Abstract
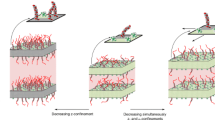
The object of the research was to investigate the influence of a semiflexible polyanion (carboxymethylcellulose) in the absence and presence of a more flexible cationic polyelectrolyte [poly(diallyldimethyl-ammonium chloride)] on structure formation in liquid-crystalline model systems consisting of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)/ decanol/water. Small-angle X-ray measurements in combination with electron microscopic investigations show the adsorption of the polycation on the SDS head groups. These polymer-modified lamellae form multilamellar vesicles. The semiflexible polyanion was embedded into the liquid crystal without macroscopic phase separation and multivesicular vesicles were formed on the supramolecular level. In combination the oppositely charged polyelectrolytes induce the formation of multivesicular structures where two lamellar structures coexist.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 July 1999/Accepted in revised form: 22 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kötz, J., Tiersch, B. & Bogen, I. Polyelectrolyte-induced vesicle formation in lamellar liquid-crystalline model systems. Colloid Polym Sci 278, 164–168 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050027