Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to describe changes in cerebral autoregulation after severe pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Materials and methods
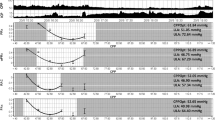
Two cerebral autoregulation tests were performed during the first 10 days after severe TBI in children <16 years. Cerebral autoregulation was quantified using the mean autoregulatory index (mARI).
Results
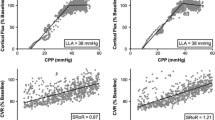
Nine (five males/four females) children (10 ± 5 years) with severe (admission Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), 5 ± 2) TBI were enrolled. Thirty (3/9) percent of initial exams revealed impaired cerebral autoregulation; all three had returned to intact cerebral autoregulation on second exam. However, in three of nine (33%) patients, cerebral autoregulation worsened on second exam. Of the factors examined, worsening mARI on second exam was associated with worsening head computed tomography (CT) lesion.
Conclusions
Cerebral autoregulation often changed and worsened during the first 9 days after severe pediatric TBI. Worsening cerebral autoregulation may mirror worsening TBI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paulson OB, Strandgaad S, Edvinsson L (1990) Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 2(2):162–192
Dohmen C, Bosche B, Graf R, Reihmeier T, Ernestus RI, Brinker G, Sobesky J, Heiss WD (2006) Identification and clinical Impact of impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation in patients with malignant middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke 22:1–6
Sundgreen C, Larsen FS, Herzog TM, Knundsen GM, Boesgaard S, Aldershvile J (2001) Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest. Stroke 32(1):128–132
Nishizama H, Kuddoh I (1993) Cerebral autoregulation is impaired in patients resuscitated after cardiac arrest. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 40(9):1149–1153
Mandura M, Laryz D, Wojitacha M (2002) Changes in cerebral hemodynamics assessed by transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography in children after head injury. Childs Nerv Syst 18:124–128
Junger EC, Newell DW, Grant GA, Avellinl AM, Ghantan S, Douville CM, Lam AM, Asslid R, Wimm HR (1997) Cerebral autoregulation following minor head injury. J Neurosurg 87(3):425–432
Sahuquillo J, Munar F, Baguena M, Poca MA, Pedraza S, Rodriguez-Baeza A (1998) Evaluation of cerebraovascular CO2-reactivity and autoregulation in patients with post-traumatic diffuse brain swelling (diffuse injury III). Acta Neurochir Suppl 7:233–236
Muizelaar JP, Ward JD, Marmarou A, Newlon PG, Wachi A (1998) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in severely head-injury children. Part 2: autoregulation. J Neurosurg 71(1):72–76
Sharples PM, Matthews DS, Eyre JA (1995) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in children with severe head injuries. Part 2: Cerebrovascular resistance and its determinants. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychistry 58(2):153–159
Vavilala MS, Lee LA, Boddu K, Visco E, Newell DW, Zimmerman JJ, Lam AM (2004) Cerebral autoregulation in Pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatr Crit Care Med 5(3):298
Vavilala MS, Muangman S, Tontisirin N, Fisk D, Roscigno C, Mitchell P, Kirkness C, Zimmerman JJ, Chesnut RM, Lam AM (2006) Impaired cerebral autoregulation and 6-month outcome in children with severe traumatic brain injury: preliminary findings. Dev Neurosci 28(4–5):348–353
Strebel S, Lam AM, Matta B, Mayberg TS, Aaslid R, Newell DW (1995) Dynamic and static cerebral autoregulation during isoflurane, desflurane and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology 83:66–76
Lam AM (1995) Intraoperative transcranial Doppler monitoring. Anesthesiology 82:1536–1537
Jennett B, Teasdale G, Braakman R, Minderhoud J, Heiden J, Kurze T (1979) Prognosis of patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 4:283–289
Lam JM, Hsiang JN, Poon WS (1997) Monitoring of autoregulation using laser Doppler flowmetry in patients with head injury. J Neurosurg 86(3):438–445
Kaiser JR, Gauss CH, William DK (2005) The effects of hypercapnia on cerebral autoregulation in ventilated very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 58(2):931–935
Cremer OL, Diephuis JC, Van Scest H, Vaessen PH, Bruens MG, Hennis PJ, Kalkman CJ (2004) Cerebral oxygen extraction and autoregulation during extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia in humans. Anesthesiology 100(5):1101–1107
Hlatky R, Valadka AB, Robertson CS (2005) Intracranial pressure response to induced hypertension: role of dynamic pressure autoregulation. Neurosurgery 57(2):917–923
Vavilala MS, Lee LA, Morris GP, Lam AM (2001) Cerebral autoregulation before and after blood transfusion in a child. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 13(3):233–236
Ainslie PN, Barach A, Murrell C, Hamlin M, Helleman J, Ogoh S (2006) Alterations in cerebral autoregulation and cerebral blood flow velocity during acute hypoxia: rest and exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:976–983
Wintermark M, Chiolero R, Van Melle G, Revelly JP, Porcher F, Regli L, Maeder P, Meuli R, Schynder P (2006) Cerebral vascular autoregulation assessed by perfusion CT in severe head trauma patients. J Neuroradiol 33(1):27–37
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Domonique Calhoun for her assistance with the preparation of this manuscript. This research was supported by National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Award K23/HD044632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tontisirin, N., Armstead, W., Waitayawinyu, P. et al. Change in cerebral autoregulation as a function of time in children after severe traumatic brain injury: a case series. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 1163–1169 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0339-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0339-0