Abstract
Background
Children with cerebral palsy (CP) have significant decrease linear growth rate and low bone mineral density (BMD).
Aims
This study is to evaluate BMD in children with CP and its relation to the levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1).
Subjects and methods
This cross-sectional study was carried out on 58 children suffering from spastic CP with the age range 4–12 years compared to 19 controls. All assessed by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) to measure BMD, serum level of IGF-1, and serum vitamin D. The patients were classified according to their GMFCS.
Results
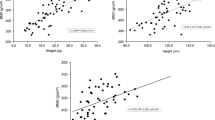
Fractures were reported in seven (12.1%) of cases. Our study demonstrated that, IGF-1 level and BMD decrease in correlation with the severity of CP. IGF-1correlates positively with serum vitamin D, BMI, and BMD. CP children with severe GMFCS level or who use anticonvulsive drugs are at a high risk for low BMD and low levels of IGF-1.
Conclusion
Both BMD and IGF-1 were significantly in low children with spastic CP; IGF-1 negatively correlates with the severity of osteopenia in children with spastic. Children with CP who are not independently ambulant or with severe GMFCS level or who use anticonvulsive drugs are at a high risk for developing low BMD.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Devesa J, Casteleiro N, Rodicio C, López N, Reimunde P (2010) Growth hormone deficiency and cerebral palsy. Ther Clin Risk Manag 6:413–418
Houlihan CM, Stevenson RD (2009) Bone density in cerebral palsy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 20:493–508
Ali O, Shim M, Fowler E, Cohen P, Oppenheim W (2007) Spinal bone mineral density, IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 in children with cerebral palsy. Horm Res 68:316–320
Giustina A, Mazziotti G, Canalis E (2008) Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, and the skeleton. Endocr Rev 29:535–559
Hamza RT, Ismail MA, Hamed AI (2011) Growth hormone deficiency in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: relation to gross motor function and degree of spasticity. Pak J Biol Sci 14:433–440
Conigilio S, Stevenson RD (1996) Apparent growth hormone deficiency in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 38:797–804
Eliasson AC, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Rösblad B, Beckung E, Arner M, Ohrvall AM, Rosenbaum P (2006) The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for children with cerebral palsy: scale development and evidence of validity and reliability. Dev Med Child Neurol 48:549–554
Holick MF (2009) Vitamin D status: measurement. Interpretation and Clinical Application Ann Epidemiol 19:73–78
Juul A, Dalgaard P, Blum WF, Bang P, Hall K, Michaelsen KF, Müller J, Skakkebaek NE (1995) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in healthy infants, children, and adolescents: the relation to IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, age, sex, body mass index, and pubertal maturation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:2534–2542
Binkovitz LA, Henwood MJ (2007) Pediatric DXA: technique and interpretation. Pediatr Radiol 37:21–31
Berry SD, Samelson EJ, Pencina MJ, McLean RR, Cupples LA, Broe KE, Kiel DP (2013) Repeat bone mineral density screening and prediction of hip and major osteoporotic fracture. JAMA 310:1256–1262
FeeleyB T, Gollapudi K, Otsuka NY (2007) Body mass index in ambulatory cerebral palsy patients. J Pediatr Orthop B 16:165–169
Henderson RC, Lark RK, Gurka MJ, Worley G, Fung EB, Conaway M, Stevenson RD (2002) Bone density and metabolism in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 110:e5–e5
Henderson RC, Kairalla JA, Abbas A, Stevenson RD (2004) Predicting low bone density in children and young adults with quadriplegic cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 46:416–419
Henderson RC, Kairalla JA, Barrington JW (2005) Longitudinal changes in bone density in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. J Pediatr 146:769–775
Gilbert SR, Gilbert AC, Henderson RC (2004) Skeletal maturation in children with quadriplegic cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 24(3):292–297
Stevenson RD, Conaway M, Barrington JW, Cuthill SL, Worley G, Henderson RC (2006) Fracture rate in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatr Rehabil 9:396–403
Jekovec-Vrhovsek M, Kocijancic A, Prezelj J (2000) Effect of vitamin D and calcium on bone mineral density in children with CP and epilepsy in full-time care. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:403–405
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (2005) Impaired skeletal growth in mice with haploinsufficiency of IGF-1: genetic evidence that differences in IGF-1 expression could contribute to peak bone mineral density differences. J Endocrinol 185:415–420
Houlihan CM (2014) Bone health in cerebral palsy: who’s at risk and what to do about it? J Pediatr Rehabil Med 7:143–153
Tasdemir HA, Buyukavci M, Akcay F, Polat P, Yildiran AKarakelleoglu C (2001) Bone mineral density in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatr Int 43:157–160
King W, Levin R, Schmidt R, Oestreich A, Heubi JE (2003) Prevalence of reduced bone mass in children and adults with spastic quadriplegia. Dev Med Child Neurol 45:12–16
Hartman C, Brik R, Tamir A, Merrick J, Shamir R (2004) Bone quantitative ultrasound and nutritional status in severely handicapped institutionalized children and adolescents. Clin Nutr 23:89–98
Chad KE, McKay HA, Zello GA, Bailey DA, Faulkner RA, Snyder RE (2000) Body composition in nutritionally adequate ambulatory and non-ambulatory children with cerebral palsy and a healthy reference group. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:334–339
Ali O, Shim M, Fowler E, Greenberg M, Perkins D, Oppenheim W, Cohen P (2007) Growth hormone therapy improves bone mineral density in children with cerebral palsy: a preliminary pilot study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:932–937
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Parents were informed about the aims and the procedures of the study. A written informed consent was signed from parents to enroll their children in the study as well as an ascent from the patient. The study was approved by the local ethical committee of our hospital.
Conflict of interest
All authors stated that no conflict of interest related to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazif, H., Shatla, R., Elsayed, R. et al. Bone mineral density and insulin-like growth factor-1 in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 625–630 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3346-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3346-9