Abstract
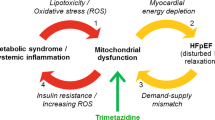
Downregulation of glucose and fatty acid oxidation occurs in heart failure (HF). Trimetazidine reduces fatty acid oxidation and increases glucose oxidation. In this single-blind study, trimetazidine, 20 mg three times per day (n = 51) or placebo (n = 36) was added to treatment of 87 HF patients receiving optimal HF therapy. Etiology of heart failure was coronary artery disease in 35 patients (68.6%) in the trimetazidine group and 22 (62.9%) in the placebo group. Fourteen (27.5%) patients in the trimetazidine group and 11 (31.4%) patients in the placebo group had diabetes. Peak systolic velocity (Vs), and the peak early diastolic (Vd) and late diastolic (Va) velocities of various segments left and right ventricles (RV) were obtained with tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) and averaged. Patients were re-evaluated three months later. Significant increases in mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (33.3% ± 5.6% to 42.4% ± 6.3%, P < 0.001 and 30.6% ± 8.2% to 33.2% ± 6.6%, P = 0.021) and LV and RV myocardial velocities and mitral and tricuspid annular TDI velocities were observed in both groups. However, compared to placebo, increments in LVEF (9.1% ± 4.2% vs. 2.5% ± 1.4%, P < 0.001) and myocardial velocities were significantly higher with trimetazidine (P < 0.001 for LV Vs, Vd, Va; P = 0.035 for RV Vd; and P < 0.001 for RV Va and Vs). Increase in LVEF with trimetazidine was significantly correlated with presence of diabetes (r = 0.524, P < 0.001). With trimetazidine LVEF increased significantly more in diabetic patients compared to nondiabetics (P < 0.001). Also, patients having both diabetes and ischemic HF tended to have greater improvement in LVEF compared to ischemic HF patients without diabetes (P = 0.063). Addition of trimetazidine to current treatment of HF, especially for those who are diabetic, may improve LV and RV functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopaschuk GD, Stanley WA, Lopaschuk CC (2005) Metabolic approach in heart failure: the rationale for metabolic interventions. Heart Metab 27:5–10
Stanley WC, Chandler MP (2002) Energy metabolism in the normal and failing heart: potential for therapeutic interventions. Heart Fail Rev 7:115–130
Kantor PF, Lucien A, Kozak R, Lopaschuk GD (2000) The antianginal drug trimetazidine shifts cardiac energy metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose oxidation by mitochondrial longchain 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase. Circ Res 86:580–588
Lopaschuk GD, Barr R, Thomas PD, Dyck JR (2003) Beneficial effects of trimetazidine in ex vivo working ischemic hearts are due to a stimulation of glucose oxidation secondary to inhibition of long-chain 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase. Circ Res 93:33–37
Brottier L, Barat L, Combe C, Boussens B, Bonnet J, Bricaud H (1990) Therapeutic value of a cardio protective agent in patients with severe ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 11:207–212
Lu C, Dabrowski P, Fragasso G, Chierchia SL (1998) Effects of trimetazidine on ischemic left ventricular dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Am J Cardiol 82:898–901
Belardinelli R, Purcaro A. (2001) Effects of trimetazidine on the contractile response of chronically dysfunctional myocardium to low-dose dobutamine in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 22:2164–2170
Di Napoli P, Taccardi AA, Barsotti A (2005) Long term cardioprotective action of trimetazidine and potential effects on the inflammatory process in patients with ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart 91:161–165
Vitale C, Wajngaten M, Sposato B, Gebara O, Rossini P, Fini M, Volterrani M, Rosano GM (2004) Trimetazidine improves left ventricular function and quality of life in elderly patients with coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 25:1814–1821
Fragasso G, Piatti Md PM, Monti L, Palloshi A, Setola E, Puccetti P, Calori G, Lopaschuk GD, Margonato A (2003) Short- and long-term beneficial effects of trimetazidine in patients with diabetes and ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J 146:E18
Rosano GM, Vitale C, Sposato B, Mercuro G, Fini M (2003) Trimetazidine improves left ventricular function in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 28;2:16
Nagueh SF, Middleton K, Kopelen H, Zoghbi WA, Quinones MA (1997) Doppler tissue imaging: a noninvasive technique for evaluation of left ventricular relaxation and estimation of filling pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1527–1533
Gulati VK, Katz WE, Follansbee WP, Gorcsan J (1996) Mitral annular descent velocity by tissue Doppler echocardiography as an index of global left ventricular function. Am J Cardiol 77: 979–984
Yamazaki N, Mine Y, Sano A, Uematsu M, Yamazaki N, Mine Y, Sano A, Hirama M (1994) Analysis of ventricular wall motion using color-coded tissue Doppler imaging system. Jpn J Appl Phys 33:3141–3146
Wang M, Yip GW, Wang AY, Zhang Y, Ho PY, Tse MK, Lam PK, Sanderson JE (2003) Peak early mitral annulus velocity by tissue Doppler imaging adds independent and incremental prognostic value. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:820–826
Sogaard P, Egeblad H, Kim WY, Jensen HK, Pedersen AK, Kristensen BO, Mortensen PT (2002) Tissue Doppler imaging predicts improved systolic performance and reversed left ventricular remodeling during long-term cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 40:723–730
Terzi S, Sayar N, Bilsel T, Enc Y, Yildirim A, Ciloglu F, Yesilcimen K (2007) Tissue Doppler imaging adds incremental value in predicting exercise capacity in patients with congestive heart failure. Heart Vessels 22:237–244
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiography 18:1440–1463
Cooke GA, Marshall P, al-Timman JK, Wright DJ, Riley R, Hainsworth R, Tan LB (1998) Physiological cardiac reserve: development of a non-invasive method and first estimates in man. Heart 79:289–294
Marzilli M (2003) Cardioprotective effects of trimetazidine: a review. Curr Med Res Opin 19:661
Fragasso G, Palloshi A, Puccetti P, Silipigni C, Rossodivita A, Pala M, Calori G, Alfieri O, Margonato A (2007) A randomized clinical trial of trimetazidine, a partial free fatty acid oxidation inhibitor, in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 48:992–998
Sisakian H, Torgomyan A, Barkhudaryan A. The effect of trimetazidine on left ventricular systolic function and physical tolerance in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Acta Cardiol 62: 493–499
El-Kady T, El-Sabban K, Gabaly M, Sabry A, Abdel-Hady S (2005) Effects of Trimetazidine on myocardial perfusion and contractile response of electronically dysfunctional myocardium in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 5:271–278
Di Napoli P, Di Giovanni P, Gaeta MA, D’Apolito G, Barsotti A (2007) Beneficial effects of trimetazidine treatment on exercise tolerance and B-type natriuretic peptide and troponin T plasma levels in patients with stable ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J 154:602.e1–e5
Taegtmeyer H (1994) Energy metabolism of the heart: from basic concepts to clinical applications. Curr Probl Cardiol 19:59–113
Wolff AA, Rotmensch HH, Stanley WC, Ferrari R (2002) Metabolic approaches to the treatment of ischemic heart disease: The clinicians’ perspective. Heart Fail Rev 7:187–203
Rodriques B, Cam MC, McNeill JH (1998) Metabolic disturbances in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem 180:53–57
Galrinho A, Branco L, Soares R, Timoteo A, Abreu J, Leal A, Silva S, Ferraira R (2006) Prognostic implications of tissue Doppler in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Rev Port Cardiol 25: 797–798
Meluzin J, Spinarova L, Bakala J, Toman J, Krejcí J, Hude P, Kara T, Soucek M (2001) Pulsed Doppler tissue imaging of the velocity of tricuspid annular systolic motion; a new, rapid and non-invasive method of evaluating right ventricular systolic function. Eur Heart J 22:280–282
Sengupta R, Patel R, Dokainish H (2006) Right ventricular tissue Doppler is an independent predictor of outcome in patients with left ventricular heart failure. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19:624a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunes, Y., Guntekin, U., Tuncer, M. et al. Improved left and right ventricular functions with trimetazidine in patients with heart failure: a tissue Doppler study. Heart Vessels 24, 277–282 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-008-1118-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-008-1118-x