Abstract
Introduction
Surgery for craniosynostosis remains a crucial element in successful management. Intervention by both endoscopic and open approaches has been proven effective. Given the differences in timing and indications for these procedures, differences in perioperative outcomes have yet to be thoroughly compared between the two approaches. The aim of the systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the available evidence of perioperative outcomes between the two approaches in order to better influence the management paradigm of craniosynostosis.
Methods
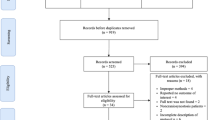
We followed recommended PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. Seven electronic databases were searched to identify all potentially relevant studies published from inception to February 2018 which were then screened against a set of selection criteria. Data were extracted and analyzed using meta-analysis of proportions.
Results
Twelve studies satisfied all the selection criteria to be included, which described a pooled cohort involving 2064 craniosynostosis patients, with 965 (47%) and 1099 (53%) patients undergoing surgery by endoscopic and open approaches respectively. When compared to the open approach, it was found that the endoscopic approach conferred statistically significant reductions in blood loss (MD = 162.4 mL), operative time (MD = 112.38 min), length of stay (MD = 2.56 days), and rates of perioperative complications (OR = 0.58), reoperation (OR = 0.37) and transfusion (OR = 0.09), where all p < 0.001.
Conclusion
Both endoscopic and open approaches for the surgical management of craniosynostosis are viable considerations. The endoscopic approach confers a significant reduction in operative and postoperative morbidity when compared to the open approach. Given that specific indications for either approach should be considered when managing a patient, the difference in perioperative outcomes remain an important element of this paradigm. Future studies will validate the findings of this study and consider long-term outcomes, which will all contribute to rigor of craniosynostosis management.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GRADE:
-
Grading of Recommendations Assessment
Development and Evaluation
- NOS:
-
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- RR:
-
Relative risk
- MD:
-
Mean difference
- SMD:
-
Standardized mean difference
References
Abbott MM, Rogers GF, Proctor MR, Busa K, Meara JG (2012) Cost of treating sagittal synostosis in the first year of life. J Craniofac Surg 23:88–93
Arts S, Delye H, van Lindert EJ (2018) Intraoperative and postoperative complications in the surgical treatment of craniosynostosis: minimally invasive versus open surgical procedures. J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:112–118
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S et al (2004) Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 328:1490
Bonfield CM, Sharma J, Cochrane DD, Singhal A, Steinbok P (2016) Minimizing blood transfusions in the surgical correction of craniosynostosis: a 10-year single-center experience. Childs Nerv Syst 32:143–151
Chan JWH, Stewart CL, Stalder MW, St Hilaire H, McBride L, Moses MH (2013) Endoscope-assisted versus open repair of craniosynostosis: a comparison of perioperative cost and risk. J Craniofac Surg 24:170–174
Cook DA, Reed DA (2015) Appraising the quality of medical education research methods: the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale-Education. Acad Med 90:1067–1076
Farber SJ, Nguyen DC, Skolnick GB (2017): Anthropometric outcome measures in patients with metopic craniosynostosis. Journal of: Available: https://journals.lww.com/jcraniofacialsurgery/Abstract/2017/05000/Anthropometric_Outcome_Measures_in_Patients_With.32.aspx
Garber ST, Karsy M, Kestle JRW, Siddiqi F, Spanos SP, Riva-Cambrin J (2017) Comparing outcomes and cost of 3 surgical treatments for sagittal synostosis: a retrospective study including procedure-related cost analysis. Neurosurgery 81:680–687
Ghenbot RG, Patel KB, Skolnick GB, Naidoo SD, Smyth MD, Woo AS (2015) Effects of open and endoscopic surgery on skull growth and calvarial vault volumes in sagittal synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 26:161–164
Han RH, Nguyen DC, Bruck BS, Skolnick GB, Yarbrough CK, Naidoo SD, Patel KB, Kane AA, Woo AS, Smyth MD (2016) Characterization of complications associated with open and endoscopic craniosynostosis surgery at a single institution. J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:361–370
Hinojosa J, Esparza J, Muñoz MJ (2007) Endoscopic-assisted osteotomies for the treatment of craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1421–1430
Jimenez DF, Barone CM (2012) Bilateral endoscopic craniectomies in the treatment of an infant with Apert syndrome. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:310–314
Jimenez DF, Barone CM (1998) Endoscopic craniectomy for early surgical correction of sagittal craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 88:77–81
Jimenez DF, Barone CM, Cartwright CC, Baker L (2002) Early management of craniosynostosis using endoscopic-assisted strip craniectomies and cranial orthotic molding therapy. Pediatrics 110:97–104
Jimenez DF, Barone CM, McGee ME, Cartwright CC, Baker CL (2004) Endoscopy-assisted wide-vertex craniectomy, barrel stave osteotomies, and postoperative helmet molding therapy in the management of sagittal suture craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 100:407–417
Keshavarzi S, Hayden MG, Ben-Haim S, Meltzer HS, Cohen SR, Levy ML (2009) Variations of endoscopic and open repair of metopic craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 20:1439–1444
Lane LC (1892) Pioneer craniectomy for relief of mental imbecility due to premature sutural closure and microcephalus. JAMA XVIII:49–50
Lannelongue M (1890) De La Craniectomie Dans La Microcephalie. CR Seances Acad Sci 110:1382
Lee HQ, Hutson JM, Wray AC, Lo PA, Chong DK, Holmes AD, Greensmith AL (2012) Analysis of morbidity and mortality in surgical management of craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 23:1256–1261
Le M-B, Patel K, Skolnick G, Naidoo S, Smyth M, Kane A et al (2014) Assessing long-term outcomes of open and endoscopic sagittal synostosis reconstruction using three-dimensional photography. J Craniofac Surg 25:573–576
Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P 2009 Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Available: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097, 6, e1000097
Murad G, Clayman M, Seagle MB, White S: Endoscopic-assisted repair of craniosynostosis. Neurosurgical:2005 Available: http://thejns.org/doi/abs/10.3171/foc.2005.19.6.7
Nguyen DC, Patel KB, Skolnick GB, Naidoo SD, Huang AH, Smyth MD, Woo AS (2015) Are endoscopic and open treatments of metopic synostosis equivalent in treating trigonocephaly and hypotelorism? J Craniofac Surg 26:129–134
Panchal J, Marsh JL, Park TS, Kaufman B, Pilgram T, Huang SH (1999) Sagittal craniosynostosis outcome assessment for two methods and timings of intervention. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1574–1584
Seymour-Dempsey K, Baumgartner JE, Teichgraeber JF, Xia JJ, Waller AL, Gateno J (2002) Molding helmet therapy in the management of sagittal synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 13:631–635
Shah MN, Kane AA, Petersen JD, Woo AS, Naidoo SD, Smyth MD (2011) Endoscopically assisted versus open repair of sagittal craniosynostosis: the St. Louis Children’s Hospital experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:165–170
Thompson DR, Zurakowski D, Haberkern CM, Stricker PA, Meier PM, Bannister C, Benzon H, Binstock W, Bosenberg A, Brzenski A, Budac S, Busso V, Capehart S, Chiao F, Cladis F, Collins M, Cusick J, Dabek R, Dalesio N, Falcon R, Fernandez A, Fernandez P, Fiadjoe J, Gangadharan M, Gentry K, Glover C, Goobie S, Gries H, Griffin A, Groenewald CB, Hajduk J, Hall R, Hansen J, Hetmaniuk M, Hsieh V, Huang H, Ingelmo P, Ivanova I, Jain R, Koh J, Kowalczyk-Derderian C, Kugler J, Labovsky K, Martinez JL, Mujallid R, Muldowney B, Nguyen KP, Nguyen T, Olutuye O, Soneru C, Petersen T, Poteet-Schwartz K, Reddy S, Reid R, Ricketts K, Rubens D, Skitt R, Sohn L, Staudt S, Sung W, Syed T, Szmuk P, Taicher B, Tetreault L, Watts R, Wong K, Young V, Zamora L, Pediatric Craniofacial Collaborative Group (2018) Endoscopic versus open repair for craniosynostosis in infants using propensity score matching to compare outcomes: a multicenter study from the pediatric craniofacial collaborative group. Anesth Analg 126:968–975
Tobias JD, Johnson JO, Jimenez DF, Barone CM, McBride DS Jr (2001) Venous air embolism during endoscopic strip craniectomy for repair of craniosynostosis in infants. Anesthesiology 95:340–342
van Nunen DPF, Stubenitsky BM, Woerdeman PA, Han KS, Breugem CC, Mink van der Molen AB et al (2016) Minimally invasive strip craniectomy simplifies anesthesia practice in patients with isolated sagittal synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 27:1985–1990
Vogel TW, Woo AS, Kane AA, Patel KB, Naidoo SD, Smyth MD (2014) A comparison of costs associated with endoscope-assisted craniectomy versus open cranial vault repair for infants with sagittal synostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 13:324–331
Zubovic E, Woo AS, Skolnick GB, Naidoo SD, Smyth MD, Patel KB (2015) Cranial base and posterior cranial vault asymmetry after open and endoscopic repair of isolated lambdoid craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 26:1568–1573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No funding sources or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental table 1
(DOCX 78.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, A., Lu, V.M., Yolcu, Y.U. et al. Endoscopic versus open approach in craniosynostosis repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 1627–1637 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3852-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3852-4