Abstract
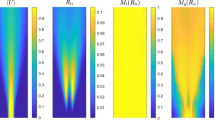
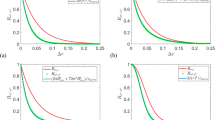
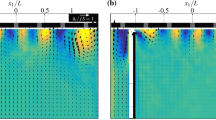
The phase-averaging window size is shown to affect the measurement of phase-averaged turbulence quantities in unsteady turbulent flows. The flow turbulence is usually estimated on the assumption of quasi-constant flow velocity during the duration of the phase-averaging window. The calculated turbulence level then consists of two parts: one due to the turbulent velocity fluctuations and the other due to the changes in the mean flow velocity. This second part is shown to be directly proportional to the averaging window size. In order to determine the true turbulence the averaging window size has to be made as small as possible, especially if the unsteady flow exhibits large temporal gradients and the flow turbulence itself is small.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 April 1996/Acceped: 17 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Eisele, K. & Hirt, F. The influence of phase-averaging window size on the determination of turbulence quantities in unsteady turbulent flows. Experiments in Fluids 22, 265–267 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050046
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050046