Abstract
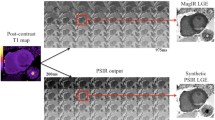
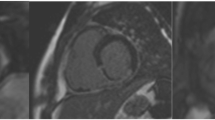
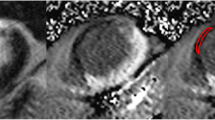
The purpose of this study was to clarify the characteristics of black-blood echo-planar imaging (BB-EPI) in the assessment of infarct-related myocardial edema (IRME), compared with T2-weighted imaging (T2WI). Thirteen acute myocardial infarction (MI) patients after reperfusion and 11 old MI patients underwent BB-EPI and T2WI, excluding those with posterior MI. In acute MI patients, signal intensity ratio (SI ratio) of edema to normal myocardium was measured. Black-blood echo-planar imaging revealed hyperintensity in the same region identified as IRME on T2WI in all acute MI patients, and SI ratio was significantly higher in BB-EPI (2.66 ± 1.58) than in T2WI (1.44 ± 0.22) (P < 0.05). However, BB-EPI showed hyperintensity in posterior wall, where there is no clinical evidence of acute MI, in 2 out of 13 acute MI patients. Both T2WI and BB-EPI detected no IRME in known old infarct area of all old MI patients, but BB-EPI showed hyperintensity in the posterior wall of 4 out of 11 old MI patients. Black-blood echo-planar imaging can depict IRME with sufficient suppression of background and blood flow signals, and with excellent edema-to-normal myocardium contrast resolution. However, BB-EPI sometimes shows an inconsistent signal area with T2WI specifically in posterior wall. The wide practical use of BB-EPI requires the solution to this serious problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willerson JT, Scales F, Mukherjee A, Platt M, Templeton GH, Fink GS, Buja LM (1977) Abnormal myocardial fluid retention as an early manifestation of ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 87:159–188
Yu ZX, Sekiguchi M, Hiroe M, Take M, Hirosawa K (1984) Histopathological findings of acute and convalescent myocarditis obtained by serial endomyocardial biopsy. Jpn Circ J 48:1368–1374
Herskowitz A, Soule LM, Mellits ED, Traill TA, Achuff SC, Reitz BA, Borkon AM, Baumgartner WA, Baughman KL (1987) Histologic predictors of acute cardiac rejection in human endomyocardial biopsies: a multivariate analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 9: 802–810
Abdel-Aty H, Simonetti O, Friedrich MG (2007) T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:452–459
Kellman P, Aletras AH, Mancini C, McVeigh ER, Arai AE (2007) T2-prepared SSFP improves diagnostic confidence in edema imaging in acute myocardial infarction compared to turbo spin echo. Magn Reson Med 57:891–897
Abdel-Aty H, Schulz-Menger J (2007) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance T2-weighted imaging of myocardial edema in acute myocardial infarction. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov 2:63–68
Abdel-Aty H, Simonetti O, Friedrich MG. (2007) T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:452–459
Aletras AH, Kellman P, Derbyshire JA, Arai AE (2008) ACUT2E TSE-SSFP: a hybrid method for T2-weighted imaging of edema in the heart. Magn Reson Med 59:229–235
Hartmann M, van Es J, Galjee MA, van der Burgh PH, de Bruin WI, Said SA, von Birgelen C (2007) Cardiac imaging in a symptomatic patient with multiple coronary artery-left ventricular microfistulae. Heart Vessels 22:428–431
Krishnan U, McCann GP, Hickey M, Schmitt M (2008) Role of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in detecting early adverse remodeling and subacute ventricular wall rupture complicating myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 23:430–432
Abdel-Aty H, Zagrosek A, Schulz-Menger J, Taylor AJ, Messroghli D, Kumar A, Gross M, Dietz R, Friedrich MG (2004) Delayed enhancement and T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging differentiate acute from chronic myocardial infarction. Circulation 109:2411–2416
García-Dorado D, Oliveras J, Gili J, Sanz E, Pérez-Villa F, Barrabés J, Carreras MJ, Solares J, Soler-Soler J (1993) Analysis of myocardial oedema by magnetic resonance imaging early after coronary artery occlusion with or without reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res 27:1462–1469
Miller S, Helber U, Kramer U, Hahn U, Carr J, Stauder NI, Hoffmeister HM, Claussen CD (2001) Subacute myocardial infarction: assessment by STIR T2-weighted MR imaging in comparison to regional function. MAGMA 13:8–14
Aletras AH, Tilak GS, Natanzon A, Hsu LY, Gonzalez FM, Hoyt RF Jr, Arai AE (2006) Retrospective determination of the area at risk for reperfused acute myocardial infarction with T2-weighted cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: histopathological and displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) functional validations. Circulation 113:1865–1870
Stork A, Lund GK, Muellerleile K, Bansmann PM, Nolte-Ernsting C, Kemper J, Begemann PG, Adam G (2006) Characterization of the peri-infarction zone using T2-weighted MRI and delayedenhancement MRI in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Radiol 16:2350–2357
Seelos KC, von Smekal A, Vahlensieck M, Gieseke J, Reiser M (1993) Cardiac abnormalities: assessment with T2-weighted turbo spin-echo MR imaging with electrocardiogram gating at 0.5 T. Radiology 189:517–522
Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, Laub G, Henry DA (1996) “Black blood” T2-weighted inversion-recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology 199:49–57
Wisenberg G, Prato FS, Carroll SE, Turner KL, Marshall T (1988) Serial nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of acute myocardial infarction with and without reperfusion. Am Heart J 115:510–518
Okayama S, Onoue K, Takemoto Y, Iwama H, Somekawa S, Takeda Y, Uramoto H, Watanabe M, Kawata H, Horii M, Yamamoto H, Sakaguchi E, Nakajima T, Hohda K, Uemura S, Saito Y (2007) A new approach to the evaluation of myocardial tissue character using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (abstract). The 71st Annual Scientific Meeting of the Japanese Circulation Society
Okayama S, Tomaya H, Minami M, Shima K, Onoue K, Takemoto Y, Omori S, Iwama H, Uramoto H, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe M, Nakanishi S, Kubota Y, Uemura S, Saito Y (2007) Measurement of apparent diffusion coefficient of myocardium using echo-planar imaging. Jiki-kyomei Igakukai Zasshi 27:79–85
Okayama S, Uemura S, Saito Y (2009) Detection of infarct-related myocardial edema using cardiac diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Cardiol 133:e20–e21
Sheehan FH, Braunwald E, Canner P, Dodge HT, Gore J, Van Natta P, Passamani ER, Williams DO, Zaret B (1987) The effect of intravenous thrombolytic therapy on left ventricular function: a report on tissue-type plasminogen activator and streptokinase from the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI Phase I) trial. Circulation 75:817–829
Schulz-Menger J, Gross M, Messroghli D, Uhlich F, Dietz R, Friedrich MG (2003) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance of acute myocardial infarction at a very early stage. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:513–518
Carr JC, Simonetti O, Bundy J, Li D, Pereles S, Finn JP (2001) Cine MR angiography of the heart with segmented true fast imaging with steady-state precession. Radiology 219:828–834
Schreiber WG, Schmitt M, Kalden P, Mohrs OK, Kreitner KF, Thelen M (2002) Dynamic contrast-enhanced myocardial perfusion imaging using saturation-prepared TrueFISP. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:641–652
Huber AM, Schoenberg SO, Hayes C, Spannagl B, Engelmann MG, Franz WM, Reiser MF (2005) Phase-sensitive inversionrecovery MR imaging in the detection of myocardial infarction. Radiology 237:854–860
Nagayama M, Watanabe Y, Okumura A, Tabuchi T, Mitsui H, Morimoto N, Nakada K, Kumashiro M, Kiyono T, Amoh Y, Nakashita S, Dodo Y, Geraats D, Cauteren MV (2002) Blackblood T2-weighted SE-EPI imaging of the liver (abstract). Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of ISMRM
Hussain SM, De Becker J, Hop WC, Dwarkasing S, Wielopolski PA (2005) Can a single-shot black-blood T2-weighted spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence with sensitivity encoding replace the respiratory-triggered turbo spin-echo sequence for the liver? An optimization and feasibility study. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:219–229
Takahara T, Sakurada A, Cauteren MV, Kawada S, Ichikawa T, Horie T, Imai Y (2006) Selective visualization of hypokinetic small bowel loop using small motion probing gradient with low b value (abstract). Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of ISMRM
Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Ter Beek L, Haspeslagh M, Bipat S, Stoker J, Van Kerkhove F, Steyaert L, Rigauts H, Casselman JW (2007) Improved focal liver lesion detection: comparison of singleshot diffusion-weighted echoplanar and single-shot T2 weighted turbo spin echo techniques. Br J Radiol 80:524–531
Ross BD, Moffat BA, Lawrence TS, Mukherji SK, Gebarski SS, Quint DJ, Johnson TD, Junck L, Robertson PL, Muraszko KM, Dong Q, Meyer CR, Bland PH, McConville P, Geng H, Rehemtulla A, Chenevert TL (2003) Evaluation of cancer therapy using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Mol Cancer Ther 2:581–587
Bragadeesh T, Jayaweera AR, Pascotto M, Micari A, Le DE, Kramer CM, Epstein FH, Kaul S (2008) Post-ischaemic myocardial dysfunction (stunning) results from myofibrillar oedema. Heart 94:166–171
Edelman RR, Gaa J, Wedeen VJ, Loh E, Hare JM, Prasad P, Li W (1994) In vivo measurement of water diffusion in the human heart. Magn Reson Med 32:423–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okayama, S., Uemura, S., Watanabe, M. et al. Novel application of black-blood echo-planar imaging to the assessment of myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 25, 104–112 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-009-1172-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-009-1172-z