Abstract
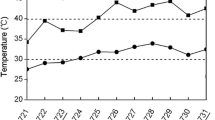
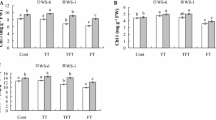
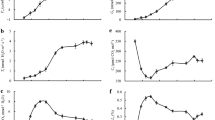
In this study, two herbaceous peony cultivars with different heat tolerances (‘Fenyunu’ FYN low sensitivity and ‘Qiaoling’ QL high sensitivity) were used as research materials. An integrated view of the factors underlying the decrease in photosynthetic rate under high-temperature (HT) stress was provided by analyzing the biochemical parameters, chloroplast ultrastructure, gas-exchange parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence, and modulated 820 nm reflection of herbaceous peony leaves. The results showed that hydrogen peroxide, superoxide anion, malondialdehyde, and electrical conductivity increased significantly, while the photosynthetic pigments content and photosynthetic capacity decreased significantly in QL than in FYN under HT. The contents of soluble sugars and proline increased greatly in FYN than in QL, while the activity of SOD decreased markedly in QL than in FYN after HT. Compared with FYN, the ultrastructure of QL was more seriously disrupted under HT. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis showed that HT changed the shapes of OJIP curve, resulting in the increase of K phase and J phase. The PSII acceptor side was more damaged than the donor side, and the electron transfer was seriously blocked. The energy flow in the process of light energy absorption, capture, and electron transfer were significantly changed after HT stress. Meanwhile, PSI was also significantly inhibited, and the coordination of both photosystems decreased. The variation of these parameters in FYN was less than that in QL. These results suggested that FYN featured a more heat-tolerance ability as evidenced by the good performances on the antioxidant system, osmoregulatory capacity, and the thermostability of membranes and photosystems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Brestic M, Zivcak M, Kunderlikova K, Allakhverdiev SI (2016) High temperature specifically affects the photoprotective responses of chlorophyll b-deficient wheat mutant lines. Photosynth Res 130:251–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0249-7
Cai HL, Xie PF, Zeng WA, Zhai ZG, Zhou W, Tang Z (2019) Root-specific expression of rice OsHMA3 reduces shoot cadmium accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Mol Breeding 39:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-0964-9
Chalanika De Silva HC, Asaeda T (2017) Effects of heat stress on growth, photosynthetic pigments, oxidative damage and competitive capacity of three submerged macrophytes. J Plant Interact 12:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2017.1322153
Chang QS, Zhang LX, Hou XG, Wang Z, Wang N, Gong MG, Zhang QM, Chen H, Shi ZQ, Deng CC (2019) The anatomical, physiological and molecular analysis of a chlorophyll-deficient mutant in tree peony (Paeonia Suffruticosa). Photosynthetica 57(3):724–730
Chen J, Burke JJ, Xin Z (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis revealed essential roles of FtsH11 protease in regulation of the adaptive responses of photosynthetic systems to high temperature. BMC Plant Biol 18:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1228-2
Cruz JA, Avenson TJ (2021) Photosynthesis: a multiscopic view. J Plant Res 134:665–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-021-01321-4
Djanaguiraman M, Boyle DL, Welti R, Jagadish SVK, Prasad PVV (2018) Decreased photosynthetic rate under high temperature in wheat is due to lipid desaturation, oxidation, acylation, and damage of organelles. BMC Plant Biol 18:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1263-z
Dogru A (2021) Effects of heat stress on photosystem II activity and antioxidant enzymes in two maize cultivars. Planta 253:85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03611-6
Dong F, Wang CZ, Sun XD, Bao ZL, Dong C, Sun CH, Ren YQ, Liu SQ (2019) Sugar metabolic changes in protein expression associated with different light quality combinations in tomato fruit. Plant Growth Regul 88:267–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00506-1
Feng B, Liu P, Li G, Dong ST, Wang FH, Kong LA, Zhang JW (2014) Effect of heat stress on the photosynthetic characteristics in flag leaves at the grain-filling stage of different heat-resistant winter wheat varieties. J Agron Crop Sci 200:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12045
Hao ZJ, Zhou CH, Liu D, Wei MR, Tao J (2017) Effects of high temperature stress on photosynthesi, chlorophyll fluorescence and ultrastructure of herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Mol Plant Breeding 15:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.08.001
Hao LH, Guo LL, Li RQ, Cheng Y, Huang L, Zhou HR, Xu M, Li F, Zhang XX, Zheng YP (2019) Responses of photosynthesis to high temperature stress associated with changes in leaf structure and biochemistry of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Sci Hortic 246:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.11.007
Hegde S, Umekawa Y, Watanabe E, Kasajima I (2020) High-Temperature Tolerance of Flowers. In: Hasanuzzaman M (ed) Plant Ecophysiology and Adaptation under Climate Change: Mechanisms and Perspectives I. Springer, Singapore
IPCC (2021) Intergovernmental panel on climate change. www.ipcc.ch/. Accessed 7 Aug 2021
Ivanov AG, Velitchkova MY, Allakhverdiev SI, Huner NPA, Tomo T, Allakhverdiev SI (2017) Heat stress-induced effects of photosystem I: an overview of structural and functional responses. Photosynthesis Res 133:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-017-0383-x
Johal N, Kaur J, Grewal SK, Singh S, Kushwah A (2020) Physiological and biochemical responses of chickpea accessions at reproductive stage under receding moisture conditions. Agric Res 9:554–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-020-00466-3
Kalaji MH, Govindjee BK, Koscielniak J, Golaszewska KZ (2011) Effects of salt stress on photosystem II efficiency and CO2 assimilation of two Syrian barley landraces. Environ Exp Bot 73:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.10.009
Karkute SG, Ansari WA, Singh AK, Singh PM, Rai N, Bahadur A, Singh J (2021) Characterization of high-temperature stress-tolerant tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L) genotypes by biochemical analysis and expression profiling of heat-responsive genes. Biotech 11:45
Kohila S, Gomathi R (2018) Adaptive physiological and biochemical response of sugarcane genotypes to high-temperature stress. Indian J Plant Physiol 23:245–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0363-y
Kumar P, Yadav S, Singh MP (2020) Possible involvement of xanthophyll cycle pigments in heat tolerance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Pla 26:1773–1785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00870-7
Li G, Gao HY, Zhao B, Dong ST, Zhang JW, Yang JS, Wang JF, Liu P (2009) Effects of drought stress on activity of photosystems in leaves of maize at grain filling stage. Acta Agron Sin 35:1916–1922. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2009.01916
Li G, Gao HY, Liu P, Yang JS, Dong ST, Zhang JW, Wang JF (2010) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on photosynthetic performance in maize leaf at grain filling stage. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 16:536–542. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.37-38.1549
Li XN, Brestic M, Tan DX, Zivcak M, Zhu XC, Liu SQ, Song FB, Reiter RJ, Liu FL (2018) Melatonin alleviates low PS I-limited carbon assimilation under elevated CO2 and enhances the cold tolerance of offspring in chlorophyll b-deficient mutant wheat. J Pineal Res 64:e12453. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12453
Li YT, Xu WW, Ren BZ, Zhao B, Zhang JW, Liu P, Zhang ZS (2020) High temperature reduces photosynthesis in maize leaves by damaging chloroplast ultrastructure and photosystem II. J Agron Crop Sci 206:548–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12401
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Lin XH, Shi MT, Lin SM (2014) Effects of high-temperature stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, sod activity and electrolyte leakage of Anoectochilus Roxburghii (wall) lindl and Anoectochilus Formosanus hayata. Chin J Tropical Crops 35:1137–1142
Liu M, Fang YL (2020) Effects of heat stress on physiological indexes and ultrastructure of grapevines. Sci Agri Sin 53:1444–1458. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.07.013
Liu G, Cai HY, Jia HT, Zhang S, Jiao CH (2021) Physiological basis of heat tolerance of African rice germplasm SDWG005 at seedling stage. J Plant Genetic Resources 22:646–653
Liu J, Wang YS (2020) Proline metabolism and molecular cloning of Am P5CS in the mangrove Avicennia marina under heat stress. Ecotoxicology 29:698–706
Liu AR, Wang MM, Liu DL, Chang R, Wang ZH, Lin XM, Bai B, Chen SC, Ahammed GJ (2016) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus alleviates chilling stress by boosting redox poise and antioxidant potential of tomato seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 35:109–120
Liu QQ, Ma SB, Feng XH, Sun Y, Yi YJ, Liu WX (2016) Effects of grafting on the fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction dynamics of pepper seedlings under temperature stress. Acta Hortic Sin 43:885–896
Luo HB, Ma L, Duan W, Li SH, Wang LJ (2010) Influence of heat stress on photosynthesis in Vitis vinifera L. cv. cabernet sauvignon. Sci Agri Sin 43:2744–2750
Lv CP, Liu LY (2008) Effects of high temperature on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Paeonia lactiflora. J Hunan Agri Univ (Nat Sci) 34:664–667
Ma DD, Li YF, Fu HF (2020) Effect of high temperature on the balance between photosynthetic light absorption and energy utilization in Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorophyceae). J Oceanol Limnol 38:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8369-5
Mathur S, Jajoo A, Mehta P, Bharti S (2011) Analysis of elevated temperature-induced inhibition of photosystem II using chlorophyll a fluorescence induction kinetics in wheat leaves (Triticum aestivum). Plant Biol 13:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00319.x
Mathur S, Mehta P, Jajoo A (2013) Effects of dual stress (high salt and high temperature) on the photochemical efficiency of wheat leaves (Triticum aestivum). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-012-0151-5
Meravi N, Prajapati SK (2018) Temporal variation in chlorophyll fluorescence of different tree species. Biol Rhythm Res 49:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/09291016.2018.1528694
Ohmiya A, Hirashima M, Yagi M, Tanase K, Yamamizo C (2014) Identification of genes associated with chlorophyll accumulation in flower petals. PLoS ONE 9:e113738. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113738
Rai KK, Rai N, Rai SP (2018) Investigating the impact of high temperature on growth and yield of Lablab purpureus L. inbred lines using integrated phenotypical, physiological, biochemical and molecular approaches. Indian J Plant Physiol 23:209–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0364-x
Rintamaki E, Kettunen R, Aro EM (1996) Differential D1 dephosphorylation in functional and photodamaged photosystem II centers. J Biol Chem 271:14870–14875. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.25.14870
Ruelland E, Zachowski A (2010) How plants sense temperature. Environ Exp Bot 69:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.05.011
Siddiqui SA, Khatri K, Patel D, Rathore MS (2021) Photosynthetic gas exchange and chlorophyll a fluorescence in Salicornia brachiata (Roxb) under osmotic stress. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10311-8
Strasser BJ (1997) Donor side capacity of Photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients. Photosynthesis Res 52:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005896029778
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Michael M, Qiang S, Goltsev V (2010) Simultaneous in vivo recording of prompt and delayed fluorescence and 820-nm reflection changes during drying and after rehydration of the resurrection plant Haberlea rhodopensis. BBA-Biomembranes 1797:1313–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.03.008
Sun BJ, Li ZX, Luo SB, Li ZL, Liang ZQ (2010) Effects of continuous heat stress on several physiological indexes of eggplant seedlings. Chin J Tropical Crops 31:1528–1534. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2010.09.018
Sun YJ, Fu YD, Du YP, Zhai H (2013) Effects of different temperature and light treatments on photosynthetic system ii in Vitis Vinifera L. cv. cabernet sauvignon. Sci Agric Sin 46:1191–1200. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.06.012
Sun YJ, Liu XH, Zhai H, Gao HY, Yao YX, Du YP (2016) Responses of photosystem II photochemistry and the alternative oxidase pathway to heat stress in grape leaves. Acta Physiol Plant 38:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2235-2
Sun YJ, Du YP, Zhai H (2014) Effects of different light intensity on PSII activity and recovery of Vitis Vinifera cv. cabernet sauvignon leaves under high temperature stress. Plant Physiol J 50:1209–1215
Szabados L, Savoure A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends in Plant Sci 15:89–97
Tan SL, Yang YJ, Huang W (2020) Moderate heat stress accelerates photoinhibition of photosystem I under fluctuating light in tobacco young leaves. Photosynth Res 144:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.11.009
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-reated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Vuleta A, Manitašević JS, Tucić B (2016) Adaptive flexibility of enzymatic antioxidants SOD, APX and CAT to high light stress: The clonal perennial monocot Iris pumila as a study case. Plant Physiol Bioch 100:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.01.011
Wang QL, Chen JH, He NY, Guo FQ (2018) Metabolic reprogramming in chloroplasts under heat stress in plants. Int J Mol Sci 19:849–870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030849
Wang RM, Xiong XY (2016) Effect of temperature stress on growth and metabolism in perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 25:81–90
Wei ZQ, Lv MJ, Wan W, Yu F, Cao XY, Meng LS (2019) Transformation of eIF5B1 gene into Chrysanthemum to gain calluses of high temperature tolerance. Biologia 74:1271–1277. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00312-0
Wu DC, Zhu JF, Shu ZZ, Wang W, Yan C, Xu SB, Wu DX, Wang CY, Dong ZR, Sun GL (2020) Physiological and transcriptional response to heat stress in heat-resistant and heat-sensitive maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines at seedling stage. Protoplasma 257:1615–1637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-020-01538-5
Yuan QL, Yu XN (2011) Flower culture of peony and chinese herbaceous peony with landscape garden in China. J Beijing Forestry Univ (Social Sci) 10:53–57
Zhang ZS, Jia YJ, Gao HY, Zhang LT, Li HD, Meng QW (2011) Characterization of PSI recovery after chilling-induced photoinhibition in cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.). Planta 234:883–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1447-3
Zhang ZS, Liu MJ, Scheibe R, Selinski J, Zhang LT, Yang C, Meng XL, Gao HY (2017) Contribution of the alternative respiratory pathway to psii photoprotection in C3 and C4 Plants. Mol Plant 10:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.10.004
Zhang HL, Marian B, Katarina O, Li G, Meng QW, Yang XH (2015) Photochemical activity and energy distribution on wheat varieties with different heat-sensitivity under high temperature stress. Plant Physiol J 51:1142–1150
Zhang JP, Li DQ, Nie JJ, Xia YP (2016) Physiological and biochemical responses to the high temperature stress and heat resistance evaluation of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. Cultivars. J Nucl Agr Sci 30:1848–1856
Zhang HH, Long JH, Wang RJ, Ru XY, Ma SL, Ning Q, Xu N (2019) Effects of different salt stress conditions on growth of sorghum seedlings and function of leaf photosynthetic apparatus. Chin J Ecol 38:161–172
Zhang LX, Chang QS, Hou XG, Chen SD, Zhang QM, Wang JZ, Liu SS, Li S (2021) Biochemical and photosystem characteristics of wild-type and Chl b-deficient mutant in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Photosynthetica 59:256–265
Zhao DQ, Han CX, Tao J (2015) Heat tolerance identification of different herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) cultivars. J Yangzhou Univ (Agri and Life Sci Edition) 36:105–109
Zou MQ, Yuan LY, Zhu SD, Liu S, Ge JT, Wang CG (2017) Effects of heat stress on photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure of a heat-sensitive and heat-tolerant cultivar of wucai (Brassica campestris L.). Acta Physiol Plant 39:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2319-z
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Henan Province (212102110475, 202102110232), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (182300410082), National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1804233, 31870093, 31800096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LXZ, conducted experiments, wrote and revised the manuscript; QSC, conducted experiments, wrote the manuscript; XGH conceived and designed research; JZW, SDC, QMZ, ZW, YY analyzed data, JKL helped and processed the ultrastructural pictures. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest and competing interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vijay Pratap Singh.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Chang, Q., Hou, X. et al. The Effect of High-Temperature Stress on the Physiological Indexes, Chloroplast Ultrastructure, and Photosystems of two Herbaceous Peony Cultivars. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 1631–1646 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10647-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10647-9