Abstract
Purpose
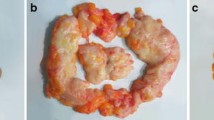
Idiopathic gynecomastia is a common diagnosis in children and adolescents. Though medical treatments reveal potentially harmful side effects, surgical interventions are performable in numerous techniques. In children and adolescents, only minimal evidence exists. This retrospective study presents our experiences with two common surgical techniques, namely subcutaneous mastectomy and combination with liposuction.
Patients and methods
This retrospective study included all patients <18 years who underwent surgery due to idiopathic gynecomastia. Height, weight and grade of gynecomastia according to Simon’s classification before surgery were reviewed in all patients’ files. Additionally, duration of surgery, inpatient stay and postoperative complications were documented. Follow-up examinations were performed with assessment of scar formation, numbness and retraction of the nipple region. Furthermore, patients were asked to report on general satisfaction with surgery (satisfactory/not satisfactory) and esthetic outcome on a numeric scale (1 = good, 6 = bad).
Results
37 patients underwent surgery for verified idiopathic gynecomastia. Grade of gynecomastia was I° in 13.5 % (n = 5), II° in 40.5 % (n = 15) and III° in 46 % (n = 17) of cases. Subcutaneous mastectomy was applied in 11 patients (group I, 30 %) and both subcutaneous mastectomy and liposuction in 26 patients (group II, 70.3 %). Postoperative complications occurred in two patients. Long-term follow-up was performed in 32 patients after a median of 34 months (range 6–96 months). Hypertrophic scar formation was seen in one patient (3 %) and nipple retraction in two patients (5 %). Recurrence of gynecomastia occurred in two patients (5 %). Patient rating was satisfactory in 9 % of cases and esthetic outcome was received with a median of 2.0 (1–5). In comparing both surgical techniques, combination of mastectomy and liposuction revealed better results in every measure except for surgical duration (median 73 vs. 90 min).
Conclusion
Surgical correction of gynecomastia remains a purely elective intervention. In contrast to adults, skin in children and adolescents provides high retractability. Therefore, open reduction combined with minimally invasive liposuction was proven useful.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathur R, Braunstein GD (1997) Gynecomastia: pathomechanisms and treatment strategies. Horm Res 48(3):95–102 pii:HRE48095
Bembo SA, Carlson HE (2004) Gynecomastia: its features, and when and how to treat it. Cleve Clin J Med 71(6):511–517
Mahoney CP (1990) Adolescent gynecomastia. differential diagnosis and management. Pediatr Clin North Am 37(6):1389–1404
Kumanov P, Deepinder F, Robeva R, Tomova A, Li J, Agarwal A (2007) Relationship of adolescent gynecomastia with varicocele and somatometric parameters: a cross-sectional study in 6200 healthy boys. J Adolesc Health 41(2):126–131. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.03.010
Nydick M, Bustos J, Dale JH Jr, Rawson RW (1961) Gynecomastia in adolescent boys. JAMA 178:449–454
Gikas P, Mokbel K (2007) Management of gynaecomastia: an update. Int J Clin Pract 61(7):1209–1215. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01095.x
Nordt CA, DiVasta AD (2008) Gynecomastia in adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr 20(4):375–382. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e328306a07c
Braunstein GD (1993) Diagnosis and treatment of gynecomastia. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 28(10A):37–46
Treves N (1958) Gynecomastia; the origins of mammary swelling in the male: an analysis of 406 patients with breast hypertrophy, 525 with testicular tumors, and 13 with adrenal neoplasms. Cancer 11(6):1083–1102
Nuzzi LC, Cerrato FE, Erickson CR, Webb ML, Rosen H, Walsh EM, DiVasta AD, Greene AK, Labow BI (2013) Psychosocial impact of adolescent gynecomastia: a prospective case-control study. Plast Reconstr Surg 131(4):890–896. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182818ea8
Derman O, Kanbur N, Kilic I, Kutluk T (2008) Long-term follow-up of tamoxifen treatment in adolescents with gynecomastia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 21(5):449–454
Herbst AL, Griffiths CT, Kistner RW (1964) Clomiphene citrate (Nsc-35770) in disseminated mammary carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Rep 43:39–41
Artero A, Tarin JJ, Cano A (2012) The adverse effects of estrogen and selective estrogen receptor modulators on hemostasis and thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 38(8):797–807. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1328883
Kreher NC, Eugster EA, Shankar RR (2005) The use of tamoxifen to improve height potential in short pubertal boys. Pediatrics 116(6):1513–1515. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-0577
Simon BE, Hoffman S, Kahn S (1973) Classification and surgical correction of gynecomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 51(1):48–52
Laituri CA, Garey CL, Ostlie DJ, St Peter SD, Gittes GK, Snyder CL (2010) Treatment of adolescent gynecomastia. J Pediatr Surg 45(3):650–654. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.11.016
Mauras N, Bishop K, Merinbaum D, Emeribe U, Agbo F, Lowe E (2009) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anastrozole in pubertal boys with recent-onset gynecomastia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(8):2975–2978. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-2527
Derman O, Kanbur NO, Kutluk T (2003) Tamoxifen treatment for pubertal gynecomastia. Int J Adolesc Med Health 15(4):359–363
Serels S, Melman A (1998) Tamoxifen as treatment for gynecomastia and mastodynia resulting from hormonal deprivation. J Urol 159(4):1309 pii:S0022-5347(01)63595-X
Plourde PV, Reiter EO, Jou HC, Desrochers PE, Rubin SD, Bercu BB, Diamond FB Jr, Backeljauw PF (2004) Safety and efficacy of anastrozole for the treatment of pubertal gynecomastia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(9):4428–4433. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0082
Lapid O, van Wingerden JJ, Perlemuter L (2013) Tamoxifen therapy for the management of pubertal gynecomastia: a systematic review. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 26(9–10):803–807. doi:10.1515/jpem-2013-0052
Fradet Y, Egerdie B, Andersen M, Tammela TL, Nachabe M, Armstrong J, Morris T, Navani S (2007) Tamoxifen as prophylaxis for prevention of gynaecomastia and breast pain associated with bicalutamide 150 mg monotherapy in patients with prostate cancer: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Eur Urol 52(1):106–114. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2007.01.031
Perdona S, Autorino R, De Placido S, D’Armiento M, Gallo A, Damiano R, Pingitore D, Gallo L, De Sio M, Bianco AR, Di Lorenzo G (2005) Efficacy of tamoxifen and radiotherapy for prevention and treatment of gynaecomastia and breast pain caused by bicalutamide in prostate cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 6(5):295–300. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70103-0
Di Lorenzo G, Perdona S, De Placido S, D’Armiento M, Gallo A, Damiano R, Pingitore D, Gallo L, De Sio M, Autorino R (2005) Gynecomastia and breast pain induced by adjuvant therapy with bicalutamide after radical prostatectomy in patients with prostate cancer: the role of tamoxifen and radiotherapy. J Urol 174(6):2197–2203. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000181824.28382.5c
Alagaratnam TT (1987) Idiopathic gynecomastia treated with tamoxifen: a preliminary report. Clin Ther 9(5):483–487
Doughty JC, Wilson CR (2003) Tamoxifen is unproved for gynaecomastia. BMJ 327(7422):1050. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7422.1050-b
Webster JP (1946) Mastectomy for gynecomastia through a semicircular intra-areolar incision. Ann Surg 124(3):557–575
Teimourian B, Perlman R (1983) Surgery for gynecomastia. Aesthetic Plast Surg 7(3):155–157
Becker H (1990) The treatment of gynecomastia without sharp excision. Ann Plast Surg 24(4):380–383
Rosenberg GJ (1994) A new cannula for suction removal of parenchymal tissue of gynecomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 94(3):548–551
Rosenberg GJ (1987) Gynecomastia: suction lipectomy as a contemporary solution. Plast Reconstr Surg 80(3):379–386
Samdal F, Kleppe G, Aabyholm F (1991) A new suction-assisted device for removing glandular gynecomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 87(2):383–385
Aiache AE (1991) Male chest correction. pectoral implants and gynecomastia. Clin Plast Surg 18(4):823–828
Aiache AE (1989) Surgical treatment of gynecomastia in the body builder. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(1):61–66
Voigt M, Walgenbach KJ, Andree C, Bannasch H, Looden Z, Stark GB (2001) Minimally invasive surgical therapy of gynecomastia: liposuction and exeresis technique. Chirurg 72(10):1190–1195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, S., Hirsch, T., Hirche, C. et al. Surgical treatment of primary gynecomastia in children and adolescents. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 641–647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3508-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3508-8