Abstract
Objective
Bioresorbable devices are an attractive alternative to metal instrumentation for internal fixation of bone, and have been used extensively in orthopedic and craniofacial surgery. In neurosurgery, the reported literature is predominantly confined to pediatric craniofacial procedures, with encouraging results and minimal complications. We have used bioreabsorbable plates and screws in cranial and spinal pediatric neurosurgery procedures. We report four complications related to their usage.
Materials and methods
Bioabsorbable instrumentation was used in pediatric patients for fixation of bone after cranial or spinal procedures.
Results
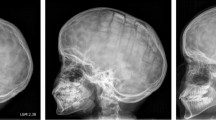
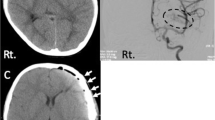
Four patients developed complications related to the instrumentation: 2 following cranial surgery for epilepsy, 1 after correction of a growing skull fracture, and 1 after laminotomy for an intramedullary tumor. Two patients had fibrous encapsulation with granuloma formation and 2 patients had osteolysis following the fixation.
Conclusion
Bioabsorbable fixation devices for the stabilization of bone following craniotomy and laminotomy in pediatric patients may be associated with complications, including granuloma formation and osteolysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai H, Sato K, Okuda O, Miyajima M, Hishii M, Nakanishi H, Ishii H (2000) Early experience with poly l-lactic acid bioabsorbable fixation system for paediatric craniosynostosis surgery. Report of 3 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:187–192
Bergsma EJ, Rozema FR, Bos RR, de Bruijn WC (1993) Foreign body reactions to resorbable poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws used for the fixation of unstable zygomatic fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 51:666–670
Bergsma JE, de Bruijn WC, Rozema FR, Bos RR, Boering G (1995) Late degradation tissue response to poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws. Biomaterials 16:25–31
Bostman OM (1991) Osteolytic changes accompanying degradation of absorbable fracture fixation implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73:679–682
Bostman O, Vainionpaa S, Hirvensalo E, Makela A, Vihtonen K, Tormala P, Rokkanen P (1987) Biodegradable internal fixation for malleolar fractures. A prospective randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:615–619
Bostman O, Hirvensalo E, Makinen J, Rokkanen P (1990) Foreign-body reactions to fracture fixation implants of biodegradable synthetic polymers. J Bone Joint Surg Br 72:592–596
Eppley BL, Prevel CD (1997) Nonmetallic fixation in traumatic midfacial fractures. J Craniofac Surg 8:103–109
Eppley BL, Sadove AM (1995) A comparison of resorbable and metallic fixation in healing of calvarial bone grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:316–322
Eppley BL, Sadove AM, Havlik RJ (1997) Resorbable plate fixation in pediatric craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:1–7; discussion 8–13
Kumar AV, Staffenberg DA, Petronio JA, Wood RJ (1997) Bioabsorbable plates and screws in pediatric craniofacial surgery: a review of 22 cases. J Craniofac Surg 8:97–99
Kurpad SN, Goldstein JA, Cohen AR (2000) Bioresorbable fixation for congenital pediatric craniofacial surgery: a 2-year follow-up. Pediatr Neurosurg 33:306–310
Pietrzak WS, Sarver D, Verstynen M (1996) Bioresorbable implants—practical considerations. Bone 19:109S–119S
Pietrzak WS, Sarver DR, Verstynen ML (1997) Bioabsorbable polymer science for the practicing surgeon. J Craniofac Surg 8:87–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, C.R., Sood, S. & Ham, S. Complications of bioresorbable fixation systems in pediatric neurosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 21, 205–210 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-0997-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-0997-0