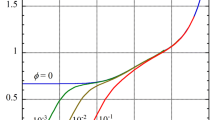
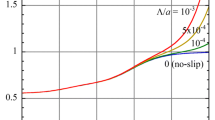
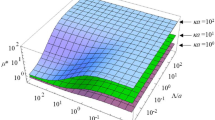
Abstract
The theory of Watterson and White (J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II, 77: 1115, 1981) on the primary electroviscous effect in a dilute suspension of charged spherical colloidal particles in an electrolyte solution is extended to cover the case where liquid slip occurs on the particle surface on the basis of the Navier boundary condition suitable for a hydrophobic surface. The general expressions for the effective viscosity and the primary electroviscous coefficient of the suspension as well as their low-zeta potential approximate expressions are derived.

Primary electroviscous coefficient


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein A (1906) Eine neue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen. Ann Phys 324:289–306 Einstein A (1911) Berichtigung zu meiner Arbeit “Eine neue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen”ibid 339: 591-592
Taylor GI (1932) The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another fluid. Proc Roy Soc London Ser A 138:41–48
Booth F (1950) The electroviscous effect for suspensions of solid spherical particles. Proc R Soc A 203:533–551
Russel WB (1978) Bulk stresses due to deformation of the electrical double layer around a charged sphere. J Fluid Mech 85:673–683
Lever DA (1979) Large distortion of the electric double layer around a charged particle by a shear flow. J Fluid Mech 92:421–433
Sherwood DJ (1980) The primary electroviscous effect in a suspension of spheres. J Fluid Mech 101:609–629
Watterson IG, White LR (1981) Primary electroviscous effect in suspensions of charged spherical particles. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 77:1115–1128
Hinch EJ, Sherwood JD (1983) The primary electroviscous effect in a suspension of spheres with thin double layers. J Fluid Mech 132:337–347
Duhkin AS, van de Ven TGM (1993) A spherical particle surrounded by a thin double layer in a simple shear flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 158:85–95
Rubio-Hernández FJ, Ruiz-Reina E, Gómez-Merino AI (1998) The influence of a dynamic stern layer on the primary electroviscous effect. J Colloid Interface Sci 206:334–337
Rubio-Hernández FJ, Ruiz-Reina E, Gómez-Merino AI (2000) Primary electroviscous effect with a dynamic Stern layer: low κa results. J Colloid Interface Sci 226:180–184
Sherwood JD, Rubio-Hernández FJ, Ruiz-Reina E (2000) The primary electroviscous effect: thin double layers (aκ⪢1) and a Stern layer. J Colloid Interface Sci 228:7–13
Rubio-Hernández FJ, Ruiz-Reina E, Gómez-Merino AI (2001) The additional surface conductance: its role in the primary electroviscous effect. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 192:349–356
Rubio-Hernández FJ, Ruiz-Reina E, Gómez-Merino AI, Sherwood JD (2001) Rheology of a dilute suspension: analytical expression for the viscosity in the limit of low zeta-potentials. Rheol Acta 40:230–237
Natraj V, Chen SB (2002) Primary electroviscous effect in a suspension of charged porous spheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 251:200–207
Ruiz-Reina E, Carrique F, Rubio-Hernández FJ, Gómez-Merino AI, García-Sánchez P (2003) Electroviscous effect of moderately concentrated colloidal suspensions. J Phys Chem B 107:9528–9534
Rubio-Hernández FJ, Carrique F, Ruiz-Reina E (2004) The primary electroviscous effect in colloidal suspensions. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 107:51–60
Ohshima H (2006) Primary electroviscous effect in a dilute suspension of charged mercury drops. Langmuir 22:2863–2869
Ohshima H (2007) Primary electroviscous effect in a moderately concentrated suspension of charged spherical colloidal particles. Langmuir 23:12061–12066
Ohshima H (2008) Primary electroviscous effect in a dilute suspension of soft particles. Langmuir 24:6453–6461
Ohshima H (2009) Effective viscosity of a concentrated suspension of uncharged porous spheres. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 347:33–37
Ohshima H (2010) Effective viscosity of a concentrated suspension of uncharged spherical soft particles. Langmuir 26:6287–6294
Mendoza CI (2011) Effective static and high-frequency viscosities of concentrated suspensions of soft particles. J Chem Phys 135:054904
Khair AS, Star AG (2013) The bulk electroviscous effect. Rheol Acta 52:255–269
Sengupta R, Lynn M, Walker LM, Khair AS (2018) Effective viscosity of a dilute emulsion of spherical drops containing soluble surfactant. Rheol Acta 57:481–491
Prakash J, Sekhar GPR (2019) Effective viscosity of a concentrated suspension of composite porous spherical particles. Meccanica 54:799–813
Henry DC (1931) The cataphoresis of suspended particles. Part I. The equation of cataphoresis. Proc Roy Soc London Ser A 133:106–129
Overbeek JTG (1943) Theorie der Elektrophorese. Kolloid-Beihefte 54:287–364
Booth F (1950) The cataphoresis of spherical, solid non-conducting particles in a symmetrical electrolyte. Proc Roy Soc London Ser A 203:514–533
Dukhin SS, Semenikhin NM (1970) Theory of double layer polarization and its influence on the electrokinetic and electrooptical phenomena and the dielectric permeability of disperse systems. Calculation of the electrophoretic and diffusiophoretic mobility of solid spherical particles. Kolloidn Zh 32:360–368
Dukhin SS, Derjaguin BV (1974) Nonequilibrium double layer and electrokinetic phenomena. In: Matievic E (ed) Surface and Colloid Science, vol 2. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, pp 273–336
O’Brien RW, White LR (1978) Electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 74:1607–1626
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science. Academic Press, New York
Ohshima H, Healy TW, White LR (1983) Approximate analytic expressions for the electrophoretic mobility of spherical colloidal particles and the conductivity of their dilute suspensions. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 79:1613–1628
van de Ven TGM (1989) Colloid hydrodynamics. Academic Press, New York
Hunter RJ (1989) Foundations of colloid science, Vol 2. Oxford University Press, London/New York
Dukhin SS (1993) Non-equilibrium electric surface phenomena. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 44:1–134
Ohshima H (1994) A simple expression for Henry’s function for the retardation effect in electrophoresis of spherical colloidal particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 168:269–271
Lyklema J (1995) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science, solid-liquid interfaces, Vol 2. Academic Press, New York
Delgado AV (ed) (2000) Electrokinetics and Electrophoresis. Dekker, New York
Dukhin AS, Goetz PJ (2002) Ultrasound for characterizing colloids: particle sizing, zeta potential, rheology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Spasic A, Hsu J-P (eds) (2005) Finely dispersed particles. micro-. nano-, atto-engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Masliyah JH, Bhattacharjee S (2006) Electrokinetic and Colloid Transport Phenomena. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Ohshima H (2006) Theory of colloid and interfacial electric phenomena. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Ohshima H (2010) Biophysical chemistry of biointerfaces. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Vinogradova O (1999) Slippage of water over hydrophobic surfaces. Int J Miner Process 56:31–60
Churaev NV, Ralston J, Sergeeva IP, Sobolev VD (2002) Electrokinetic properties of methylated quartz capillaries. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 96:265–278
Neto C, Evans DR, Bonaccurso E, Butt HJ, Craig VSJ (2005) Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids: a review of experimental studies. Rep Prog Phys 68:2859–2897
Bocquet L, Barrat J-L (2007) Flow boundary conditions from nano-to microscales. Soft Matter 3:685–693
Bouzigues CI, Tabeling P, Bocquet L (2008) Nanofluidics in the Debye layer at hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 101:114503
Khair AS, Squires TM (2009) The influence of hydrodynamic slip on the electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle. Phys Fluids 21:042001
Park HM (2013) Electrophoresis of particles with Navier velocity slip. Electrophoresis 34:651–661
Bhattacharyya S, Majee PS (2017) Electrophoresis of a polarizable charged colloid with hydrophobic surface: a numerical study. Phys Rev E 95:042605
Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya S, Ohshima H (2017) On the similarity between the electrophoresis of a liquid drop and a spherical hydrophobic particle. Colloid Polym Sci 295:2077–2082
Kumar B, Gopmandal PP, Sinha RK, Ohshima H (2019) Electrophoresis of hydrophilic/hydrophobic rigid colloid with effects of relaxation and ion size. Electrophoresis 40:1282–1292
Ohshima H (2019) Electrokinetic phenomena in a dilute suspension of spherical solid colloidal particles with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an aqueous electrolyte solution. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 272:101996
Ohshima H (2019) Electrophoretic mobility of a cylindrical colloidal particle with a slip surface. Colloid Polym Sci 298:151–156 Note that the curly braces are missing on the right-hand side of Eq. (45), which should be μ// = (εrεoζ/η){1 + K1(κa)κΛ/K0(κa)}
Ohshima H (2020) Dynamic electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloidal particle with a hydrodynamically slipping surface in an oscillating electric field. Colloid Polym Sci 298:459–462
Lamb H (1975) Hydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press
Luo H, Pozrikidis C (2008) Effect of surface slip on Stokes flow past a spherical particle in infinite fluid and near a plane wall. J Eng Math 62:1–21
Acknowledgments
I thank Dr. Partha P. Gopmandal of the National Institute of Technology Durgapur and Prof. Somnath Bhattacharyya of Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur for introducing me to the field of electrokinetics of colloidal particles with a slip surface.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, H. Primary electroviscous effect in a dilute suspension of charged spherical colloidal particles with a slip surface. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1551–1557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04741-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04741-1