Abstract.
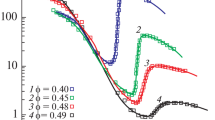
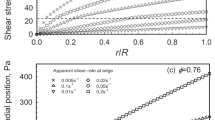
Concentrated suspensions of charged latex particles of poly(styrene-butadiene) have been used as model systems to investigate the influence of surface charges on the rheology of colloidal suspensions. The suspensions were found to behave as elastic solids at small strains and to require a finite stress to flow. This was related to an ordered structure of the suspensions at rest, resulting from electrostatic and van der Waals forces. Important shear-thinning effects were observed as a consequence of structure rearrangements under shear. At a fixed shear rate, the steady-shear viscosity as a function of the ionic strength exhibits a minimum. Under oscillatory shear flow, the behavior of the concentrated suspensions was found to be non-linear above a very small strain amplitude. The non-linear output signal from dynamic experiments was analyzed using a fast Fourier transform algorithm. A maximum in the third harmonic intensity as a function of the strain amplitude was observed and the intensity of higher harmonics decreased with increasing ionic strength. The behavior of the suspensions could be adequately described using the structural model of Yziquel et al. (Yziquel F, Carreau PJ, Moan M, Tanguy PA (1999) Rheological modeling of concentrated colloidal suspensions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 86:133–155).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alince B (1999) Cationic latex as a multifunctional papermaking wet-additive. TAPPI J 82(3):175–186
Barbesta F, Bousfield DW, Rigdhal M (2001) Modeling of rheological properties of coating colours. J Rheol 45:139–160
Barnes HA (1995) A review of the slip (wall depletion) of polymer solutions, emulsions and particle suspensions in viscometers: its cause, character, and cure. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 56:221–251
Chatterjee AK (1983) Colloidal structure-property relationships in carboxylated styrene-butadiene latexes. Rubber Chem Technol 56:995–1010
Chonde Y, Shabrang M (1997) Dielectric spectroscopy of high-solids, styrene-butadiene latex dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 186:248–253
Chow RS, Takamura K (1988) Effects of surface roughness (hairiness) of latex particles on their electrokinetic potentials. J Colloid Interface Sci 125(1):226–236
Citerne GP, Carreau PJ, Moan M (2001) Rheological properties of peanut butter. Rheol Acta 40:86–96
Crocker JC, Grier DG (1998) Interactions and dynamics in charge-stabilized colloid. MRS Bull 23:24–31
d'Antonio C (1996) Processes for the production of latex-cement composites. Coat Compos Mater 4(13):22–27
Eagland D, Crum RM, Oldfield LM (1996) Comparison of steady shear and oscillatory rheology of carboxylated acrylic latices. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress on Rheology, Quebec City, pp 530–531
Elimelech M, O'Melia CR (1990) Effect of electrolyte type on the electrophoretic mobility of polystyrene latex colloids. Colloids Surf 44:165–178
Greene BW (1973) Quantitative determination of surface carboxyl groups in vinyl acid modified styrene/butadiene copolymer latexes. I. Latexes prepared with acrylic acid. J Colloid Interface Sci 43(2):449–461
Heymann L, Peukert S, Aksel N (2002) Investigation of the solid-liquid transition of highly concentrated suspensions in oscillatory amplitude sweeps. J Rheol 46:93–112
Hiemenz PC (1986) Principles of colloid and surface chemistry. Dekker, New York
Kallus S, Willenbacher N, Kirsch S, Distler D, Neidhöfer T, Wilhelm M, Spiess HW (2001) Characterisation of polymer dispersions by Fourier transform rheology. Rheol Acta 40:552–559
Krieger IM (1972) Rheology of monodisperse lattices. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 3:111–136
Krieger IM, Dougherty IJ (1959) A mechanism for non-Newtonian flow in suspensions of rigid spheres. Trans Soc Rheol 3:137–152
Krieger IM, Eguiluz M (1976) The second electroviscous effect in polymer lattices. Trans Soc Rheol 20(1):29–45
Leoni R (1999) Safer chemistry for the building industry: chemical products in and on cement. Chim Ind 81(5):611–615
Maier PG, Göritz D (1996) Molecular interpretation of the Payne effect. Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 49(1):18–21
Midmore BR, Hunter RJ (1988) The effect of electrolyte concentration and co-ion type on the ζ-potential of polystyrene latices. J Colloid Interface Sci 122(2):521–529
Ogawa A, Yamada H, Matsuda S, Okajima K (1997) Viscosity equation for concentrated suspensions of charged colloidal particles. J Rheol 41(3):769–785
Ottow S, Zimehl R (2000) Polystyrene particles with proton-ionisable groups: pH-dependent stability of lattices with weakly acidic groups. Colloid Polym Sci 278:176–180
Polverari M, van de Ven TGM (1994) Dynamic light scattering of suspensions of PEO-coated latex particles. Colloids Surf A 86:209–228
Raghavan SR, Khan SA (1995) Shear-induced microstructural changing in flocculated suspensions of fumed silica. J Rheol 40:167–186
Roland CM (1990) Dynamic mechanical behavior of filled rubber at small strains. J Rheol 34:25–34
Russel WB (1980) Review of the role of colloidal forces in the rheology of suspensions. J Rheol 24(3):287–317
Russel WB, Saville DA, Schowalter WR (1989) Colloidal dispersions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sakota K, Okaya T (1976) Preparation and characterization of carboxylated isoprene/styrene copolymer latexes. J Appl Polym Sci 20:1735–1744
Schulz SF, Gisler T, Borkovec M, Sticher H (1994) J Colloid Interface Sci 164:88–98
Seebergh JE, Berg JC (1995) Evidence of a hairy layer at the surface of polystyrene latex particles. Colloids Surf 100:139–153
Thun C, van de Ven TGM (1998) Deposition of hairy latex particles onto a glass surface. Colloids Surf A 145:205–212
van der Vorst B, van den Ende D, Mellema J (1995) Linear viscoelastic properties of ordered latices. J Rheol 39(6):1183–1200
Wilhelm M (2001) Fourier-transform-rheology. Thesis for the German Habilitation, Mainz, Germany
Wilhelm M, Maring D, Spiess HW (1998) Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 37:399–405
Wilhelm M, Reinheimer P, Ortseifer M (1999) High sensitivity Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 38:349–356
Wilhelm M, Reinheimer P, Ortseifer M, Neidhöfer T, Spiess HW (2000) The crossover between linear and non-linear mechanical behavior in polymer solutions as detected by Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 39:241–247
Wu X, van de Ven TGM (1996) Characterization of hairy particles with colloidal particle scattering. Langmuir 12(16):3858–3865
Yziquel F, Carreau PJ, Moan M, Tanguy PA (1999a) Rheological modeling of concentrated colloidal suspensions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 86:133–155
Yziquel F, Carreau PJ, Tanguy PA (1999b) Non-linear viscoelastic behavior of fumed silica suspensions. Rheol Acta 38:14–25
Zimehl R, Priewe J (1996) Colloid stability of hydrophilic latexes. Progr Colloid Polym Sci 101:116–119
Zimehl R, Lagaly G, Ahrens J (1990) Some aspects of polymer colloids. I. Preparation and properties of different types of latex particles. Colloid Polym Sci 268:924–933
Acknowledgements.
Acknowledgements are due to the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada for the financial support. The authors thank Dr. K. Takamura from BASF for kindly providing the latex samples and to Dr. M. Wilhelm from the Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung, Mainz, Germany for the set-up used in Fourier transform analysis. We are also thankful to Dr. A. Ouhlal, Dr. J. Petlicki, and Mr. F. Cotton for technical help, and to Dr. J. Finch from Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Department of McGill University for the permission of using the Zeta-Plus Analyzer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Craciun, L., Carreau, P.J., Heuzey, MC. et al. Rheological properties of concentrated latex suspensions of poly(styrene-butadiene). Rheol Acta 42, 410–420 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-003-0295-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-003-0295-x