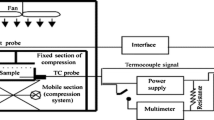
Abstract
The effect of high-pressure treatments on the gelation of egg yolk dispersions was studied by using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and small amplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS). The influence of pressure of processing and pH were analysed. The DSC results suggest a progressive decrease in thermal denaturation enthalpy as pressure level increases related to protein denaturation. SAOS was used to evaluate the effect of different pressure levels on the linear viscoelastic behaviour of egg yolk dispersions. An increase in the pressure level produces a dramatic change in the linear viscoelastic behaviour undergoing a sol–gel transition. High hydrostatic pressure (HHP) processing was also analysed as a function of pH and solids content. The results obtained confirm that the impact of high pressure on aggregation and network formation can be modulated by pH. HHP processing of egg yolk systems is highly affected by protein concentration particularly when it is compared to heat processing.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam M, Lairez D (1996) In: Cohen Addad JP (ed) Physical properties of polymeric gels. Wiley, New York, pp 88–139
Brandts JF, Oliveira RJ, Westort C (1970) Thermodynamics of protein denaturation. Effect of pressure on the denaturation of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry 9:1038–1047
Bridgman PW (1914) The coagulation of albumen by pressure. J Biol Chem 19:511–512
Chambon F, Winter HH (1987) Linear viscoelasticity at the gel point of a crosslinking PDMS with imbalanced stoichiometry. J Rheol 31:683–697
Cordobés F, Partal P, Guerrero A (2004) Rheology and microstructure of heat-induced egg yolk gels. Rheol Acta 43:184–195
de Gennes PG (1979) Scaling concepts in polymer physics. Cornell Univ. Press, Ithaca
De Rosa ME, Winter HH (1994) The effect of entanglements on the rheological behavior of polybutadiene critical gels. Rheol Acta 33:220–237
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Galazka VB, Ledward DA (1988) In: Hill SE, Ledward DA, Mitchell JR (eds) Functional properties of food macromolecules. Aspen, Maryland, pp 278–301
Guerrero A, Carmona JA, Martínez I, Partal P (2004) Effect of pH and added electrolyte on the thermal-induced transitions of egg yolk. Rheol Acta 43:539–549
Harrison LJ, Cunningham FE (1986) Influence of salt on properties of liquid yolk and functionality in mayonnaise. Poultry Sci 65:915–921
Hawley SA (1971) Reversible pressure–temperature denaturation of chymotrypsinigen. Biochemistry 10:2436–2442
Hayakawa I, Kajihara J, Morikawa K, Oda M, Fujio Y (1992) Denaturation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and ovoalbumin by high pressure, heat and chemicals. J Food Sci 57(2):288–292
Hayashi R, Kawamura Y, Nakasa T, Okinaka O (1989) Application of high pressure to food processing: pressurization of egg white and yolk, and properties of the gel formed. Agric Biol Chem 53:2935–2939
Hegg P (1982) Conditions for the formation of heat-induced gels of some globular food proteins. J Food Sci 47:1241–1244
Hsu S (1999) Rheological studies on gelling behavior of soy protein isolates. J Food Sci 64:136–140
Hsu S, Lu S, Huang C (2000) Viscoelastic changes of rice starch suspensions during gelatinization. J Food Sci 65:215–220
Kiosseoglou VD, Sherman P (1983) The influence of egg yolk lipoproteins on the rheology and stability of O/W emulsions and mayonnaise. Colloid Polym Sci 261:502–507
Knorr D (1996) In: Hayashi R, Balny C (eds) High pressure bioscience and biotechnology. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 279–289
Martinet V, Saulnier P, Beaumal V, Courthaudon JL, Anton M (2003) Surface properties of hen egg yolk low-density lipoproteins spread at the air–water interface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 31:185–194
McCully KA, Mok CC, Common RH (1962) Paper electrophotetic characterization of proteins and lipoproteins of hen’s yolk. Can J Biochem Physiol 40:937–952
Messens W, Van Camp J, Huyghebaert A (1997) The use of high pressure to modify the functionality of food proteins. Trends Food Sci Technol 8:107–112
Okamoto M, Kawamura Y, Hayashi R (1990) Application of high pressure to food processing: Textural comparison of pressure and heat-induced gels of food proteins. Agric Biol Chem 54:183–189
Sánchez C, Burgos J (1997) Gelation of Sunflower Globulin Hydrolysates: Rheological and Calorimetric studies. J Agric Food Chem 45:2407–2412
Scanlan JC, Winter HH (1991) Composition dependence of the viscoelasticity of end-linked poly(dimethylsiloxane) at the gel point. Macromolecules 24:47–54
Shenstone FS (1968) In: Carter TC (eds) Egg quality: A study of the hen’s egg, Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh, pp 26–66
Speroni F, Puppo C, Chapleau N, De Lamballerie M, Castellani O, Anon MC, Anton M (2005) High pressure induced physicochemical and functional modifications of low-density lipoproteins from hen egg yolk. J Agric Food Chem 57:5719–5725
Suzuki K, Miyosawa Y, Suzuki C (1963) Protein denaturation by high pressure. Measurement of turbidity of isoelectric ovoalbumin and horse serum albumin under high pressure. Arch Biochem Biophys 101:225–228
Te Nijenhuis K (1981) Investigation into the aging process in gels of gelatin/water systems by the measurements of their dynamic moduli I Phenomenology. Colloid Polym Sci 259:522–535
Winter HH (1987) Can the gel point of a cross-linking polymer be detected by the G′–G″ crossover? Polym Eng Sci 27:1698–1702
Winter HH, Chambon F (1986) Analysis of the linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol 30:367–382
Wright DJ (1986) In: Hudson BJF (ed) Developments in food proteins, vol 4. Applied Science, London, pp 61–90
Zipp A, Kauman W (1973) Pressure denaturation of metmyoglobin. Biochemistry 12:4217–4228
Acknowledgements
This work was part of a research project no. AGL2002-01106, supported by the Spanish MCYT. The financial support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilar, J.M., Cordobés, F., Jerez, A. et al. Influence of high pressure processing on the linear viscoelastic properties of egg yolk dispersions. Rheol Acta 46, 731–740 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0170-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0170-2