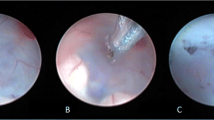
Abstract
Introduction
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) is considered by many authors the initial surgical procedure of choice for the treatment of non-communicant hydrocephalus. However, this procedure has early and late complications that neurosurgeons must be aware of when performing it.
Materials and results
A retrospective study of infants and children treated with ETV at Children’s Memorial Hospital (Chicago, IL) between 1993 and 2004 is presented. A total of 136 ETVs in 122 patients were performed with 8.8% early complication rate (hemorrhage, CSF leak, infection, diabetes insipidus, and seizures). There were no fatalities but one patient had severe neurological disturbances due to intracranial hemorrhage at the second ETV. We identified several significant factors that influence the late ETV failure rate: age under 12 months (p=0.012), cases performed early in our experience (p=0.009), patients with hydrocephalus without expansive lesions (p=0.026), patients that had an external ventricular drain (EVD) after ETV (p<0.005), and patients who developed early complications (p=0.035).
Conclusion
A careful patient selection and preoperative planning lead to better results of ETV. A higher early and late complication rate in children younger than 1-year-old were noted in our series. There is definitely a learning curve for this technique, and several technical considerations are helpful to avoid adverse events. Most of the early complications are transient, while potential devastating injuries can occur. Long-term follow-up is needed to identify delayed closure of the fenestration. Ventricular access devise is helpful for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes during the follow-up.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi JU, Kim DS, Kim SH (1999) Endoscopic surgery for obstructive hydrocephalus. Yonsei Med J 40:600–607
Guiot G (1973) Ventriculo-cisternostomy for stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius. Puncture of the floor of the third ventricle with a leucotome under television control. Acta Neurochir 28:275–289
Kelly PJ (1991) Stereotactic third ventriculostomy in patients with nontumoral adolescent/adult onset aqueductal stenosis and symptomatic hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 75:865–873
Teo C, Jones R (1996) Management of hydrocephalus by endoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients with myelomeningocele. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:57–63
Buxton N, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vloeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopy in the premature population. Child’s Nerv Syst 14:649–652
Grant JA, McLone DG (1997) Third ventriculostomy: a review. Surg Neurol 47:210–212
McLaughlin MR, Wahlig JB, Kaufmann AM, Albright AL (1997) Traumatic basilar aneurysm after endoscopic third ventriculostomy: case report. Neurosurgery 41:1400–1404
Siomin V, Cinalli G, Grotenhuis A, Golash A, Oi S, Kothbauer K et al (2002) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients with cerebrospinal fluid infection and/or hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 97:519–524
Brockmeyer D, Abtin K, Carey L, Walker ML (1998) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: an outcome analysis. Pediatr Neurosurg 28:236–240
Gangemi M, Donati P, Maiuri F, Longatti P, Godano U, Mascari C (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 42:128–132
Hopf NJ, Grunert P, Fries G, Resch KD, Perneczky A (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Neurosurgery 44:795–806
Jones RF, Kwok BC, Stening WA, Vonau M (1994) The current status of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 37:28–36
Schroeder HWS, Niendorf W, Gaab MR (2002) Complications of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J Neurosurg 96:1032–1040
Teo C (1998) Third ventriculostomy in the treatment of hydrocephalus: experience with more than 120 cases. In: Hellwig D, Bauer BL (eds) Minimally invasive techniques for neurosurgery. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 73–76
Beems T, Grotenhuis JA (2004) Long-term complications and definition of failure of neuroendoscopic procedures. Child’s Nerv Syst 20:868–877
Buxton N, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vloeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients less than 1 year old. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:73–76
Feng H, Huang G, Liao X, Fu K, Tan H, Pu H et al (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of obstructive hydrocephalus: an outcome analysis. J Neurosurg 100:626–633
Santamarta D, Onzain I, Blázquez JA, Gomez-Moreta JA, Morales F (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: risk factor for failure and evolution of ventricular size. Neurocirugía 15:248–257 (Spanish)
Teo C, Jones RFC, Stening WA, Kwok B (1991) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy. In: Matsumoto S (ed) Hydrocephalus: pathogenesis and treatment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 680–691
Teo C, Rahman S, Boop FA, Cherny B (1996) Complications of endoscopic neurosurgery. Child’s Nerv Syst 12:248–253
Walker ML (2004) Complications of third ventriculostomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:61–66
Saint-Rose C, Chumas P (1996) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Tech Neurosurg 1:176–184
Handler MH, Abbott R, Lee M (1994) A near-fatal complication of endoscopic third ventriculostomy: case report. Neurosurgery 35:525–528
Mobbs RJ, Vonau M, Davies M (2003) Death after late failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy: a potential solution. Neurosurgery 53:384–386
Abtin K, Thompson BG, Walker ML (1998) Basilar artery perforation as a complication of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Pediatr Neurosurg 28:35–41
El-Dawlatly AA, Murshid WR, Elshimy A, Magboul MA, Samarkandi A, Takroury MS (2000) The incidence of bradycardia during endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Anesth Analg 91:1142–1144
Enya S, Masuda Y, Terui K (1997) Respiratory arrest after a ventriculoscopic surgery in infants: two case reports. Masui 46:416–420 (Japanese)
Kim BS, Jallo GI, Kothbauer K, Abbott R (2004) Chronic subdural hematoma as a complication of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Surg Neurol 62:64–68
Kramer U, Kanner AA, Siomin V, Harel S, Constantini S (2001) No evidence of epilepsy following endoscopic third ventriculostomy: a short-term follow-up. Pediatr Neurosurg 34:121–123
Hader WJ, Drake J, Cochrane D, Sparrow O, Johnson ES, Kestle J (2002) Death after late failure of third ventriculostomy in children. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 97:211–215
Rekate HL (2004) Selecting patients for endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:29–49
Brockmeyer D (2004) Techniques of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:51–59
van Aalst J, Beuls EAM, van Nie FA, Vles JS, Cornips EM (2002) Acute distortion of the anatomy of the third ventricle during third ventriculostomy. J Neurosurg 96:597–599
Bellotti A, Rapana A, Iaccarino C, Schonauer M (2001) Intracranial pressure monitoring after endoscopic third ventriculostomy: an effective method to manage the ‘adaptation period’. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 103:223–227
Nishiyama K, Mori H, Tanaka R (2003) Changes in cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics following endoscopic third ventriculostomy for shunt-dependent noncommunicating hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 98:1027–1031
Fukuhara T, Vorster SJ, Luciano MG (2000) Risk factors for failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 46:1100–1111
Koch D, Wagner W (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants of less than 1 year of age: which factors influence the outcome? Child’s Nerv Syst 20:405–411
Gorayeb RP, Cavalheiro S, Zymberg ST (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children younger than 1 year of age. J Neurosurg (Pediatrics 5)100:427–429
Cinalli G, Sainte-Rose C, Chumas P, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Lot Guillaume, Pierre-Kahn A, Renier D (1999) Failure of third ventriculostomy in the treatment of aqueductal stenosis in children. J Neurosurg 90:448–454
Siomin V, Weiner H, Wisoff J, Cinalli G, Pierre-Kahn A, Saint-Rose C (2001) Repeat endoscopic third ventriculostomy: is it worth trying? Child’s Nerv Syst 17:551–555
St. George Edward, Natarajan K, Sgouros S (2004) Changes in ventricular volume in hydrocephalic children following successful endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Child’s Nerv Syst 20:834–838
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank Susana Ochoa M.S. from Hospital Sant Joan de Deu Foundation for her thoughtful suggestions and statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro, R., Gil-Parra, R., Reitman, A.J. et al. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children: early and late complications and their avoidance. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 506–513 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-0031-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-0031-1