Abstract
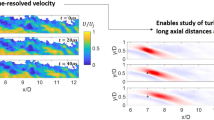
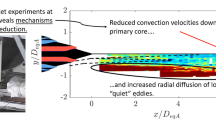
A novel point Doppler velocimeter (pDV) based upon the Doppler global velocimetry principle is presented, which is capable of three-component velocity vector measurements at 100 kHz mean rates over extended time periods. In this implementation, two laser beams are multiplexed to illuminate the flow over alternating time windows, providing for a reduction in the number of sensors required. The implications of this multiplexing paradigm coupled with the fundamental limits set by the optical absorption filter are examined in detail, and uncertainties are predicted via instrumentation modeling and representative synthetic flow data. The results indicate that the multiplexing pDV instrument provides the required temporal and velocity resolution for turbulent shear flows at velocities of nominally 500 m/s. As a demonstration and validation of this time-resolved technique, statistics of three-velocity component measurements in a cold, supersonic, over-expanded jet at jet exit Mach number M j = 1.4 (design Mach number M d = 1.65) are presented. Time resolution up to 250 kHz and instantaneous velocity uncertainties between 6.6 and 11.1 m/s were obtained. Comparisons of mean pDV data with laser Doppler velocimetry data are consistent with uncertainty predictions for the technique. The ultimate value of the instrument is exhibited in the analysis of Reynolds stress spectra in the screeching jet, exposing the spatial development of motions at the harmonics of the screech tone, variable phase-coordinated shock motions, and growth of turbulent fluctuations in the developing shear layer of the jet. From the data presented, the screech tone phenomenon is suspected to be linked to the production of radial–azimuthal shear stresses in extended regions beyond the potential core.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkislar MB, Krothapalli A, Lourenco LM (2003) Structure of a screeching rectangular jet: a stereoscopic particle image velocimetry study. J Fluid Mech 489:121–154
Benedict LH, Nobach H, Tropea C (2000) Estimation of turbulent velocity spectra from laser Doppler data. Meas Sci Technol 11(8):1089
Bridges JE, Wernet MP (2008) Turbulence associated with broadband shock noise in hot jets. NASA/TM-2008-215274
Brooks DR, Ecker T, Lowe KT, Ng WF (2014a) Experimental Reynolds stress spectra in hot supersonic round jets. AIAA SciTech (52nd Aerospace sciences meeting)
Brooks DR, Lowe KT (2014b) Fluctuating flow acceleration in a heated supersonic jet. In: Proceedings of the 17th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 7–10 July
Cadel DR, Ecker T, Lowe KT (2014a) Time-domain cross-correlation scan DGV (CCS-DGV) for mean-velocity boundary layer measurements. AIAA SciTech (52nd Aerospace sciences meeting)
Cadel DR, Ecker T, Lowe KT (2014b) Volumetric vector velocity measurements in a hot supersonic jet. In: Proceedings of the 17th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 7–10 July
Cavone AA, Meyers JF, Lee JW (2006) Development of point Doppler velocimetry for flow field investigations. In: Proceedings of the 13th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–29 June
Chan VSS, Heyes AL, Robinson DI, Turner JT (1995) Iodine absorption filters for Doppler global velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 6(6):784–794
Charrett TOH, Ford HD, Nobes DS, Tatam RP (2004) Two-frequency planar Doppler velocimetry (2v-PDV). Rev Sci Instrum 75:4487–4496
Charrett TOH, Nobes DS, Tatam RP (2007) Investigation into the selection of viewing configurations for three-component planar Doppler velocimetry measurements. Appl Opt 46(19):4102–4116
Clancy PS, Samimy M, Erskine WR (1999) Planar Doppler velocimetry: three-component velocimetry in supersonic jets. AIAA J 37(6):700–707
Coherent Inc. white paper, Wavelength control and locking with sub-MHz precision. http://www.coherent.com/download/6823/Wavelength-Control-and-Locking-with-Sub-MHz-Precision.pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2014
Ecker T, Lowe KT, Simpson RL (2012) Novel laser Doppler acceleration measurements of particle lag through a shock wave. In: 50th AIAA aerospace sciences meeting including the New Horizons forum and aerospace exposition
Ecker T, Lowe KT, Ng WF, Brooks DR (2014a) Fourth-order spectral statistics in the developing shear layers of hot supersonic jets. In: Propulsion and power (50th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference)
Ecker T, Brooks DR, Lowe KT, Ng WF (2014b) Spectral analysis of over-expanded cold jets via 3-component point Doppler velocimetry. AIAA Scitech (52nd Aerospace sciences meeting)
Edgington-Mitchell D, Oberleithner K, Honnery DR, Soria J (2014) Coherent structure and sound production in the helical mode of a screeching axisymmetric jet. J Fluid Mech 748:822–847
Elliott GS, Beutner TJ (1999) Molecular filter based planar Doppler velocimetry. Prog Aerosp Sci 35(8):799–845
Fischer M, Heinze J, Matthias K, Röhle I (2000) Doppler global velocimetry in flames using a newly developed, frequency stabilized, tunable, long pulse Nd: YAG laser. In: Proceedings of the 10th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–13 July
Fischer A, Büttner L, Czarske J, Eggert M, Grosche G, Müller H (2007) Investigation of time-resolved single detector Doppler global velocimetry using sinusoidal laser frequency modulation. Meas Sci Technol 18(8):2529–2545
Fischer A, Büttner L, Czarske J, Eggert M, Müller H (2008) Measurement uncertainty and temporal resolution of Doppler global velocimetry using laser frequency modulation. Appl Opt 47(21):3941–3953
Fischer A, Pfister T, Czarske J (2010) Derivation and comparison of fundamental uncertainty limits for laser-two-focus velocimetry, laser Doppler anemometry and Doppler global velocimetry. Measurement 43:1556–1574
Fischer A, Büttner L, Czarske J (2011) Simultaneous measurements of multiple flow velocity components using frequency modulated lasers and a single molecular absorption cell. Opt Commun 284:3060–3064. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2011.02.070
Fischer A, König J, Haufe D, Schlüßler R, Büttner L, Czarske J (2013) Optical multi-point measurements of the acoustic particle velocity with frequency modulated Doppler global velocimetry. J Acoust Soc Am 134(2):1102–1111
Forkey JN (1996) Development and demonstration of filtered Rayleigh scattering: a laser based flow diagnostic for planar measurement of velocity, temperature and pressure. PhD Thesis, Princeton University
Forkey JN, Lempert WR, Miles RB (1997) Corrected and calibrated I2 absorption model at frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser wavelengths. Appl Opt AO 36:6729–6738
Freund JB, Lele SK, Moin P (2000) Compressibility effects in a turbulent annular mixing layer: part 1. Turbulence and growth rate. J Fluid Mech 421:229–267
Fussell J (2003) Refinement and verification of the Virginia Tech Doppler global velocimeter (DGV). MS Thesis, Virginia Tech
Jones T (2001) Development and testing of the Virginia Tech Doppler global velocimeter (DGV). MS Thesis, Virginia Tech
Komine H (1990) US Patent No. 4,919,536. U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, Washington, DC
Komine H, Brosnan SJ, Litton AB, Stappaerts EA (1991) Real-time, Doppler global velocimetry. In: 29 h AIAA aerospace sciences meeting
Kuhlman J, Collins P, Scarberry T (2001) Two-component point Doppler velocimetry data in circular jets. Meas Sci Technol 12(4):395–408
Lau JC, Morris PJ, Fisher MJ (1979) Measurements in subsonic and supersonic free jets using a laser velocimeter. J Fluid Mech 93:1–27
Lighthill MJ (1952) On sound generated aerodynamically. I. General theory. In: Proceedings of the royal society A: mathematical, physical and engineering sciences, vol 211, pp 564–587
Lowe KT, Ng WF, Ecker T (2012) Early development of time-resolved volumetric Doppler velocimetry for new insights in hot supersonic jet noise. In: 18th AIAA/CEAS aeroacoustics conference (33rd AIAA aeroacoustics conference)
Meyers JF, Komine H (1991) Doppler global velocimetry: a new way to look at velocity. Laser Anemometry 1:289–296
Meyers J, Lee J (2010) Boundary layer measurements in a supersonic wind tunnel using Doppler global velocimetry. In: Proceedings of the 15th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 05–08 July
Meyers JF, Lee JW, Schwartz RJ (2001) Characterization of measurement error sources in Doppler global velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 12:357–368
Müller H, Lehmacher T, Grosche G (1999). Profile sensor based on Doppler global velocimetry. In 8th International conference laser anemometry advances and applications, pp 475–482
Nobes DS, Ford HD, Tatam RP (2004) Instantaneous, three-component planar Doppler velocimetry using imaging fibre bundles. Exp Fluids 36(1):3–10
Pope SB (2000) Turbulent flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Powell A (1953) On the mechanism of choked jet noise. Proc Phys Soc Lond Sect B 66(12):1039
Powers RW, McLaughlin DK (2012) Acoustic measurements of scale models of military style supersonic beveled nozzle jets with interior corrugations. In: AIAA Paper, 2116, 18th AIAA/CEAS aeroacoustics conference (33rd AIAA aeroacoustics conference)
Reinath MS (1997) Doppler Global velocimeter development for the large wind tunnels at Ames Research Center. NASA TM 112210
Smith MW (1998) Application of a planar Doppler velocimetry system to a high Reynolds number compressible jet. In: Presented at the 36th AIAA aerospace sciences meeting and exhibit, Reno, NV
Tam CK (1995) Supersonic jet noise. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 27(1):17–43
Thurow BS, Lynch KP (2009) Development of a high-speed three-dimensional flow visualization technique. AIAA J 47(12):2857–2865
Thurow BS, Jiang N, Lempert WR, Samimy M (2005) Development of megahertz-rate planar Doppler velocimetry for high speed flows. AIAA J 43(3):500–511
Tropea C, Yarin AL, Foss JF (eds) (2007) Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics, vol 1. Springer, Berlin
Umeda Y, Ishii R (2001) On the sound sources of screech tones radiated from choked circular jets. J Acoust Soc Am 110(4):1845–1858
Wernet MP (2007) Temporally resolved PIV for space–time correlations in both cold and hot jet flows. Meas Sci Technol 18(5):1387
Acknowledgments
The work described was supported by the Office of Naval Research Hot Jet Noise Reduction Basic Research Challenge and DURIP, Grants N00014-11-1-0754 and N00014-12-1-0803 under program managers Drs. Brenda Henderson and Joseph Doychak.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ecker, T., Brooks, D.R., Lowe, K.T. et al. Development and application of a point Doppler velocimeter featuring two-beam multiplexing for time-resolved measurements of high-speed flow. Exp Fluids 55, 1819 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1819-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1819-0