Abstract
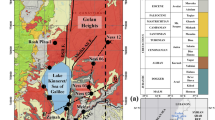
Gas hydrate (GH) accumulation in subsurface sediments was discovered at shallow depth within the Malenkiy vent structure in the southern basin of Lake Baikal. The hydrated gas consists mainly of methane. Interstitial water chemistry indicates that water discharged within the study area is enriched with salts, especially Ca, Cl, and SO4 ions. The ascending water delivering gas into the GH stability zone is thought to be the main GH-forming fluid. Geochemical data together with noble gas isotopic ratios suggest that the GH in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal originated from a deep source of water with anomalous composition assumed to be derived from buried paleolakes. As a whole, the GH accumulation corresponds to the area of the Malenkiy structure and is represented by several small-scale GH occurrences coincident with local fluid discharge manifestations. It is filtrational in origin, related to fluid flow features and controlled by tectonic setting.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray CJ, Karig DE (1985) Porosity of sediments in accretionary prisms and some implications for dewatering processes. J Geophys Res 90:768–778
Brooks YM, Kennicutt MC II, Fay RR, McDonald TY, Sassen R (1984) Thermogenic gas hydrates in the Gulf of Mexico. Science 225:409–411
Brooks YM, Field ME, Kennicutt MC II (1991) Observation of gas hydrates in marine sediments, offshore northern California. Mar Geol 96:103–109
Chersky NV, Tsarev VP (1972) Features of helium accumulation within permafrost regions (in Russian). In: Geological structure, perspectives of gas and oil-bearing pool in Jakutsk ASSR. JF SO AN SSSR, pp 124–132
Davidson DW, Leaist DG, Hesse R (1983) Oxygen-18 enrichments in the water of a clathrate hydrate. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:2293–2295
De Batist M, Klerkx J, Van Rensbergen P, Vanneste M, Poort J, Golmshtock A, Kremlev A, Khlystov O, Krinitsky P (2002) Active hydrate destabilization in Lake Baikal, Siberia? Terra Nova 14(6):436–442
Dzyuba AA, Kulagina NV (2000) Relict salt lakes in the Selenga-river delta (in Russian). In: Proc 3rd Th. Vereschagin Conf Baikal Lake, Irkutsk, Russia, p 76
Falkner KK, Chris I, Measures SEH, Edmond JM, Weiss RF (1991) The major and minor element geochemistry of Lake Baikal. Limnol Oceanogr 36(3):413–423
Ferronskiy VI, Dubinchuk VT, Polyakov VA, Seletskiy YB, Kuptsov VM, Yakubovskiy AV (1975) Natural isotopes of hydrosphere. Nedra, Moscow
Ginsburg GD, Soloviev VA (1998) Submarine gas hydrates. VNIIOkeangeologia, Saint-Petersburg
Ginsburg GD, Soloviev VA, Cranston RE, Lorenson TD, Kvenvolden KA (1993) Gas hydrates from the continental slope, offshore Sakhalin Island, Okhotsk Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 13:41–48
Golmshtock AJ, Duchkov AD, Hutchinson DR, Khanukaev SB, Elnikov AI (1997) Estimation of heat flow on Baikal from seismic data on the lower boundary of the gas hydrate layer. Russian Geol Geophys 38:1714–1727
Golubev VA, Klerkx J, Kipfer R (1993) Heat flow, hydrothermal vents and static stability of discharging thermal water in Lake Baikal (south-eastern Siberia). Bull Centre Rech Elf Exploration Production 17:54–65
Grachev AF, Drubetskoy EP, Martyunova MA, Prasolov EM, Dedenkov YN, Sukhanov AA (1982). First data on He isotopic composition in Baikal rift rocks and Baikal Lake water. In: Proc 9th USSR Symp Stable Isotopes in Geochemistry, Moscow, Russia, pp 114–116
Granina LZ, Callender E, Lomonosov IS, Mats VD, Golobokova LP (2001) Anomalies in the composition of Baikal pore waters. Russian Geol Geophys 42(1/2):362–372
Hovland M, Judd AG (1988) Seabed pockmarks and seepages. Impact on geology, biology, and the marine environment. Graham and Trotman, London
Hutchinson DR, Lee MW, Agena WF, Golmshtock AJ, Moskalenko VN, Karapetov K, Coleman DF, Akentiev L (1992) Processing of Lake Baikal marine multichannel seismic reflection data. USGS Open-File Rep 93-201:1–24
Kendall C, Coplen TB (1985) Multisample conversion of water to hydrogen by zinc for stable isotope determinations. Anal Chem 57:1437–1440
Kuzmin MI, Karabanov EB, Kawai T, Williams D, Bychinskii VA, Kerber EV, Kravchinskii VA, Bezrukova EV, Prokopenko AA, Geletij VF, Kalmuchkov CV, Goreglyad AV, Antipin VS, Khomotova Mj, Soshina NM, Ivanov EV, Khursevich GK, Tkachenko LL, Solotchina EP, Ioshida N, Gvozdkov AN (2001) Deep drilling on Lake Baikal: main results. Russian Geol Geophys 42(1/2):8–35
Moore TG, Klitgord KD, Golmshtock AJ, Weber E (1997) The Central and North Basins of Lake Baikal: the early phase of basin formation. Geol Soc Am Bull 9(6):746–766
Orange DL, Yun J, Maher N, Barry J, Greene G (2002) Tracking California seafloor seeps with bathymetry, backscatter and ROVs. Cont Shelf Res 22:2273–2290
Ozima M, Podosek FA (1983) Noble gas geochemistry. Cambridge University Press, London
Polyakov VA, Bobkov AF (1994) Reconstruction of the production mass spectrometer MI-1201 for precise measurement of hydrogen isotope composition (in Russian). Geol izuchenie nedr Moscow Geoinformmark 7/8:30–33
Prasolov EM (1990) Isotope geochemistry and origin of the natural gases. Nedra, Saint-Petersburg
Prasolov EM, Tokarev IV, Ginsburg GD, Soloviev VA, Eltsova GM (1999) Helium and other noble gases in gas-hydrate sediments of the Haakon Mosby Mud Volcano. Geo-Mar Lett 19:84–88
Scholz CA, Klitgord KD, Hutchinson DR, ten Brink US, Zonenshain LP, Golmshtock AY, Moor TC (1993) Results of 1992 seismic reflection experiment in Lake Baikal. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 74:465–470
Sloan ED (1990) Clathrate hydrates of natural gases. Marcel Dekker, New York
Suess E, Torres ME, Bohrmann G, Collier RW, Rickert D, Goldfinger C, Linke P, Heuser A, Sahling H, Heeschen K, Jung C, Nakamura K, Greinert J, Pfannkuche O, Trehu A, Klinkhammer G, Whiticar MJ, Eisenhauer B, Teichert B, Elvert M (2001) Sea floor methane hydrates at Hydrate Ridge, Cascadia Margin. In: Natural gas hydrates: occurrence, distribution and detection. AGU Geophys Monogr, pp 87–98
Tolstikhin IN (1986) Isotopic geochemistry of helium, argon, and rare gases (in Russian). Nauka, Leningrad
Vanneste M, De Batist M, Golmshtock A, Kremlev A, Versteeg W (2001) Multi-frequency seismic study of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in Lake Baikal, Siberia. Mar Geol 172:1–21
Van Rensbergen P, De Batist M, Klerkx J, Hus R, Poort J, Vanneste M, Granin N, Khlystov O, Krinitsky P (2002) Sublacustrine mud volcanoes and cold seeps caused by dissociation of gas hydrate in Lake Baikal. Geology 30(7):631–634
Zonenshain LP, Kazmin VG, Kuzmin MI (1992) New data on the Baikal rift geology: results of submarine geological observations. IPPCCE Newslett 6:10–20
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank A.F. Bobkov and V.A. Polyakov for analyses of water isotopic composition, and N.A. Lobkova for determination of GH gas composition. The authors would like to acknowledge the Scientific Party of the Baikal expedition-2000 for fruitful cooperation, and personally O. Khlystov (Irkutsk Limnological Institute SB RAS). The Russian Foundation for Basic Research has supported this work (projects 02-05-64346 and 02-0506321). We also wish to thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matveeva, T.V., Mazurenko, L.L., Soloviev, V.A. et al. Gas hydrate accumulation in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal (Eastern Siberia). Geo-Mar Lett 23, 289–299 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0144-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0144-z