Abstract
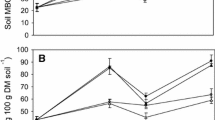
In a cropping systems experiment in southeastern Norway, ecological (ECO), integrated (INT) and conventional (CON) forage (FORAGE) and arable (ARABLE) model farms were compared. After 5 experimental years, topsoil was sampled in spring from spring grain plots and incubated for 449 days at controlled temperature (15 °C) and moisture content (50% water-holding capacity). There were no detectable differences between model farms in terms of total soil C or N. For INT and CON, however, values of microbial biomass C and N, microbial quotient (Cmic/Corg), and C and N mineralization were, or tended to be, higher for FORAGE than for ARABLE. For the ECO treatment, values were similar for FORAGE and ARABLE and did not differ significantly from that of CON-FORAGE. For INT and CON, the metabolic quotient (qCO2) was lower for FORAGE than for ARABLE. Again, for the ECO treatment, values were similar for FORAGE and ARABLE and did not differ significantly from that of CON-FORAGE. We estimated the sizes of conceptual soil organic matter pools by fitting a decomposition model to biomass and mineralization data. This resulted in a 48% larger estimate for CON-FORAGE than for CON-ARABLE of physically protected biomass C. For physically protected organic C the difference was 42%. Moreover, the stability of soil aggregates against artificial rainfall was substantially greater for CON-FORAGE than for CON-ARABLE. On this basis, we hypothesized that the lower qCO2 values in the FORAGE soils were mainly caused by a smaller proportion of active biomass due to enclosure of microorganisms within aggregates. Altogether, our results indicated a poorer inherent soil fertility in ARABLE than in FORAGE rotations, but the difference was small or absent in the ECO system, probably owing to the use of animal and green manures and reduced tillage intensity in the ECO-ARABLE rotation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breland, T., Eltun, R. Soil microbial biomass and mineralization of carbon and nitrogen in ecological, integrated and conventional forage and arable cropping systems. Biol Fertil Soils 30, 193–201 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050608
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050608