Abstract
Purpose
Intracranial aneurysms are relatively rare in the pediatric population. The objective of this study was to highlight the clinical and radiological features and the therapeutic outcome and clarify the choice of therapeutic strategies for pediatric intracranial aneurysms.
Materials and methods
Twenty-four consecutive children (age ≤14 years) who were diagnosed and treated for intracranial aneurysms in our institute in the last 23 years were included in this study.
Results
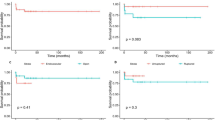
There were nine (36%) patients with posterior circulation aneurysms and eight (32%) with giant aneurysms. Eleven (46%) patients presented with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Fifteen patients underwent endovascular treatment, and four received microsurgical therapy. Five patients were treated conservatively. Ninety-two percent (n = 22) of the patients showed favorable outcomes.
Conclusions
Pediatric intracranial aneurysms differ in many ways from those in adults: male predominance; high incidence of giant, dissecting, and fusiform aneurysms; high incidence of aneurysms in the posterior circulation; high incidence of spontaneous thrombosis; better Hunt–Hess grades at presentation; and better therapeutic outcome. For children with intracranial aneurysms, both microsurgical approaches and endovascular treatment were effective. For many complex aneurysms, endovascular therapy was the best choice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerosa M, Licata C, Fiore DL, Iraci G (1980) Intracranial aneurysms of childhood. Childs Brain 6:295–302
Meyer FB, Sundt Jr TM, Fode NC, Morgan MK, Forbes GS, Mellinger JF (1989) Cerebral aneurysms in childhood and adolescence. J Neurosurg 70:420–425
Ostergaard JR, Voldby B (1983) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in children and adolescents. J Neurosurg 58:832–837
Vaid VK, Kumar R, Kalra SK, Mahapatra AK, Jain VK (2008) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: an institutional experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 44:296–301
International study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Lasjaunias PL, Campi A, Rodesch G, Alvarez H, Kanaan I, Taylor W (1997) Aneurysmal disease in children. Review of 20 cases with intracranial arterial localisations. Interv Neuroradiol 3:215–229
Allison JW, Davis PC, Sato Y, James CA, Haque SS, Angtuaco EJC, Glasier CM (1998) Intracranial aneurysms in infants and children. Pediatr Radiol 28:223–229
Agid R, Souza MP, Reintamm G et al (2005) The role of endovascular treatment for pediatric aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 21:1030–1036
Sekhar LN, Heros RC (1981) Origin, growth, and rupture of saccular aneurysms: a review. Neurosurgery 8:248–260
Stehbens WE (1989) Etiology of intracranial berry aneurysms. J Neurosurg 70:823–831
Huang J, McGirt MJ, Gailloud P, Tamargo RJ (2005) Intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population case series and literature review. Surg Neurol 63:424–432 discussion 432–433
Sanai N, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Gupta NM, Perry V, Sun PP, Wilson CB, Lawton MT (2006) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: durability of treatment following microsurgical and endovascular management. J Neurosurg; 104(suppl 2):82–89
Proust F, Toussaint P, Garnieri J, Hannequin D, Legars D, Houtteville JP, Freger P (2001) Pediatric cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 94:733–739
Sharma BS, Sinha S, Mehta VS, Suri A, Gupta A, Mahapatra A (2007) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms—clinical characteristics and outcome of surgical treatment. Childs Nerv Syst 23:327–333
Pasqualin A, Mazza C, Cavazzani P, Scienza R, Da Pian R (1986) Intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage in children and adolescents. Childs Nerv Syst 2:185–190
Ostergaard JR (1991) Aetiology of intracranial saccular aneurysms in childhood. Br J Neurosurg 5:575–580
Menon G, Furtado SV, Nair S (2005) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in children and adolescents. Indian J Cerebrovasc Surg 1:80–84
Ferrante L, Fortuna A, Celli P (1988) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in early childhood. Surg Neurol 29:39–56
Herman JM, Rekate HL, Spetzler RF (1991–1992) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: simple and complex cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 17:66–73
Lazinski D, Willinsky R, ter Brugge KG, Montanera W (2000) Dissecting aneurysms of the posterior cerebral artery: angioarchitecture and a review of the literature. Neuroradiology 42:128–133
Massimi L, Moret J, Tamburrini G, Di Rocco C (2003) Dissecting giant vertebro-basilar aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 19:204–210
International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group (2002) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2,143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomized trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Lasjaunias P, Wuppalapati S, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Ozanne A (2005) Intracranial aneurysms in children aged under 15 years: review of 59 consecutive children with 75 aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 21:437–450
Agid R, Jonas Kimchi T, Lee SK, Ter Brugge KG (2007) Diagnostic characteristics and management of intracranial aneurysms in children. Neuroimaging Clin North Am 17:153–163
Cohen JE, Ferrario A, Caratto R, Miranda C, Lylyk P (2003) Reconstructive endovascular approach for cavernous aneurysm in infancy. Neurol Res 25:492–496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Bao, Y., Zhang, H. et al. The clinical features and treatment of pediatric intracranial aneurysm. Childs Nerv Syst 25, 317–324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0725-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0725-2