Abstract
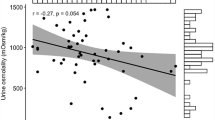
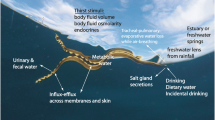
Bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) are marine mammals with body water needs challenged by little access to fresh water and constant exposure to salt water. Osmoregulation has been studied in marine mammals for a century. Research assessing the effects of ingested fresh water or seawater in dolphins, however, has been limited to few animals and sampling times. Nine 16- to 25-h studies were conducted on eight adult dolphins to assess the hourly impact of fresh water, seawater, and seawater with protein ingestion on plasma and urine osmolality, urine flow rate (ufr), urinary and plasma solute concentrations, and solute clearance rates. Fresh water ingestion increased ufr. Fresh water ingestion also decreased plasma and urine osmolality, sodium and chloride urine concentrations, and solute excretion rates. Seawater ingestion resulted in increased ufr, sodium, chloride, and potassium urine concentrations, sodium excretion rates, and urine osmolality. Seawater with protein ingestion was associated with increased ufr, plasma osmolality, sodium excretion, and sodium, chloride, potassium, and urea urine concentrations. In conclusion, bottlenose dolphins appear to maintain water and plasma solute balance after ingesting fresh water or seawater by altering urine osmolality and solute clearance. Ingestion of protein with seawater appears to further push osmoregulation limits and urine solute concentrations in dolphins.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPTR:
-
High protein test ration
- MMP:
-
Navy Marine Mammal Program
References
Albrecht CB (1950) Toxicity of sea water in mammals. Am J Physiol 163:370–385
Bengoumi M, Riad F, Giry J, de la Farge F, Safwate A, Davicco MJ, Barlet JP (1993) Hormonal control of water and sodium in plasma and urine of camels during dehydration and rehydration. Gen Comp Endocrinol 89:378–386
Bie P (1977) Sustained water diuresis in anesthetized dogs: antidiuresis in response to intravenous and bilateral introcarotid infusion of hyper-osmolar solutions of sodium chloride. Act Physiol Scand 101:446–457
Birukawa N, Ando H, Goto M, Kanda N, Pastene LA, Nakatsuji H, Hata H, Urano A (2005) Plasma and urine levels of electrolytes, urea, and steroid hormones involved in osmoregulation of cetaceans. Zool Sci 22:1245–1257
Blantz RC, Tucker BJ, Gushwa L, Peterson OW (1983) Mechanism of diuresis following acute modest hyperglycemia in the rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 244:F185–F194
Bouby N, Trinh-Trang-Tan MM, Coutaud C, Bankir L (1991) Vasopressin is involved in renal effects of high-protein diet: study in homozygous Brattleboro rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 260:96–100
Bradley SE, Mudge GH, Blake WD (1954) The renal excretion of sodium, potassium and water by the harbor seal (Phoce vitulina L.): effect of apnea; sodium, potassium and; pitressin; and mercurial diuresis. J Cell Comp Physiol 43:1–22
Caldwell DK, Caldwell MC (1972) World of the bottlenose dolphin. J. B. Lippincott, Co., Philadelphia
Costa DP (1982) Energy, nitrogen, electrolyte flux and sea water drinking in the sea otter Enhydra lutris. Physiol Zool 55:35–44
Daniels BS, Hostetter TH (1990) Effects of dietary protein intake on vasoactive hormones. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Physiol 258:R1095–R1100
Denke M (2001) Metabolic effects of high-protein low-carbohydrate diets. Am J Cardiol 88:59–61
Eichelberger L, Leiter L, Geiling EMK (1940) Water and electrolyte content of dolphin kidney and extraction of pressor substance (renin). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 44:356–359
Fetcher ES Jr (1939) The water balance in marine mammals. Q Rev Biol 14:451–459
Fetcher ES Jr, Fetcher GW (1942) Experiments on the osmotic regulation of dolphins. J Cell Comp Physiol 19:123–130
Gales R, Renouf D (1993) Detecting and measuring food and water intake in captive seals using temperature telemetry. J Wildl Manage 57:514–519
Geraci JR (1972) Hyponatremia and the need for dietary salt supplementation in captive pinnipeds. J Am Vet Med Assoc 161:618–623
Guyton AC, Hall JE (eds) (1996) Textbook of medical physiology, 9th edn. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia
Hendrikx A, Epstein FH (1958) Effect of feeding protein and urea on renal concentrating ability in the rat. Am J Physiol 195:539–542
Hiatt EP, Hiatt RB (1942) The effect of food on the glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow in the harbor seal (Phoca vitulina L.). J Cell Comp Physiol 19:221–227
Hong SK, Elsner R, Claybaugh JR, Ronald K (1982) Renal functions of the Baikal seal Pusa sibirica and ringed seal Pusa hispida. Physiol Zool 55:289–299
How OJ, Nordøy ES (2007) Seawater drinking restores water balance in dehydrated harp seals. J Comp Physiol B Biochem Syst Environ Physiol 177:535–542
Hui CA (1981) Seawater consumption and water flux in the common dolphin Delphinus delphi. Physiol Zool 54:430–440
Irving RA, Noakes TD, Buck R, van Zyl Smit R, Raine E, Godlonton J, Norman RJ (1991) Evaluation of renal function and fluid homeostasis during recovery from exercise-induced hyponatremia. J Appl Physiol 70:342–348
Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, Barrett EJ, Kreisberg RA, Malone JI, Wall BM (2001) Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 24:131–153
Kjeld M (2001) Concentrations of electrolytes, hormones, and other constituents in fresh postmortem blood and urine of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus). Can J Zool 79:438–446
Malvin RL, Rayner M (1968) Renal function and blood chemistry in cetacea. Am J Physiology 214:187–191
Malvin RL, Vander AJ (1967) Plasma renin activity in marine teleosts and Cetacea. Am J Physiol 213:1582–1584
Malvin RL, Ridgway S, Cornell L (1978) Renin and aldosterone levels in dolphins and sea lions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 157:665–668
Ortiz RM (2001) Osmoregulation in marine mammals. J Exp Biol 204:1831–1844
Ortiz RM, Worthy GAJ (2000) Effects of capture on adrenal steroid and vasopressin concentrations in free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 125:317–324
Ortiz RM, Adams SH, Costa DP, Ortiz CL (1996) Plasma vasopressin levels and water conservation in fasting, postweaned northern elephant seal pups (Mirounga angustirostris). Mar Mamm Sci 12:99–106
Ortiz RM, Wade CE, Costa DP, Ortiz CL (2002) Renal responses to plasma volume expansion and hyperosmolality in fasting seal pups. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R805–R817
Ortiz RM, Wade CE, Ortiz CL (2003) Body water handling in response to hypertonic-saline induced dieresis in fasting northern elephant seal pups (Mirounga angustriostris). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 134:423–428
Ortiz RM, Long B, Casper D, Ortiz L, Williams TM (2009) Biochemical and hormonal changes during acute fasting and re-feeding in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Mar Mamm Sci. doi:10.111/j.1748-7692.2009.0009.x
Pfeiffer CJ (1997) Renal cellular and tissue specializations in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and beluga whale (Dephinapterus leucas). Aquat Mammal 23:75–84
Renouf D, Noseworthy E, Scott MC (1990) Daily fresh water consumption by captive harp seals (Phoca groenlandica). Mar Mamm Sci 6:253–257
Ridgway SH (1972) Homeostasis in the aquatic environment. In: Ridgway S (ed) Mammals of the sea: biology and medicine. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, pp 590–747
Ridgway SH, Simpson JG, Patton GS, Gilmartin WG (1970) Hematologic findings in certain small cetaceans. J Am Vet Med Assoc 157:566–575
Rosenberg ME, Swanson JE, Thomas BL, Hostetter TH (1987) Glomerular and hormal responses to dietary protein intake in human renal disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 253:F1083–F1090
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1990) Animal physiology: adaptation and environment, 4th edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Schmidt-Nielsen B, Murdaugh HV, O’Dell R, Bacsanyi J (1959) Urea excretion and diving in the seal (Phoca vitulina L.). J Cell Comp Physiol 53:393–411
Shimamura MH, Yasue H, Ohshima K et al (1997) Molecular evidence from retroposons that whales form a clade within even-toed ungulates. Nature 388:666–670
Skog EB, Folkow LP (1994) Nasal heat and wter exchange is not an effector mechanism for water balance regulation in grey seals. Acta Physiol Scand 151:233–240
Storeheier PV, Nordøy ES (2001) Physiological effects of seawater intake in adult harp seals during phase I of fasting. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 128:307–315
Tarasoff F, Toews D (1972) The osmotic and ionic regulatory capacities of the kidney of the harbor seal, Phoca vitulina. J Comp Physiol 81:121–132
Tedman R, Green B (2009) Water and sodium fluxes and lactational energetic in suckling pups of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii). J Zool 212:29–42
Telfer N, Cornell LH, Prescott JH (1970) Do dolphins drink water? J Am Vet Med Assoc 157:555–558
Thewissen JGM, Madar SI (1999) Ankle morphology of the earliest cetaceans and its implications for the phylogenetic relations among ungulates. Syst Biol 48:21–30
Van Dyke D (1972) Contingency ration for California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Naval Undersea Center, Technical Report No 317. San Diego
Vander AJ (1995) Renal physiology, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York
Venn-Watson S, Jensen ED, Ridgway SH (2007) Effects of age and sex on clinicopathologic reference ranges in a healthy managed Atlantic bottlenose dolphin population. J Am Vet Med Assoc 231:596–601
Venn-Watson S, Smith CR, Dold C, Ridgway SH (2008) Use of a serum-based glomerular filtration rate prediction equation to assess renal function by age, sex, fasting, and health status in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Mar Mamm Sci 24:71–80
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr. Christopher Hammell for his assistance with data entry and the reviewers of this manuscript, including Dr. Rudy Ortiz, for their valuable contributions and discussion topics. SHR conceived the study hypotheses and implemented experimental design. SVW analyzed the data. Both authors wrote and edited the manuscript. The experiments in this study complied with the current laws of the country in which the experiments were performed.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by I. D. Hume.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ridgway, S., Venn-Watson, S. Effects of fresh and seawater ingestion on osmoregulation in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J Comp Physiol B 180, 563–576 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-009-0439-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-009-0439-0