Abstract
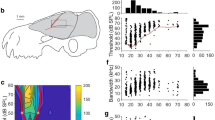
Target-distance computation by cortical neurons sensitive to echo delay is an essential characteristic of the auditory system of insectivorous bats. To assess if functional requirements such as detection of small insects versus larger stationary surfaces of plants are reflected in cortical properties, we compare delay-tuned neurons in a frugivorous (C. perspicillata, CP) and an insectivorous (P. parnellii, PP) bat species that belong to related families within the superfamily of Noctilionoidea. The bandwidth and shape of delay-tuning curves and the range of characteristic delays are similar in both species and hence are not related to different echolocation strategies. Most units respond at 2–6 ms echo delay with most sensitive thresholds of 20–30 dB SPL. In CP, units tuned to delays >12 ms are slightly more abundant and are more sensitive than in PP. All delay-tuned neurons in CP reliably respond to single pure-tone stimuli, whereas such responses are only observed in 49% of delay-tuned units in PP. The cortical representation of echo delay (chronotopy) covers a larger area in CP but is less precise than described in PP. Since chronotopy is absent in certain other insectivorous bat species, it is open if these differences in topography are related to echolocation behaviour.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel C, Kössl M (2009) Sensitive response to low-frequency cochlear distortion products in the auditory midbrain. J Neurophysiol 101:1560–1574
Dear PD, Simmons JR, Fritz J (1993a) A possible neuronal basis for representation of acoustic scenes in auditory cortex of the big brown bat. Nature 364:620–623
Dear PD, Fritz J, Haresign T, Ferragamo M, Simmons JR (1993b) Tonotopic and functional organization in the auditory cortex of the big brown bat, Eptesicus fuscus. J Neurophysiol 70:1988–2009
Edamatsu H, Suga N (1993) Differences in response properties of neurons between two delay-tuned areas in the auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Neurophysiol 69:1700–1712
Esser K-H, Eiermann A (1999) Tonotopic organization and parcellation of auditory cortex in the FM-bat Carollia perspicillata. Eur J Neurosci 11:3669–3682
Esser K-H, Eiermann A (2004) Processing of frequency-modulated sounds in the Carollia auditory and frontal cortex. In: Thomas JA, Moss CF, Vater M (eds) Echolocation in bats and dolphins. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 190–195
Esser K-H, Condon CJ, Suga N, Kanwal JS (1997) Syntax processing by auditory cortical neurons in the FM–FM area of the mustached bat Pteronotus parnellii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14019–14024
Feng AS, Simmons JA, Kick SA (1978) Echo detection and target-ranging neurons in the auditory system of the bat Eptesicus fuscus. Science 202:645–648
Fleming TH (1988) The short-tailed fruit bat. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Fleming TH (1991) The relationship between body size, diet, and habitat use in frugivorous bats, genus Carollia (Phyllostomidae). J Mammal 72:493–501
Hagemann C, Esser K-H, Kössl M (2010) A chronotopically organized target distance map in the auditory cortex of the short-tailed fruit bat. J Neurophysiol 103:322–333
Harris KD, Henze DA, Csicsvari J, Hirase H, Buzsáki G (2000) Accuracy of tetrode spike separation as determined by simultaneous intracellular and extracellular measurements. J Neurophysiol 84:401–414
Hoffmann S (2009) The auditory cortex of the bat Phyllostomus discolor: functional organization and processing of complex stimuli. Dissertation, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Hoffmann S, Schuller G, Firzlaff U (2010) Dynamic stimulation evokes spatially focused receptive fields in bat audtitory cortex. Eur J Neurosci. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.07051.x
Jones G, Teeling EC (2006) The evolution of echolocation in bats. Trends Ecol Evol 21:149–156
Lewicki MS (1998) A review of methods for spike sorting: the detection and classification of neural action potentials. Network 9:R53–R78
Mittmann DH, Wenstrup JJ (1995) Combination-sensitive neurons in the inferior colliculus. Hear Res 90:185–191
O’Neill WE (1995) The bat auditory cortex. In: Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Hearing of bats. Springer, New York, pp 416–480
O’Neill WE, Suga N (1979) Target range-sensitive neurons in the auditory cortex of the mustache bat. Science 203:69–73
O’Neill WE, Suga N (1982) Encoding of target range information and its representation in the auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Neurosci 2:17–31
Ohlemiller KK, Kanwal JS, Suga N (1996) Facilitative responses to species-specific calls in cortical FM–FM neurons of the mustached bat. Neuroreport 7:1749–1755
Portfors CV, Wenstrup JJ (1999) Delay-tuned neurons in the inferior colliculus of the mustache bat: implications for analyses of target distance. J Neurophysiol 82:1326–1338
Sanchez JT, Gans D, Wenstrup JJ (2008) Glycinergic “inhibition” mediates selective excitatory responses to combinations of sounds. J Neurosci 28:80–90
Sanderson MI, Simmons JA (2002) Selectivity for echo spectral interference and delay in the auditory cortex of the Big Brown Bat Eptesicus fuscus. J Neurophysiol 87:2823–2834
Schuller G, O’Neill WE, Radtke-Schuller S (1991) Facilitation and delay sensitivity of auditory cortex neurons in CF-FM bats, Rhinolophus rouxi and Pteronotus p. parnellii. Eur J Neurosci 3:1165–1181
Suga N, Horikawa J (1986) Multiple time axes for representation of echo delays in the auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Neurophysiol 55:776–805
Suga N, O’Neill WE (1979) Neural axis representing target range in the auditory cortex of the mustache bat. Science 206:351–353
Suga N, O’Neill WE, Kujiarai K, Manabe T (1983) Specificity of combination-sensitive neurons for processing of complex biosonar signals in auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Neurophysiol 49:1573–1626
Sullivan WE (1982) Neural representation of target distance in auditory cortex of the echolocating bat Myotis lucifugus. J Neurophysiol 48:1011–1032
Taniguchi I, Niwa H, Wong D, Suga N (1986) Response properties of FM–FM combination-sensitive neurons in the auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Comp Physiol A 159:331–337
Thies W, Kalko EKV, Schnitzler HU (1998) The roles of echolocation and olfaction in two Neotropical fruit-eating bats, Carollia perspicillata and C. castanea, feeding on Piper. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 42:397–409
Willig MR, Camilo GR, Noble SJ (1993) Dietary overlap in frugivorous and insectivorous bats from edaphic cerrado habitats of Brazil. J Mammal 74:117–128
Wong D, Shannon SL (1988) Functional zones in the auditory cortex of the echolocating bat, Myotis lucifugus. Brain Res 453:349–352
Wong D, Maekawa M, Tanaka H (1992) The effect of pulse repetition rate on the delay sensitivity of neurons in the auditory cortex of the FM bat, Myotis lucifugus. J Comp Physiol A 170:393–402
Acknowledgments
This study is dedicated to Gerhard Neuweiler. The work was supported by the DFG. We thank E. Mora and F. Coro for their support to catch adult PP in Cuba.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagemann, C., Vater, M. & Kössl, M. Comparison of properties of cortical echo delay-tuning in the short-tailed fruit bat and the mustached bat. J Comp Physiol A 197, 605–613 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-010-0530-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-010-0530-8