Abstract
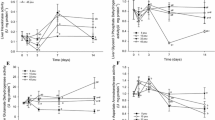
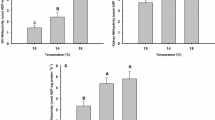
In this study we assessed changes in the osmoregulatory system of juvenile sub-Antarctic Eleginops maclovinus submitted to different environmental salinities (5, 15, 32 and 45 psu) using two different acclimation trials: (1) an end-point experiment (exposure for 14 days) and (2) a time course experiment (specimens were sampled on days 1, 3, 7 and 14 post-transfer). Plasma osmolality, cortisol and metabolites (glucose, lactate and protein) values as well as Na+, K+-ATPase (NKA) activity were assessed in several osmoregulatory tissues (gills, kidney and intestine). In both trials, acclimation to different environmental salinities for 14 days induced changes in plasma metabolites (glucose, lactate and proteins) as well as cortisol values related to salinity challenges. Plasma osmolality and gill NKA activity presented a direct and positive relationship with respect to environmental salinity, while kidney NKA activity showed a “U-shaped” relationship. Anterior intestinal NKA activity increased in response to environmental salinity and apparently did not change in the middle portion of this organ, while it was enhanced in the posterior portion in environmental salinities different than seawater. Plasma metabolite values increased under hypo- and hypersaline conditions, indicating the importance of these energy substrates in extreme environments. The time course study revealed that specimens of E. maclovinus are able to accommodate their osmotic and metabolic system to respond to osmoregulatory challenges by allostatic changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjona FJ, Vargas-Chacoff L, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2007) Osmoregulatory response of Senegalase sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858) to changes in environmental salinity. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:413–421
Arjona FJ, Vargas-Chacoff L, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Goncalves O, Páscoa I, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2009) Tertiary stress responses in Senegalase sole (Solea Senegalensis, Kaup 1858) to osmotic challenge: implications for osmoregulation, energy metabolism and growth. Aquaculture 287:419–426
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fish: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Bath RN, Eddy FB (1979) Ionic and respiratory regulation in rainbow trout during rapid transfer to seawater. J Comp Physiol 134:351–357
Beyenbach KW (1995) Secretory electrolyte transport in renal proximal tubules of fish. In: Wood CM, Shuttlewoth TJ (eds) Fish Physiology, vol XIV., Ionoregulation: cellular and molecular approachesAcademic Press, New York, pp 85–106
Boeuf G, Payan P (2001) How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp Biochem Physiol C 130:411–423
Bystriansky JS, Ballantyne JS (2007) Gill Na+-K+-ATPase activity correlates with basolateral membrane lipid composition in seawater—but not freshwater-acclimated Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R1043–R1051
Chew SF, Tng YYM, Wee NLJ, Tok CY, Wilson JM, Ip YK (2010) Intestinal osmoregulatory acclimation and nitrogen metabolism in juveniles of the freshwater marble goby exposed to seawater. J Comp Physiol B 180:511–520
Dantzler WH (2003) Regulation of renal proximal and distal tubule transport: sodium, chloride and organic anions. Comp Biochem Physiol A 136:453–478
Evans TG (2010) Co-ordination of osmotic stress responses through osmosensing and signal transduction events in fishes. J Fish Biol 76:1903–1925
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Fuentes J, Soengas JL, Rey P, Rebolledo E (1997) Progressive transfer to seawater enhances intestinal and branchial Na+-K+ ATPase activity in non-anadromous rainbow trout. Aquac Int 5:217–227
Grosell M (2006) Intestinal anion exchange in marine fish osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 209:2813–2827
Grosell M (2007) Intestinal transport processes in marine fish osmoregulation. In: Baldisserotto B, Mancera JM, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish osmoregulation, Science Publisher Enfield, New Hampshire, USA. pp 333–357
Grosell M (2011) Intestinal anion exchange in marine teleosts is involved in osmoregulation and contributes to the oceanic inorganic carbon cycle. Acta Physiol 202:421–434
Herrera M, Vargas-Chacoff L, Hachero I, Ruíz-Jarabo I, Rodiles A, Navas J, Mancera JM (2009) Osmoregulatory changes in wedge sole (Dicologoglossa cuneata, Moreau 1881) after acclimation to different environmental salinities. Aquac Res 40:762–771
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268
Imsland AK, Gunnarsson S, Foss A, Stefansson SO (2003) Gill Na+, K+-ATPase activity, plasma chloride and osmolality in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) reared at different temperatures and salinities. Aquaculture 218:671–683
Jensen MK, Madsen SS, Kristiansen K (1998) Osmoregulation and salinity effects on the expression and activity of Na+-K+ ATPase in the gills of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). J Exp Zool 282:290–300
Kaneko T, Shiraishi K, Katoh F, Hasegawa S, Hiroi J (2002) Chloride cells during early life stages of fish and their functional differentiation. Fisheries Sci 68:1–9
Kelly SP, Woo NYS (1999) Cellular and biochemical characterization of hyposmotic adaptation in a marine teleost, Sparus sarba. Zool Sci 16:505–514
Kelly SP, Chow INK, Woo NYS (1999a) Haloplasticity of black seabream (Mylio macrocephalus): hypersaline to freshwater acclimation. J Exp Zool 283:226–241
Kelly SP, Chow INK, Woo NYS (1999b) Effects of prolactin and growth hormone on strategies of hyposmotic adaptation in a marine teleost, Sparus sarba. Gen Comp Endocrinol 113:9–22
Laiz-Carrión R, Guerreiro PM, Fuentes J, Canario AVM, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2005) Branchial osmoregulatory response to salinity in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata. J Exp Zool A 303:563–576
Madsen SS, McCormick SD, Young G, Endersen JS, Nishioka RS, Bern HA (1994) Physiology of seawater acclimation in the striped bass, Morone saxatilis (Walbaum). Fish Physiol Biochem 13:1–11
Mancera JM, Laiz-Carrión R, Martín del Río MP (2002) Osmoregulatoryaction of PRL, GH, and cortisol in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol 129:95–103
Marshall WS (2002) Na+, Cl-, Ca++ and Zn++ transport by fish gills: retrospective review and prospective synthesis. J Exp Zool 292:264–283
Marshall WS, Emberley TR, Singer TD, Bryson SE, McCormick SD (1999) Time course of salinity adaptation in a strongly euryhaline estuarine teleost, Fundulus heteroclitus: a multivariable approach. J Exp Biol 202:1535–1544
Matschiner M, Hanel R, Salzburger W (2011) On the origin and trigger of the notothenioid adaptive radiation. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18911
McCormick SD (1993) Methods for nonlethal gill biopsy and measurement of Na+-K+ ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:656–658
McCormick SD (1995) Hormonal control of gill Na+, K+-ATPase and chloride cell function. In: Wood CM, Shuttlewoth TJ (eds) Fish Physiology, vol XIV., Ionoregulation: cellular and molecular approachesAcademic Press, New York, pp 285–315
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
McCormick SD (2013) Smotl physiology and endocrinology. In: McCormick SD, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Euryhaline Fishes. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 200–237
McDonald DM (2007) The renal contribution to salt and water balance. In: Baldisserotto B, Mancera JM, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish osmoregulation, Science Publishers Enfield, New Hampshire, USA. pp 309–331
Mommsen TP (1984) Metabolism of the fish gill. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish Physiology, vol XB. Academic Press, New York, pp 203–238
Mommsen TP, Walsh PJ, Moon TW (1985) Gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes and kidney of Atlantic salmon. Mol Physiol 8:89–100
Mommsen TP, Vijayan M, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleost: dymanics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Pavés H, Pequeño G, Bertrán C, Vargas L (2005) Limnetic feeding in Eleginops maclovinus (Valenciennes 1830) in the Valdivia River, Chile. Interciencia 30:120–125
Pequeño G (1989) The geographical distribution and taxonomic arrangement of South American notothenidae fishes (Osteichthyes, Notothenidae). Bol Soc Biol Concepción Chile 60:183–200
Pequeño G, Pavés H, Bertrán C, Vargas-Chacoff L (2010) Seasonal limnetic feeding regime of the “robalo” Eleginops maclovinus (Valenciennes 1830), in the Valdivia river, Chile. Gayana 74:47–56
Pérez AF, Calvo J, Tresguerres M, Luquet C (2003) Aglomerularism in Harpagifer bispinis: a subantarctic notothenioid fish living at reduced salinity. Polar Biol 26:800–805
Perry SF, Goss GG, Laurent P (1997) The interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and ionic uptake in four freshwater teleosts. Can J Zool 70:1775–1786
Polakof S, Mommsen TW, Soengas JL (2011) Glucosensing and glucose homeostasis: from fish to mammals. Comp Biochem Physiol B 160:123–149
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Laiz-Carrión R, Guzmán JM, Martín del Río MP, Miguez JM, Mancera JM, Soengas JL (2003) Acclimation of S. aurata to various salinities alters energy metabolism of osmoregulatory and nonosmoregulatory organs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R897–R907
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Arjona FJ, Martín del Río MP, Míguez JM, Mancera JM, Soengas JL (2005) Time course of osmoregulatory and metabolic changes during osmotic acclimation in Sparus aurata. J Exp Biol 208:4291–4304
Seidelin M, Madsen SS, Belnstrup H, Tipsmark CK (2000) Timecourse changes in the expression of the Na+-K+ ATPase in gills and pyloric caeca of brown trout (Salmo trutta) during acclimation to seawater. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:446–453
Staurnes M, Sigholt T, Asgard T, Baeverfjord G (2001) Effects of a temperature shift on seawater challenge test performance in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolt. Aquaculture 201:153–159
Taylor JR, Grosell M (2006) Feeding and osmoregulation: dual function of the marine teleost intestine. J Exp Biol 209:2939–2951
Taylor JR, Mager EM, Grosell M (2010) Basolateral NBCe1 plays a ratelimiting role in transepithelial intestinal HCO3− secretion, contributing to marine fish osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 213:459–468
Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Páscoa I, Gonçalves O, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2009a) Seasonal variation in osmoregulatory and metabolic parameters in earthen pond cultured gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. Aquac Res 40:1279–1290
Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Polakof S, Martín del Río MP, Soengas JL, Mancera JM (2009b) Interactive effects of environmental salinity and temperature on metabolic responses of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Comp Biochem Physiol A 154:417–424
Vargas-Chacoff L, Calvo A, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Villarroel F, Muñoz JL, Tinoco AB, Cárdenas S, Mancera JM (2011) Growth performance, osmoregulatory and metabolic modifications in red porgy fry, Pagrus pagrus, under different environmental salinities and stocking densities. Aquac Res 42:1269–1278
Venturini G, Cataldi E, Marino G, Pucci P, Garibaldi L, Bronz P (1992) Serum ions concentration and ATPase activity in gills, kidney and esophagus of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Pisces, Perciformes) during acclimation trial to fresh water. Comp Biochem Physiol A 103:451–454
Wendelaar-Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Whittamore JM (2012) Osmoregulation and epithelial water transport: lessons from the intestine of marine teleost fish. J Comp Physiol B 182:1–39
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out in the framework of FONDECYT Project 1110235. We thank Dr. Lafayette Eaton and Mr. Ignacio Ruiz-Jarabo (Departamento de Biología, Facultad de Ciencias del Mar y Ambientales, Universidad de Cádiz, España) for their help checking this manuscript and the Dirección de Investigación of the Universidad Austral de Chile (DID).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vargas-Chacoff, L., Moneva, F., Oyarzún, R. et al. Environmental salinity-modified osmoregulatory response in the sub-Antarctic notothenioid fish Eleginops maclovinus . Polar Biol 37, 1235–1245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1515-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1515-9