Abstract
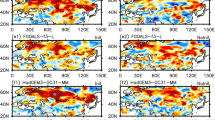
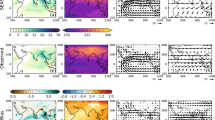
The seasonal predictability of various East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) indices was investigated in this study based on the retrospective forecasts of the five state-of-the-art coupled models from ENSEMBLES for a 46-year period of 1961–2006. It was found that the ENSEMBLES models predict five out of the 21 EAWM indices well, with temporal correlation coefficients ranging from 0.54 to 0.61. These five indices are defined by the averaged lower-tropospheric winds over the low latitudes (south of 30°N). Further analyses indicated that the predictability of these five indices originates from their intimate relationship with ENSO. A cross-validated prediction, which took the preceding (November) observed Niño3.4 index as a predictor, gives a prediction skill almost identical to that shown by the model. On the other hand, the models present rather low predictability for the other indices and for surface air temperature in East Asia. In addition, the models fail to reproduce the relationship between the indices of different categories, implying that they cannot capture the tropical-extratropical interaction related to EAWM variability. Together, these results suggest that reliable prediction of the EAWM indices and East Asian air temperature remains a challenge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan, J. C. L., and C. Y. Li, 2004: The East Asia winter monsoon. East Asian Monsoon, C. P. Chang, Ed., World Scientific Publishing Co. Pet. Ltd., 54–106.
Chang, C.-P., P. A. Harr, and H.-J. Chen, 2005: Synoptic disturbances over the equatorial South China Sea and western maritime continent during boreal winter. Mon. Wea. Rev., 133, 489–503.
Chang, C.-P., Z. Wang, and H. Hendon, 2006: The Asian winter monsoon. The Asian Monsoon, B. Wang, Ed., Praxis, Berlin, 89–127.
Chen, J., and S. Q. Sun, 1999: East Asian winter monsoon anomaly and variation of global circulation. Part I: A comparison study on strong and weak winter monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 101–111. (in Chinese)
Chen, W., H. F. Graf, and R. H. Huang, 2000: The interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon and its relation to the summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 48–60.
Cui, X. P., and Z. B. Sun, 1999: East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation analysis. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 22, 321–325. (in Chinese)
Doblas-Reyes, F. J., A. Weisheimer, T. N. Palmer, J. M. Murphy, and D. Smith, 2010: Forecast quality assessment of the ENSEMBLES seasonal-to-decadal Stream 2 hindcasts. ECMWF/TM-No. 621, 45 pp.
Fan, K., 2011: A statistical scheme for the seasonal forecasting of North China’s surface air temperature during winter. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 4, 81–85.
Fan, K., Y. Liu, and H. P. Chen, 2012: Improving the prediction of the East Asian summer monsoon: New approaches. Wea. Forecasting, 27, 1017–1030.
Feddersen, H., A. Navarra, and M. N. Ward, 1999: Reduction of model systematic error by statistical correction for dynamical seasonal prediction. J. Climate, 12, 1974–1989.
Gong, D. Y., S. W. Wang, and J. H. Zhu, 2001: East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 2073–2076.
Guo, Q. Y., 1994: Relationship between the variations of East Asian winter monsoon and temperature anomalies in China. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 5, 218–225. (in Chinese)
Hansen, J., R. Ruedy, J. Glascoe, and M. Sato, 1999: GISS analysis of surface temperature change. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 30997–31022.
Hansen, J., and Coauthors, 2006: Global temperature change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 103, 14288–14293, doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606291103.
He, S. P., H. J. Wang, and J. P. Liu, 2013: Changes in the relationship between ENSO and Asia-Pacific midlatitude winter atmospheric circulation. J. Climate, 26, 3377–3393.
Hu, Z. Z., L. Bengtsson, and K. Arpe, 2000: Impact of global warming on the Asian winter monsoon in a coupled GCM. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 4607–4624.
Huang, R. H., L. T. Zhou, and W. Chen, 2003: The progresses of recent studies on the variabilities of the East Asian monsoon and their causes. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 55–69.
Huang, R. H., J. L. Chen, and G. Huang, 2007: Characteristics and variations of the East Asian monsoon system and its impacts on climate disasters in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 993–1023, doi: 10.1007/s00376-007-0993-x.
Jhun, J. G., and E. J. Lee, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J. Climate, 17, 711–726.
Ji, L. R., S. Q. Sun, K. Arpe, and L. Bengtsson, 1997: Model study on the interannual variability of Asian winter monsoon and its influence. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 1–22, doi: 10.1007/s00376-997-0039-4.
Jiang, X., and Coauthors, 2013: Seasonal-to-interannual prediction of the Asian summer monsoon in the NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Climate, 26, 3708–3727.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40 year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Kang, I.-S., J.-Y. Lee, and C.-K. Park, 2004: Potential predictability of a dynamical seasonal prediction system with systematic error correction. J. Climate, 17, 834–844.
Lee, J.-Y., S.-S. Lee, B. Wang, K.-J. Ha, and J.-G. Jhun, 2013: Seasonal prediction and predictability of the Asian winter temperature variability. Climate Dyn., 41, 573–587, doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1588-5.
Li, C. F., R. Y. Lu, and B. W. Dong, 2012: Predictability of the western North Pacific summer climate demonstrated by the coupled models of ENSEMBLES. Climate Dyn., 39, 329–346.
Li, C. F., R. Y. Lu, and B. W. Dong, 2014: Predictability of the western North Pacific summer climate associated with different ENSO phases by ENSEMBLES multi-model seasonal forecasts. Climate Dyn., doi:10.1007/s00382-013-2010-7. (in press)
Li, C. Y., 1988: The frequent actions of the East Asian trough and the occurrences of El Niño. Sci. China (B), 31, 667–674.
Li, C. Y., 1990: Interaction between anomalous winter monsoon in East Asia and El Niño events. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 7(1), 36–46, doi: 10.1007/BF03008872.
Li, F., and H. J. Wang, 2012: Predictability of the East Asian winter monsoon interannual variability as indicated by the DEMETER CGCMS. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29(3), 441–454, doi: 10.1007/s00376-011-1115-3.
Li, Y. Q., and S. Yang, 2010: A dynamical index for the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Climate, 23, 4255–4262.
Liu, Y., K. Fan, and Y.-P. Yan, 2013: A new statistical downscaling scheme for predicting winter precipitation in China. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 6(5), 332–336, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.13.0008.
Lu, E., and J. C. L. Chan, 1999: A unified monsoon index for South China. J. Climate, 12, 2375–2385.
Lu, R.-Y., C.-F. Li, S.-H. Yang, and B. W. Dong, 2012: The coupled model predictability of the western North Pacific summer monsoon with different leading times. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 5, 219–224.
Smith, T. M., and R. W. Reynolds, 2004: Improved extended reconstruction of SST (1854–1997). J. Climate, 17, 2466–2477.
Shi, N., 1996: Features of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity on multiple time scale in recent 40 years and their relation to climate. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 7, 175–182. (in Chinese)
Sohn, S.-J., C.-Y. Tam, and C.-K. Park, 2011: Leading modes of East Asian winter climate variability and their predictability: An assessment of the APCC multi-model ensemble. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 89, 455–474, doi:10.2151/jmsj.2011-504.
Sun, B. M., and C. Y. Li, 1997: Relationship between the disturbances of East Asian trough and tropical convective activities in boreal winter. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42, 500–504. (in Chinese)
van der Linden, P., and F. J. B. Mitchell, Eds., 2009: ENSEMBLES: Climate change and its impact: Summary of research and results from ENSEMBLES project. Met Office Hadley Centre, FitzRoy Road, Exeter EX1 3PB, UK, 160 pp.
Wang, H. J., and D. B. Jiang, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and atmospheric circulation comparison between strong and weak composite. Quaternary Sciences, 24, 19–27. (in Chinese)
Wang, H. J., and K. Fan, 2009: A new scheme for improving the seasonal prediction of summer precipitation anomalies. Wea. Forecasting, 24, 548–554.
Wang, H. J., and S. P. He, 2012: Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s. Chinese Sci. Bull., 57, 3535–3540.
Wang, L., and W. Chen, 2010: How well do existing indices measure the strength of the East Asian winter monsoon?. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 27(4), 855–870, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9094-3.
Wang, L., and W. Chen, 2014: An intensity index for the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Climate, 27, 2361–2374.
Wang, L., R. H. Huang, L. Gu, W. Chen, and L. H. Kang, 2009a: Interdecadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon and their association with quasi-stationary planetary wave activity. J. Climate, 22, 4860–4872.
Wang, L., W. Chen, W. Zhou, and R. H. Huang, 2009b: Interannual variations of 500hPa East Asian trough axis and its influence on the pathway of the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Climate, 22, 600–614.
Weisheimer, A., and Coauthors, 2009: ENSEMBLES: A new multi-model ensemble for seasonal-to-annual predictions-skill and progress beyond DEMETER in forecasting tropical Pacific SSTs. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L21711, doi:10.1029/2009GL040896.
Wu, B., and J. Wang, 2002: Winter Arctic Oscillation, Siberian High and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(19), 3-1–3-4, doi: 10.1029/002GL015373.
Xu, S. Y., and J. J. Ji, 1965: The climate and weather features during the outbreak period of China’s winter monsoon. Geographical Symposium, 9, 85–101. (in Chinese)
Yang, S.-H., C. F. Li, and R. Y. Lu, 2014: Predictability of winter rainfall in South China as demonstrated by the coupled models of ENSEMBLES. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 31, 779–786, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-3172-2.
Yang, S., K. M. Lau, and K. M. Kim, 2002: Variations of the East Asian jet stream and Asian—Pacific-American winter climate anomalies. J. Climate, 15, 306–325.
Yun, W. T., L. Stefanova, A. K. Mitra, T. S. V. Vijaya Kumar, W. Dewar, and T. N. Krishnamurti, 2005: A multi-model superensemble algorithm for seasonal climate prediction using DEMETER forecast. Tellus, 57A, 280–289.
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the 86/87 and 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhang, Y., K. R. Sperber, and J. S. Boyle, 1997: Climatology and interannual variation of the East Asian winter monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 2605–2619.
Zhou, L.-T., 2011: Impact of East Asian winter monsoon on rainfall over southeastern China and its dynamical process. Int. J. Climatol., 31, 677–686, doi: 10.1002/joc.2101.
Zhou, L.-T., and R. G. Wu, 2010: Respective impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D02107, doi:10.1029/2009JD012502.
Zhu, C. W., C.-K. Park, W.-S. Lee, and W.-T. Yun, 2008: Statistical downscaling for multi-model ensemble prediction of summer monsoon rainfall in the Asia-Pacific region using geopotential height field. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25(5), 867–884, doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0867-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SH., Lu, R. Predictability of the East Asian winter monsoon indices by the coupled models of ENSEMBLES. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1279–1292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-4020-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-4020-8