Abstract
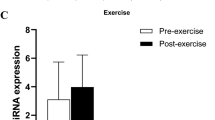
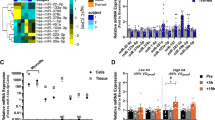
Dummerstorf marathon mice (DUhTP) are characterized by increased accretion of peripheral body fat with fast mobilization in response to mild physical activity if running wheels were included in their home cages. The obese phenotype coincides with elevated hepatic lipogenesis if compared to unselected controls. We now asked, if microRNA (miRNA) species present in the liver may contribute to the obese phenotype of DUhTP mice and if miRNAs respond to mild physical activity in our mouse model. Total RNA was extracted from livers of sedentary or physically active marathon mice and controls and analyzed by array hybridization or real-time PCR using locked nucleic acid probes. Pathway analysis of altered miRNA concentrations identified fatty acid biosynthesis as the most important target for the effects of miRNAs in the liver. A miRNA signature consisting of miR-21, 27, 33, 122, and 143 was present at higher abundance (p < 0.01) in the liver of sedentary or active DUhTP mice indicating involvement of miRNAs with hepatic lipogenesis. Furthermore, in protein lysates from the liver of DUhTP mice, significantly reduced concentrations of total and phosphorylated AKT and lower levels of phosphorylated AMPK were found (p < 0.05). Our results indicate active involvement of miRNAs in the control of hepatic energy metabolism and discuss effects on signal transduction as a potentially direct effect of miR-143 in the liver of DUhTP mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Lee H, Jung CH, Ha T (2012) Lycopene inhibits hepatic steatosis via microRNA-21-induced downregulation of fatty acid-binding protein 7 in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(11):1665–1674. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201200182
An F, Gong B, Wang H, Yu D, Zhao G, Lin L, Tang W, Yu H, Bao S, Xie Q (2012) miR-15b and miR-16 regulate TNF mediated hepatocyte apoptosis via BCL2 in acute liver failure. Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death 17(7):702–716. doi:10.1007/s10495-012-0704-7
Brenmoehl J, Walz C, Renne U, Ponsuksili S, Wolf C, Langhammer M, Schwerin M, Hoeflich A (2013) Metabolic adaptations in the liver of born long-distance running mice. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45(5):841–850. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e31827e0fca
Brenmoehl J, Ohde D, Walz C, Schultz J, Tuchscherer A, Rieder F, Renne U, Hoeflich A (2015) Dynamics of fat mass in DUhTP mice selected for running performance—fat mobilization in a walk. Obes Facts 8(6):373–385. doi:10.1159/000442399
Camera DM, Ong JN, Coffey VG, Hawley JA (2016) Selective modulation of microRNA expression with protein ingestion following concurrent resistance and endurance exercise in human skeletal muscle. Front Physiol 7:87. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00087
Chaveles I, Zaravinos A, Habeos IG, Karavias DD, Maroulis I, Spandidos DA, Karavias D (2012) MicroRNA profiling in murine liver after partial hepatectomy. Int J Mol Med 29(5):747–755. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2012.902
Falkenberg H, Langhammer M, Renne U (2000) Comparison of biochemical blood traits after long-term selection on high or low locomotor activity in mice. Arch Tierzucht 13:513–522
Ghosh A, Ghosh A, Datta S, Dasgupta D, Das S, Ray S, Gupta S, Datta S, Chowdhury A, Chatterjee R, Mohapatra SK, Banerjee S (2016) Hepatic miR-126 is a potential plasma biomarker for detection of hepatitis B virus infected hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 138(11):2732–2744. doi:10.1002/ijc.29999
Goh DL, Patel A, Thomas GH, Salomons GS, Schor DS, Jakobs C, Geraghty MT (2002) Characterization of the human gene encoding alpha-aminoadipate aminotransferase (AADAT). Mol Genet Metab 76(3):172–180
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):251–262. doi:10.1038/nrm3311
Horie T, Ono K, Horiguchi M, Nishi H, Nakamura T, Nagao K, Kinoshita M, Kuwabara Y, Marusawa H, Iwanaga Y, Hasegawa K, Yokode M, Kimura T, Kita T (2010) MicroRNA-33 encoded by an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (Srebp2) regulates HDL in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(40):17321–17326. doi:10.1073/pnas.1008499107
Ishida H, Tatsumi T, Hosui A, Nawa T, Kodama T, Shimizu S, Hikita H, Hiramatsu N, Kanto T, Hayashi N, Takehara T (2011) Alterations in microRNA expression profile in HCV-infected hepatoma cells: involvement of miR-491 in regulation of HCV replication via the PI3 kinase/Akt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412(1):92–97. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.049
Jennewein C, von Knethen A, Schmid T, Brune B (2010) MicroRNA-27b contributes to lipopolysaccharide-mediated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) mRNA destabilization. J Biol Chem 285(16):11846–11853. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.066399
Jordan SD, Kruger M, Willmes DM, Redemann N, Wunderlich FT, Bronneke HS, Merkwirth C, Kashkar H, Olkkonen VM, Bottger T, Braun T, Seibler J, Bruning JC (2011) Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 13(4):434–446. doi:10.1038/ncb2211
Li L, Liu Y, Guo Y, Liu B, Zhao Y, Li P, Song F, Zheng H, Yu J, Song T, Niu R, Li Q, Wang XW, Zhang W, Chen K (2015) Regulatory MiR-148a-ACVR1/BMP circuit defines a cancer stem cell-like aggressive subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 61(2):574–584. doi:10.1002/hep.27543
Lu YL, Jing W, Feng LS, Zhang L, Xu JF, You TJ, Zhao J (2014) Effects of hypoxic exercise training on microRNA expression and lipid metabolism in obese rat livers. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 15(9):820–829. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1400052
Meng Z, Fu X, Chen X, Zeng S, Tian Y, Jove R, Xu R, Huang W (2010) miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice. Hepatology 52(6):2148–2157. doi:10.1002/hep.23915
Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li YX, Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE, Naar AM (2010) MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science 328(5985):1566–1569. doi:10.1126/science.1189123
Ohde D, Moeller M, Brenmoehl J, Walz C, Ponsuksili S, Schwerin M, Fuellen G, Hoeflich A (2016) Advanced running performance by genetic predisposition in male Dummerstorf marathon mice (DUhTP) reveals higher sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) related mRNA expression in the liver and higher serum levels of progesterone. PLoS One 11(1):e0146748. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146748
Oliverio M, Schmidt E, Mauer J, Baitzel C, Hansmeier N, Khani S, Konieczka S, Pradas-Juni M, Brodesser S, Van TM, Bartsch D, Bronneke HS, Heine M, Hilpert H, Tarcitano E, Garinis GA, Frommolt P, Heeren J, Mori MA, Bruning JC, Kornfeld JW (2016) Dicer1-miR-328-Bace1 signalling controls brown adipose tissue differentiation and function. Nat Cell Biol 18(3):328–336. doi:10.1038/ncb3316
Parrizas M, Brugnara L, Esteban Y, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Canivell S, Murillo S, Gordillo-Bastidas E, Cusso R, Cadefau JA, Garcia-Roves PM, Servitja JM, Novials A (2015) Circulating miR-192 and miR-193b are markers of prediabetes and are modulated by an exercise intervention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(3):E407–E415. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-2574
Rayner KJ, Suarez Y, Davalos A, Parathath S, Fitzgerald ML, Tamehiro N, Fisher EA, Moore KJ, Fernandez-Hernando C (2010) MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Science 328(5985):1570–1573. doi:10.1126/science.1189862
Ritchie ME, Silver J, Oshlack A, Holmes M, Diyagama D, Holloway A, Smyth GK (2007) A comparison of background correction methods for two-colour microarrays. Bioinformatics 23(20):2700–2707. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm412
Selitsky SR, Dinh TA, Toth CL, Kurtz CL, Honda M, Struck BR, Kaneko S, Vickers KC, Lemon SM, Sethupathy P (2015) Transcriptomic analysis of chronic hepatitis B and C and liver cancer reveals microRNA-mediated control of cholesterol synthesis programs. mBio 6(6):e01500–e01515. doi:10.1128/mBio.01500-15
Szabo G, Bala S (2013) MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(9):542–552. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2013.87
Tang H, Li RP, Liang P, Zhou YL, Wang GW (2015) miR-125a inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells via suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 10(2):681–686. doi:10.3892/ol.2015.3264
Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ, Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF, Hsu MT, Wu JC, Huang HD, Shiao MS, Hsiao M, Tsou AP (2012) MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 122(8):2884–2897. doi:10.1172/jci63455
Tu X, Zhang H, Zhang J, Zhao S, Zheng X, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Chen J, Dong L, Zang Y, Zhang J (2014) MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by targeting the TGFbeta signalling pathway. J Pathol 234(1):46–59. doi:10.1002/path.4373
Vega-Badillo J, Gutierrez-Vidal R, Hernandez-Perez HA, Villamil-Ramirez H, Leon-Mimila P, Sanchez-Munoz F, Moran-Ramos S, Larrieta-Carrasco E, Fernandez-Silva I, Mendez-Sanchez N, Tovar AR, Campos-Perez F, Villarreal-Molina T, Hernandez-Pando R, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Canizales-Quinteros S (2016) Hepatic miR-33a/miR-144 and their target gene ABCA1 are associated with steatohepatitis in morbidly obese subjects. Liver Int. doi:10.1111/liv.13109
Vlachos IS, Zagganas K, Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Karagkouni D, Vergoulis T, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2015) DIANA-miRPath v3. 0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W460–W466
Wang L, Shi ZM, Jiang CF, Liu X, Chen QD, Qian X, Li DM, Ge X, Wang XF, Liu LZ, You YP, Liu N, Jiang BH (2014) MiR-143 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting N-RAS and enhances temozolomide-induced apoptosis in glioma. Oncotarget 5(14):5416–5427. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2116
Wang H, Luo J, Zhang T, Tian H, Ma Y, Xu H, Yao D, Loor JJ (2016a) MicroRNA-26a/b and their host genes synergistically regulate triacylglycerol synthesis by targeting the INSIG1 gene. RNA Biol 13:500–510. doi:10.1080/15476286.2016.1164365
Wang Y-L, C-m Chen, Wang X-M, Wang L (2016b) Effects of miR-339-5p on invasion and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 40:51–56
Yang Z, Wang L (2011) Regulation of microRNA expression and function by nuclear receptor signaling. Cell Biosci 1(1):31. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-1-31
Yang Z, Cappello T, Wang L (2015) Emerging role of microRNAs in lipid metabolism. Acta Pharm Sin B 5(2):145–150. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.002
Acknowledgments
We thank Sabine Hinrichs, Marion Spitschak, and Luong Chau for excellent technical support. We further want to express our gratitude to the complete service team from the mouse facility (LIN) at the Leibniz Institute for Farm Animal Biology (FBN) Dummerstorf for excellent support with the mouse lines and to Dr. Mark Moeller for helpful suggestions with pathway analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Daniela Ohde was supported by a grant from the H. Wilhelm Schaumann Stiftung. All other authors have nothing to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
D. Ohde and J. Brenmoehl contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohde, D., Brenmoehl, J., Walz, C. et al. Comparative analysis of hepatic miRNA levels in male marathon mice reveals a link between obesity and endurance exercise capacities. J Comp Physiol B 186, 1067–1078 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1006-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1006-0