lavayen V, Benavente E, Santa Ana MA, González G, Newcomb SB, Sotomayor Torres CM (2006) Nano-urchin: the formation and structure of high-density spherical clusters of vanadium oxide nanotubes. Chem Mater 18:3016–3022
Otsubo Y (1999) Electrorheology of whisker suspensions. Colloids Surf A 153:459–466
Parthasarathy M, Klingenberg DJ (1996) Electrorheology: mechanisms and models. Mater Sci Eng R 17:57–103
Pavlinek V, Saha P, Perez-Gonzalez J, Vargas L, Stejskal J, Quadrat O (2006) Analysis of the yielding behavior of electrorheological suspensions by controlled shear stress experiments. Appl Rheol 16:14–18
Pietron JJ, Stux AM, Compton RS, Rolison DR (2007) Dye-sensitized titania aerogels as photovoltaic electrodes for electrochemical solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91:1066–1074
Schmidt G, Nakatani AI, Han CC (2002) Rheology and flow-birefringence from viscoelastic polymer–clay solutions. Rheol Acta 41(1–2):45–54
See H, Kawai A, Ikazaki F (2002) Differences in the electrorheological response of a particle suspension under direct current and alternating current electric fields. Colloid Polym Sci 280:24–29
Sudha JD, Sasikala TS (2007) Studies on the formation of self-assembled nano/microstructured polyaniline–clay nanocomposite (PANICN) using 3-pentadecyl phenyl phosphoric acid (PDPPA) as a novel intercalating agent cum dopant. Polymer 48:338–347
Svitova T, Theodoly O, Christiano S, Hill RM, Radke CJ (2002) Wetting behavior of silicone oils on solid substrates immersed in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Langmuir 18(18):6821–6829
Wang BX, Zhao XP (2002) Electrorheological behavior of kaolinite-polar liquid intercalation composites. J Mater Chem 12:1865–1869
Wang BX, Zhao XP (2005) Wettability of bionic nanopapilla particles and their high electrorheological activity. Adv Funct Mater 15:1815–1820
Whitesides GM, Grzybowski B (2002) Self-assembly at all scales. Science 295:2418–2421
Xiang LQ, Zhao XP (2006) Preparation of montmorillonite/titania nanocomposite and enhanced electrorheological activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 296:131–140
Yang SW, Gao L (2005) Fabrication and characterization of nanostructurally flowerlike aggregates of TiO2 via a surfactant-free solution route: effect of various reaction media. Chem Lett 34:1044–1045
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2002) Preparation and electrorheological activity of mesoporous rare-earth-doped TiO2. Chem Mater 14:4633–4640
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2004) Giant electrorheological activity of high surface area mesoporous cerium-doped TiO2 templated by block copolymer. Chem Phys Lett 398:393–399
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2006) Enhanced electrorheological activity of mesoporous Cr-doped TiO2 from activated pore wall and high surface area. J Phys Chem B 110:12,916–12,925
Yin JB, Zhao XP, Xiang LQ, Xia X, Zhang ZS (2009) Enhanced electrorheology of suspensions containing sea-urchin-like hierarchical Cr-doped titania particles. Soft Matter 5:4687–4696
Yin JB, Xia X, Xiang LQ, Zhao XP (2010) Conductivity and polarization of carbonaceous nanotubes derived from polyaniline nanotubes and their electrorheology when dispersed in silicone oil. Carbon 48:2958–2967
Yu HG, Yu JG, Cheng B, Lin J (2007) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of mesoporous titania nanorod/titanate nanotube composites. J Hazard Mater 147:581–587
Zhao XP, Yin JB (2002) Preparation and electrorheological characteristics of rare-earth-doped TiO2 suspensions. Chem Mater 14:2258–2263
Zhao XP, Yin JB (2006) Advances in electrorheological fluids based on inorganic dielectric materials. J Ind Eng Chem 12:184–198
Zhao XP, Yin JB, Tang H (2006) New advances in electrorheological fluids and devices. In: Reece PL (ed) Smart materials and structures: new research. Nova Science Publishing, New York, pp 1–66
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 60778042 and 50602036)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, L., Zhao, X. & Yin, J. Micro/nano-structured montmorillonite/titania particles with high electrorheological activity. Rheol Acta 50, 87–95 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0516-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0516-z