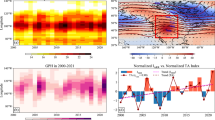
Abstract
A strong (weak) East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) is usually concurrent with the tripole pattern of North Atlantic SST anomalies on the interannual timescale during summer, which has positive (negative) SST anomalies in the northwestern North Atlantic and negative (positive) SST anomalies in the subpolar and tropical ocean. The mechanisms responsible for this linkage are diagnosed in the present study. It is shown that a barotropic wave-train pattern occurring over the Atlantic-Eurasia region likely acts as a link between the EASM and the SST tripole during summer. This wave-train pattern is concurrent with geopotential height anomalies over the Ural Mountains, which has a substantial effect on the EASM. Diagnosis based on observations and linear dynamical model results reveals that the mechanism for maintaining the wave-train pattern involves both the anomalous diabatic heating and synoptic eddy-vorticity forcing. Since the North Atlantic SST tripole is closely coupled with the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), the relationships between these two factors and the EASM are also examined. It is found that the connection of the EASM with the summer SST tripole is sensitive to the meridional location of the tripole, which is characterized by large seasonal variations due to the north-south movement of the activity centers of the NAO. The SST tripole that has a strong relationship with the EASM appears to be closely coupled with the NAO in the previous spring rather than in the simultaneous summer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnston, A. G., and R. E. Livezey, 1987: Classification, seasonality and persistence of low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 1083–1126.
Branstator, G., 1983: Horizontal energy propagation in a barotropic atmosphere with meridional and zonal structure. J. Atmos. Sci., 40, 1689–1708.
Branstator, G., 1992: The maintenance of low-frequency atmospheric anomalies. J. Atmos. Sci., 49, 1924–1945.
Cayan, D. R., 1992: Latent and sensible heat flux anomalies over the northern oceans: Driving the sea surface temperature. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 22, 859–881.
Czaja, A., and C. Frankignoul, 2002: Observed impact of Atlantic SST anomalies on the North Atlantic oscillation. J. Climate, 15, 606–623.
Deser, C., and M. Timlin, 1997: Atmosphere-ocean interaction on weekly timescales in the North Atlantic and Pacific. J. Climate, 10, 393–408.
Ding, Y. H., 1992: Summer monsoon rainfalls in China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 70, 373–396.
Duchon, C., 1979: Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions. J. Appl. Meteor., 18, 1016–1022.
Gill, A. E., 1980: Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 106, 447–462.
Gu, W., C. Y. Li, X. Wang, W. Zhou, and W. J. Li, 2009: Linkage between mei-yu precipitation and North Atlantic SST on the decadal timescale. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 101–108, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-0101-5.
Han, Z., S. Li, and M. Mu, 2011: The role of warm North Atlantic SST in the formation of positive height anomalies over the Ural Mountains during January 2008. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 28, 246–256, doi: 10.1007/s00376-010-0069-1.
Huang, R. H., and W. J. Li, 1987: Influence of the anomaly of heat source over the northwestern tropical Pacific for the subtropical high over East Asia. Proc. Inter. Conf. on the General Circulation of East Asia, Chengdu, China, 40-45.
Huang, R. H., and F. Y. Sun, 1992: Impacts of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 70, 243–256.
Jin, F.-F., L.-L. Pan, and M. Watanabe, 2006: Dynamics of synoptic eddy and low-frequency flow interaction. Part I: A linear closure. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 1677–1694.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–472.
Kug, J.-S., and F.-F. Jin, 2009: Left-hand rule for synoptic eddy feedback on low-frequency flow. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L05709, doi: 10.1029/2008GL036435.
Lau, N.-C., and E. O. Holopainen, 1984: Transient eddy forcing of the time-mean flow as indentified by geopotential tendencies. J. Atmos. Sci., 41, 313–328.
Lau, N.-C., and M. J. Nath, 1991: Variability of the baroclinic and barotropic transient eddy forcing associated with monthly changes in the midlatitude storm tracks. J. Atmos. Sci., 48, 2589–2613.
Li, J., and J. X. L. Wang, 2003: A new North Atlantic Oscillation index and its variability. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 661–676.
Li, S., 2004: Influence of the Northwest Atlantic SST anomaly on the circulation over the Ural Mountains. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 971–988.
Li, S., and L. Ji, 2001: Background circulation characteristics of the persistent anomalies of the summertime circulation over the Ural Mountains. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 59, 280–293. (in Chinese)
Li., S., M. P. Hoerling, S. Peng, and K. M. Weickmann, 2006: The annular response to tropical Pacific SST forcing. J. Climate, 19, 1802–1819.
Li., S., W. A. Robinson, M. P. Hoerling, and K. M. Weickmann, 2007: Dynamics of the extratropical response to a tropical Atlantic SST anomaly. J. Climate, 20, 560–574.
Nitta, T., 1987: Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impacts on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 65, 165–171.
Ogi, M., Y. Tachibana, and K. Yamazaki, 2003: Impact of the wintertime North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) on the summertime atmospheric circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 1704, doi: 10.1029/2003GL017280.
Pan, L.-L., 2007: Synoptic eddy feedback and air-sea interaction in the North Atlantic region. Climate Dyn., 29, 647–659.
Pan, L.-L., F.-F. Jin, and M. Watanabe, 2006: Dynamics of synoptic eddy and low-frequency flow interaction. Part III: Baroclinic model results. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 1709–1725.
Peng, S., and J. S. Whitaker, 1999: Mechanisms determining the atmospheric response to midlatitude SST anomalies. J. Climate, 12, 1393–1408.
Peng, S., W. A. Robinson, and S. Li, 2003: Mechanisms for the NAO responses to the North Atlantic SST tripole. J. Climate, 16, 1987–2004.
Ren, H.-L., F.-F. Jin, J.-S. Kug, J.-X. Zhao, and J. Park, 2009: A kinematic mechanism for positive feedback between synoptic eddies and NAO. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L11709, doi: 10.1029/2009GL037294.
Ren, H.-L., F.-F. Jin, and L. Gao, 2012: Anatomy of synoptic Eddy-NAO Interaction through eddy structure decomposition. J. Atmos. Sci., 69, 2171–2191.
Sardeshmukh, P. D., and B. J. Hoskins, 1988: The generation of global rotational flow by steady idealized tropical divergence. J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 1288–1251.
Smith, T. M., R. W. Reynolds, T. C. Peterson, and J. Lawrimore, 2008: Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880–2006). J. Climate, 21, 2283–2296.
Sung, M.-K., W.-T. Kwon, H.-J. Baek, K.-O. Boo, G.-H. Lim, and J.-S. Kug, 2006: A possible impact of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the East Asian summer monsoon precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L21713, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027253.
Takaya, K., and H. Nakamura, 2001: A formulation of a phase-independent wave-activity flux for stationary and migratory quasigeostrophic eddies on a zonally varying basic flow. J. Atmos. Sci., 58, 608–627.
Trenberth, K. E., G. W. Branstator, D. Karoly, A. Kumar, N.-C. Lau, and C. Ropelewski, 1998: Progress during TOGA in understanding and modeling global teleconnections associated with tropical sea surface temperatures. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14291–14324.
Wang, B., and Z. Fan, 1999: Choice of South Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 80, 629–638.
Watanabe, M., 2004: Asian jet waveguide and a downstream extension of the North Atlantic oscillation. J. Climate, 17, 4674–4691.
Watanabe, M., and M. Kimoto, 2000: Atmosphere-ocean thermal coupling in the North Atlantic: A positive feedback. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 126, 3343–3369.
Watanabe, M., and F.-F. Jin, 2003: A moist linear baroclinic model: Coupled dynamical-convective response to El Niño. J. Climate, 16, 1121–1139.
Wu, B. Y., and R. H. Zhang, 2011: Interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon and its association with the anomalous atmospheric circulation over the mid-high latitudes and external forcing. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 69, 219–233. (in Chinese)
Wu, R., S. Yang, S. Liu, L. Sun, Y. Lian, and Z. Gao, 2010: Change in the relationship between Northeast China summer temperature and ENSO. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D21107, doi: 10.1029/2010JD014422.
Wu, R., S. Yang, S. Liu, L. Sun, Y. Lian, and Z. Gao, 2011: Northeast China summer temperature and North Atlantic SST. J. Geophys. Res., 116, D16116, doi: 10.1029/2011JD015779.
Wu, Z., B. Wang, J. Li, and F.-F. Jin, 2009: An empirical seasonal prediction model of the East Asian summer monsoon using ENSO and NAO. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D18120, doi: 10.1029/2009JD011733.
Xie, P., and P. A. Arkin, 1997: Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78, 2539–2558.
Xie, S.-P., and J. A. Carton, 2004: Tropical Atlantic variability: Patterns, mechanisms, and impacts. Earth Climate: The Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction, C. Wang, S.-P. Xie, and J. A. Carton, Eds., Geophysical Monograph, 121–142.
Zhang, Q. Y., and S. Y. Tao, 1998: Influence of Asian mid-high latitude circulation on East Asian summer rainfall. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 56, 199–211. (in Chinese)
Zhou, T., R. Yu, Y. Gao, and H. Drange, 2006: Oceanatmosphere coupled model simulation of North Atlantic interannual variability I: Local air-sea interaction. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 64, 1–17. (in Chinese)
Zuo, J. Q., W. J. Li, H. L. Ren, and L. J. Chen, 2012: Change of the relationship between spring NAO and East Asian summer monsoon and its possible mechanism. Chinese Journal of Geophysics., 55, 23–34. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, J., Li, W., Sun, C. et al. Impact of the North Atlantic sea surface temperature tripole on the East Asian summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 30, 1173–1186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2125-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2125-5