Abstract
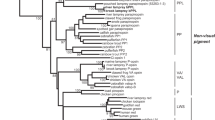
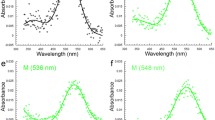
Crayfish have two classes of photoreceptors in the retinas of their reflecting superposition eyes. Long-wavelength-sensitive photoreceptors, comprised of microvilli from R1–7 cells, make up the main rhabdoms. Eighth retinular cells, located distal to the main rhabdoms, house short-wavelength-sensitive photoreceptors. While the opsin involved in long-wavelength sensitivity has long been known, we present the first description of the short-wavelength-sensitive opsin in the retina of the red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. The expression patterns of these SWS and LWS opsin proteins in the retina are consistent with the previously described locations of SWS and LWS receptors. Crayfish also have a well-characterized extraocular photoreceptor, called the caudal photoreceptor, located in the sixth abdominal ganglion. To search for retinal opsins in the caudal photoreceptor (and elsewhere in the CNS), we used RT-PCR and immunohistochemical labeling. We found both SWS and LWS opsin transcripts not only in the sixth abdominal ganglion, but also in all ganglia of the nerve cord. Immunolabeling shows that both opsins are expressed in nerve fibers that extend from the brain through the entire length of the CNS. Thus, the same two photopigments are used both for vision in the retina and for extraocular functions throughout the CNS of crayfish.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AG:
-
Abdominal ganglion
- CG:
-
Cerebral ganglion (brain)
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CPR:
-
Caudal photoreceptor
- LWS:
-
Long-wavelength-sensitive opsin
- SEG:
-
Subesophageal ganglion
- SWS:
-
Short-wavelength-sensitive opsin
- TG:
-
Thoracic ganglion
References
Bruno MS, Kennedy D (1962) Spectral sensitivity of photoreceptor neurons in the sixth ganglion of the crayfish. Comp Biochem Phys A 6:41–46
Cronin TW, Goldsmith TH (1982) Photosensitivity spectrum of crayfish rhodopsin measured using fluorescence of metarhodopsin. J Gen Physiol 79:313–332
Cummins D, Goldsmith TH (1981) Cellular identification of the violet receptor in the crayfish eye. J Comp Physiol 142:199–202
de Couet HG, Sigmund C (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to crayfish rhodopsin. I Biochemical characterization and cross-reactivity. Eur J Cell Biol 38:106–112
Hariyama T, Tsukahara Y (1988) Seasonal variation of spectral sensitivity in crayfish retinula cells. Comp Biochem Phys A 91A:529–533
Hariyama T, Ozaki K, Tokunaga F, Tsukahara Y (1993) Primary structure of crayfish visual pigment deduced from cDNA. FEBS J 315:287–292
Larimer JL (1966) A functional caudal photoreceptor in blind cavernicolous crayfish. Nature 210:204–205
Larimer JL, Trevino DL, Ashby EA (1966) A comparison of spectral sensitivities of caudal photoreceptors of epigeal and cavernicolous crayfish. Comp Biochem Phys A 19:409–415
Prosser CL (1934) Action potentials in the nervous system of the crayfish. J Cell Comp Physiol 4:363–377
Sandeman D, Sandeman R, Derby C, Schmidt M (1992) Morphology of the brain of crayfish, crabs, and spiny lobsters: A common nomenclature for homologous structures. Biol Bull 183:304–326
Simon TW, Edwards DH (1990) Light-evoked walking in crayfish: behavioral and neuronal responses triggered by the caudal photoreceptor. J Comp Physiol A 166:745–755
Welsh JH (1934) The caudal photoreceptor and responses of the crayfish to light. J Cell Comp Physiol 4:379–388
Wilkens LA (1988) The crayfish caudal photoreceptor—advances and questions after the first half century. Comp Biochem Physiol C 91:61–68
Wilkens LA, Larimer JL (1972) The CNS photoreceptor of crayfish: morphology and synaptic activity. J Comp Physiol 80:389–407
Wilkens LA, Larimer JL (1976) Photosensitivity in the sixth abdominal ganglion of decapod crustaceans: a comparative study. J Comp Physiol 106:69–75
Zeiger J, Goldsmith TH (1989) Spectral properties of porphyropsin from an invertebrate. Vis Res 29:519–527
Acknowledgments
We thank Hiroko Awata for contributing to sequencing the short-wavelength-sensitive opsin.
Funding
This research was supported by the Office of Naval Research Basic Research Challenge (Grant No. N00014-10-0989 to T.W.C. and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Grant No. FA9550-12-1-0321) to T.W.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
359_2015_1043_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1 Predicted amino acid sequences of Procambarus clarkii transcripts from the retina and central nervous system. Full-length sequences of LWS opsin are identical in the retina, brain, thoracic ganglia 1-5, and abdominal ganglia 1-6 (TIFF 10196 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 2 Predicted amino acid sequences of Procambarus clarkii transcripts from the retina and central nervous system. Full-length sequences of SWS opsin are identical in the retina, brain, thoracic ganglia 1-5, and abdominal ganglia 1-6 (TIFF 10241 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 3 Secondary-only control Western blots using Procambarus clarkii retinal tissues. (a) Western blots using solubilized retinal protein labeled with anti-rabbit HRP show no labeling. (b) Western blots using solubilized retinal protein labeled with anti-chicken HRP show no labeling (TIFF 2110 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 4 Peptide absorption control Western blots using Procambarus clarkii retinal tissues. (a) Western blots using solubilized retinal protein labeled with LWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide show no labeling. (b) Western blots using solubilized retinal protein labeled with SWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide show no labeling (TIFF 2121 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 5 Secondary-only control immunolabeling in Procambarus clarkii retina. (a) Retinal tissues labeled with only anti-rabbit 488 show little autofluorescence and no non-specific labeling. Main rhabdom (R) is indicated by the arrowhead. (b) Retinal tissues labeled with only anti-chicken 555 show no autofluorescence or non-specific labeling. Eighth retinular cell (R8) is indicated by the arrowhead. Scale bars, 25 μm (TIFF 651 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 6 Peptide absorption control immunolabeling in Procambarus clarkii retina. (a) Retinal tissues labeled with LWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide show little autofluorescence and no non-specific labeling. Main rhabdom (R) is indicated by the arrowhead. (b) Retinal tissues labeled with SWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide show no autofluorescence or non-specific labeling. Eighth retinular cell (R8) is indicated by the arrowhead. Scale bars, 25 μm (TIFF 1354 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM7_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 7 Secondary-only control immunolabeling in Procambarus clarkii brain and abdominal ganglion 6. (a) In the cerebral ganglion, the deuterocerebrum shows little autofluorescence and no non-specific labeling when labeled with anti-rabbit 488 and anti-chicken 555. (b) Abdominal ganglion six labeled with anti-rabbit 488 and anti-chicken 555 shows little autofluorescence and no non-specific labeling. Scale bars, 25 μm (TIFF 4074 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM8_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 8 Peptide absorption control immunolabeling in Procambarus clarkii brain. (a) In the cerebral ganglion, the deuterocerebrum shows little autofluorescence and no labeling when labeled with LWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide. (b) In the cerebral ganglion, the deuterocerebrum labeled with SWS antibody absorbed with antigenic peptide shows little autofluorescence and no non-specific labeling. Scale bars, 25 μm (TIFF 3454 kb)
359_2015_1043_MOESM9_ESM.docx
Supplemental Table 1 Gene specific primer sequences used to characterize opsin transcripts in the retina and nervous system of Procambarus clarkii (DOCX 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kingston, A.C.N., Cronin, T.W. Short- and long-wavelength-sensitive opsins are involved in photoreception both in the retina and throughout the central nervous system of crayfish. J Comp Physiol A 201, 1137–1145 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-1043-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-1043-2