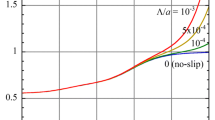
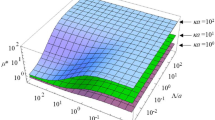
Abstract
A theory is developed of the electrophoresis of a spherical colloidal particle with a slip surface in a concentrated suspension on the basis of Kuwabara’s cell model. We introduce the slipping length on the particle surface, which is the measure of the particle surface hydrophobicity. We derive the general expression of the particle electrophoretic mobility and its approximate analytic expressions for a particle carrying a low zeta potential. Expressions for other electrokinetics, that is, electrical conductivity, sedimentation velocity, and potential in concentrated suspensions, are also derived. Furthermore, it is shown that as in the case of a dilute suspension, a similarity is found between the electrokinetics of charged spherical solid particles with a slip surface in a concentrated suspension and that for liquid drops.

Electrophoretic mobility of a sphere with a slip surface in a concentrated suspension


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuwabara S (1959) The forces experienced by randomly distributed parallel circular cylinders or spheres in a viscous flow at small Reynolds numbers. J Phys Soc Jpn 14:527–532
Levine S, Neale GH (1974) The prediction of electrokinetic phenomena within multiparticle systems. I. Electrophoresis and electroosmosis. J Colloid Interface Sci 47:520–529
Shilov VN, Zharkikh NI, Borkovskaya YB (1981) Theory of non-equilibrium electrosurface phenomena in concentrated disperse systems. I. Application of nonequilibrium thermodynamics to cell. Colloid J 43:434–438
Kozak MW, Davis EJ (1986) Electrokinetic phenomena in fibrous porous media. J Colloid Interface Sci 112:403–411
Kozak MW, Davis EJ (1989) Electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions and porous media: I Thin electrical double layers. J Colloid Interface Sci 127:497–510
Kozak MW, Davis EJ (1989) Electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions and porous media: 2 Moderately thick electrical double layers. J Colloid Interface Sci 129:166–174
Ohshima H (1997) Electrophoretic mobility of spherical colloidal particles in concentrated suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 188:481–485
Ohshima H (1999) Electrokinetic phenomena in a concentrated dispersion of charged mercury drops. J Colloid Interface Sci 218:535–544
Lee E, Chu J-W, Hsu J-P (1999) Electrophoretic mobility of a concentrated suspension of spherical particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 209:240–246
Ohshima H (2000) Cell model calculation for electrokinetic phenomena in concentrated suspensions: an Onsager relation between sedimentation potential and electrophoretic mobility. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 88:1–18
Hsu J-P, Lee E, Yen F-Y (2000) Electrophoresis of concentrated spherical particles with a charge-regulated surface. J Chem Phys 112:6404–6410
Carrique F, Arroyo FJ, Delgado AV (2001) Electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions of spherical colloidal particles: effect of a dynamic Stern layer on electrophoresis and DC conductivity. J Colloid Interface Sci 243:351–361
Ding JM, Keh HJ (2001) The electrophoretic mobility and electric conductivity of a concentrated suspension of colloidal spheres with arbitrary double-layer thickness. J Colloid Interface Sci 236:180–193
Carrique F, Arroyo FJ, Delgado AV (2002) Electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions of spherical colloidal particles with surface conductance, arbitrary zeta potential, and double-layer thickness in static electric fields. J Colloid Interface Sci 252:126–137
Carrique F, Cuquejo J, Arroyo FJ, Jiménez ML, Delgado AV (2005) Influence of cell-model boundary conditions on the conductivity and electrophoretic mobility of concentrated suspensions. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 118:43–50
Zholkovskij EK, Masliyah JH, Shilov VN, Bhattacharjee S (2007) Electrokinetic phenomena in concentrated disperse systems: general problem formulation and spherical cell approach. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 134-135:279–321
von Smoluchowski M (1921) Elektrische endosmose und strömungsströme. In: Greatz E (ed) Handbuch der Elektrizität und des Magnetismus, Band II Stationäre ströme. Barth, Leipzig, pp 366–428
Henry DC (1931) The cataphoresis of suspended particles. Part I. The equation of cataphoresis. Proc R Soc London Ser A 133:106–129
Overbeek JTG (1943) Theorie der Elektrophorese. Kolloid-Beihefte 54:287–364
O'Brien RW, White LR (1978) Electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 74:1607–1626
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science. Academic Press, New York
Ohshima H, Healy TW, White LR (1983) Approximate analytic expressions for the electrophoretic mobility of spherical colloidal particles and the conductivity of their dilute suspensions. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 79:1613–1628
van de Ven TGM (1989) Colloid hydrodynamics. Academic Press, New York
Hunter RJ (1989) Foundations of colloid science, vol 2. Oxford University Press, London/New York
Dukhin SS (1993) Non-equilibrium electric surface phenomena. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 44:1–134
Ohshima H (1994) A simple expression for Henry’s function for the retardation effect in electrophoresis of spherical colloidal particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 168:269–271
Lyklema J (1995) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science, Solid-Liquid Interfaces, vol 2. Academic Press, New York
Delgado AV (ed) (2000) Electrokinetics and electrophoresis. Dekker, New York
Dukhin AS, Goetz PJ (2002) Ultrasound for characterizing colloids: particle sizing, zeta potential, rheology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Spasic A, Hsu J-P (2005) Finely dispersed particles. Micro-, nano-, atto-engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Masliyah JH, Bhattacharjee S (2006) Electrokinetic and colloid transport phenomena. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Ohshima H (2006) Theory of colloid and interfacial electric phenomena. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Vinogradova O (1999) Slippage of water over hydrophobic surfaces. Int J Miner Process 56:31–60
Churaev NV, Ralston J, Sergeeva IP, Sobolev VD (2002) Electrokinetic properties of methylated quartz capillaries. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 96:265–278
Neto C, Evans DR, Bonaccurso E, Butt HJ, Craig VSJ (2005) Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids: a review of experimental studies. Rep Prog Phys 68:2859–2897
Bocquet L, Barrat J-L (2007) Flow boundary conditions from nano-to microscales. Soft Matter 3:685–693
Bouzigues CI, Tabeling P, Bocquet L (2008) Nanofluidics in the Debye layer at hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 101:114503
Kobayashi M (2020) An analysis on electrophoretic mobility of hydrophobic polystyrene particles with low surface charge density: effect of hydrodynamic slip. Colloid Polym Sci 298:1313–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04716-2
Khair AS, Squires TM (2009) The influence of hydrodynamic slip on the electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. Phys Fluids 21:042001
Park HM (2013) Electrophoresis of particles with Navier velocity slip. Electrophoresis 34:651–661
Bhattacharyya S, Majee PS (2017) Electrophoresis of a polarizable charged colloid with hydrophobic surface: a numerical study. Phys Rev E 95:042605
Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya SS, Ohshima H (2017) On the similarity between the electrophoresis of a liquid drop and a spherical hydrophobic particle. Colloid Polym Sci 295:2077–2082
Ohshima H (2019) Electrokinetic phenomena in a dilute suspension of spherical solid colloidal particles with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an aqueous electrolyte solution. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 272:101996
Ohshima H (2020) Electrophoretic mobility of a cylindrical colloidal particle with a slip surface. Colloid Polym Sci 298:151–156 Note that the curly braces are missing on the right-hand side of Eq. (45), which should be μ// = (εrεoζ/η){1+K1(κa)κΛ/K0(κa)}
Ohshima H (2020) Dynamic electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an oscillating electric field. Colloid Polym Sci 298:459–462
Ohshima H (2020) Primary electroviscous effect in a dilute suspension of charged spherical colloidal particles with a slip surface. Colloid Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04741-1
Acknowledgments
I thank Dr. Partha P. Gopmandal of the National Institute of Technology Durgapru and Prof. Somnath Bhattacharyya of the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur for introducing me in the field of electrokinetics of a colloidal particle with a slip surface.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, H. Electrokinetics of spherical colloidal particles with a slip surface in a concentrated suspension. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1679–1684 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04755-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04755-9