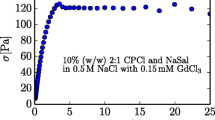
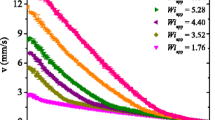
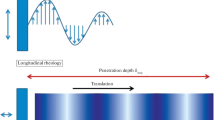
Abstract
The phenomenon of shear banding in complex fluids has been investigated using NMR velocimetry and NMR spectroscopy, mostly in wormlike micelle systems, but more recently in colloidal systems and multilayer vesicles. A particular advantage of NMR is the ability to simultaneously investigate structural ordering and to compare such ordering with local strain rates. In this paper, we describe the basics of Rheo-NMR and summarise its recent application to the study of shear banding.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abragram A (1961) The principles of nuclear magnetism. Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK
Baudez JC, Rodts S, Chateau X, Coussot P (2004) New technique for reconstructing instantaneous velocity profiles from viscometric tests: Application to pasty materials. J Rheol 48:69–82
Becu L, Manneville S, Colin A (2004) Spatiotemporal dynamics of wormlike micelles under shear. Phys Rev Lett 93:018301
Bertola V, Bertrand F, Tabuteau H, Bonn D, Coussot P (2003) Wall slip and yielding in pasty materials. J Rheol 47:1211–1226
Berret J-F, Roux DC (1995) Rheology of nematic wormlike micelles. J Rheol 39:725–741
Berret J-F, Appell J, Porte G (1993) Linear rheology of entangled wormlike micelles. Langmuir 9:2851–2854
Berret J-F, Roux DC (1994) Porte G Isotropic-to-nematic transition in wormlike micelles under shear. J Phys II France 4:1261–1279
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1997a) Two-phase shear band structures at uniform stress. Phys Rev Lett 78:4930–4933
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1997b) NMR visualisation of anomalous flow in cone-and-plate rheometry. J Rheol 41:1365–1386
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1999) Shear banding instability in wormlike micellar solutions. Eur Phys J B7:37–249
Callaghan PT (1991) Principles of NMR Microscopy., Oxford University Press, (published in paperback, 1993) pp 492
Callaghan PT (1999) Rheo-NMR: nuclear magnetic resonance and the rheology of complex fluids. Rep Prog Phys 62:599–670
Callaghan PT, Stepisnik J (1995) Frequency domain analysis of spin motion using modulated gradient NMR. J Magn Reson A117:118–122
Callaghan PT, Gil AM (2000) Rheo-NMR of semi-dilute polyacrylamide in water. Macromolecules 33:4116–4124
Callaghan PT, Eccles CD, Xia Y (1988) NMR Microscopy of Dynamic Displacements: k-space and q-space imaging. J Phys E 21:820–822
Callaghan PT, Cates ME, Rofe CJ, Smeulders JBAF (1996) A study of the “Spurt Effect” in wormlike micelles using nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy. J Phys II 6:375–393
Cappelaere E, Berret J-F, Decruppe JP, Cressely R, Lindner P (1997) Rheology, birefringence, and small-angle neutron scattering in a charged micellar system: Evidence of a shear-induced phase transition. Phys Rev E 56:1869–1878
Cates ME (1987) Reptation of living polymers: dynamics of entangled polymers in the presence of reversible chain-scission reactions. Macromolecules 20:2289–2296
Cates ME (1988) Dynamics of Living Polymers and flexible surfactant micelles: scaling laws for dilution. J Phys France 49:1593–1600
Cates ME (1990) “Nonlinear viscoelasticity of wormlike micelles (and other reversibly breakable polymers). J Phys Chem 94:371–375
Cates ME, Candau SJ (1990) Statics and dynamics of worm-like surfactant solutions. J Phys Condens Matter 2:6869–6892
Cates ME, McLeish TCB, Marrucci G (1993) The rheology of entangled polymers at very high shear rates. Europhys Lett 21:451–456
Coussot P, Raynaud JS, Bertrand F, Moucheront P, Guilbaud JP, Huynh HT, Jarny S, Lesueur D (2002) Coexistence of liquid and solid phases in flowing soft-glassy materials. Phys Rev Lett 88:218301
Coussot P, Tabuteau H, Chateau X, Tocquer L, Ovarlez G (2006) Aging and solid or liquid behavior in pastes. J Rheol 50:975–994
Decruppe JP, Cressely R, Makhloufi R, Cappelaere E (1995) Flow birefringence experiments showing a shear banding structure in a CTAB solution. Colloid and Polym Sci 275:346–351
Douglass BS, Colby RH, Madsen LA, Callaghan PT (2007) Rheo-NMR of wormlike micelles formed from non-ionic pluronic surfactants. Macromolecules (in press)
Ernst RR, Bodenhausen G, Wokaun A (1987) Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance in one and two dimensions. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Fielding SM (2005) Linear instability of planar shear banded flow. Phys Rev Lett 95:134501
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003a) Flow phase diagrams for concentration-coupled shear banding. Eur Phys J E 11:65–83
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003b) Early stage kinetics in a unified model of shear-induced demixing and mechanical shear banding instabilities. Phys Rev Lett 90:224501
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003c) Kinetics of the shear banding instability in startup flows. Phys Rev E 68:036313
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2004) Spatiotemporal oscillations and rheochaos in a simple model of shear banding. Phys Rev Lett 92:084502
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2006) Nonlinear dynamics of an interface between shear bands. Phys Rev Lett 96:104502
Fischer P (2000) Time dependent flow in equimolar micellar solutions: transient behaviour of the shear stress and first normal stress difference in sheer induced structures coupled with flow instabilities. Rheol Acta 39:234–240
Fischer E, Callaghan PT (2000) Is a birefringence band a shear band? Europhys Lett 50:803–809
Fischer E, Callaghan PT (2001) Shear banding and the isotropic to nematic transition in wormlike micelles. Phys Rev E 6401:1501
Fuller GG (1995) Optical rheometry of complex fluids. Oxford University Press, New York
Galvosas P, Callaghan PT (2006) Fast magnetic resonance imaging and velocimetry for liquids under high flow rates. J Magn Reson 181:119–125
Goldman M (1991) Quantum description of high-resolution NMR in liquids. Oxford University Press, New York
Grabowski DA, Schmidt C (1994) Simultaneous measurement of shear viscosity and director orientation of a side-chain liquid-crystalline polymer by rheo-NMR. Macromolecules 27:2632–2643
Hanlon AD, Gibbs SJ, Hall LD, Laycock DE, Frith WJ, Ablett S (1998) Magn Reson Imaging.16:953–961
Holmes WM, López-González MR, Callaghan PT (2003a) Fluctuations in shear banded flow seen by NMR velocimetry. Eur Phys Lett 64:274–280
Holmes WM, López-González MR, Callaghan PT (2003b) Shear-induced constraints to amphiphile chain dynamics in wormlike micelles. Eur Phys Lett 66:132–138
Holmes WM, Callaghan PT, Vlassopoulos D, Roovers J (2004) Shear banding in ultra soft colloidal glasses. J Rheol 48:1085–1102
Janeschitz-Kriegl J (1983) Polymer melt rheology and flow birefringence. Springer, New York
Kalus J, Neubauer G, Schemlzer U (1990) A new shear apparatus for small-angle neutron-scattering (SANS) measurements. Rev Sci Instr 61:3384
Kilfoil ML, Callaghan PT (2000) NMR measurement of the alignment tensor for a polymer melt under strong shearing flow. Macromolecules 33:6828–6833
López-González MR, Photinos P, Holmes WM, Callaghan PT (2004) Fluctuations and order for wormlike micelles under shear. Phys Rev Lett 93:268302–268305
López-González MR, Holmes WM, Callaghan PT (2006) Rheo-NMR phenomena of wormlike micelles. Soft Matter 2:855–869
Lutti A, Callaghan PT (2006) Measurement of diffusion in the presence of shear flow. J Magn Reson 180:83–92
Lutti A, Callaghan PT (2007) Effect of shear on an onion texture. Eur Phys J E 24:129–137
Mair RW, Callaghan PT (1996) (719–724) Observation of shear banding in wormlike micelles by NMR velocity imaging. Europhys Letters 36:719–724
Makhloufi R, Decruppe JP, Ait-Ali A, Cressely R (1995) Rheo-optical Study of worm-like micelles undergoing a shear banding flow. Europhys Lett 32:253–258
Manneville S, Becu L, Colin A (2004) High-frequency ultrasonic speckle velocimetry in sheared complex fluids. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 28:361–373
Nakatani A, Waldo DA, Han CC (1992) A rheometer with 2-dimensional area detection for light-scattering-studies of polymer melts and solutions. Rev Sci Instr 63:3590
Olmsted PD (1999) Dynamics and flow-induced phase separation in polymeric fluids. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 4:95–100
Plano RJ, Safinya CR, Sirota EB, Wenzel LJ (1993) X-ray couette shear cell for nonequilibrium structural studies of complex fluids under flow. Rev Sci Instr 64:1309
Radulescu O, Olmsted PD, Lu CYD (1999) Shear banding in reaction-diffusion models. Rheol Acta 38:606–613
Raynaud JS, Moucheront P, Baudez JC, Bertrand F, Guilbaud JP, Coussot P (2002) Direct determination by nuclear magnetic resonance of the thixotropic and yielding behavior of suspensions. J Rheol 46:709–732
Rehage H, Hoffman H (1988) Rheological properties of viscoelastic surfactant systems. J Phys Chem 92:4712–4719
Rehage H, Hoffman H (1991) Viscoelastic surfactant solutions: model systems for rheological research. Mol Phys 74:933–973
Salmon JB, Manneville S, Colin A (2003a) Shear banding in a lyotropic lamellar phase. I. Time-averaged velocity profiles. Phys Rev E 68:051503
Salmon JB, Manneville S, Colin A (2003b) Shear banding in a lyotropic lamellar phase. II. Temporal fluctuations. Phys Rev E 68:051504
Schmidt-Rohr K, Spiess H-W (1994) Multi-dimensional solids state NMR and polymers. Academic Press, London
Slichter CP (1990) Principles of magnetic resonance. Springer, Berlin
Spenley NA, Cates ME, McLeish TCB (1993) Nonlinear rheology of wormlike micelles. Phys Rev Lett 71:939–942
Spenley NA, Yuan XF, Cates ME (1996) Nonmonotonic constitutive laws and the formation of shear-banded flows. J Phys II France 6:551–571
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependant magnetic field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Stepisnik J (1981) Analysis of NMR self-diffusion by a density matrix calculation. Physica B and C 104:350–364
Wassenius H, Callaghan PT (2005) NMR velocimetry and the steady-shear rheology of a concentrated hard-sphere colloidal system. Eur Phys J 18:69–84
Wilson HJ, Fielding SM (2006) Linear instability of planar shear banded flow of both diffusive and non-diffusive Johnson-Segalman fluids. J Non-newton Fluid Mech 138:181–196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Callaghan, P.T. Rheo NMR and shear banding. Rheol Acta 47, 243–255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0251-2