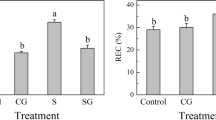
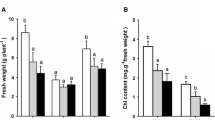
Abstract
Salt stress is the main factor limiting plant growth. Researches on physiological and biochemical mechanisms of plant responses to salt stress are of great significance in exploring and improving plant salinity tolerance. Gladiolus gandavensis is an ornamental plant with beautiful flowers and good adversity adaptability that is native to the southeastern coast of China. The purpose of this study was to identify the salt tolerance level of G. gandavensis and explore the mechanism by which exogenous spermidine (Spd) adjusts the growth of G. gandavensis under different NaCl conditions. A pot experiment was conducted to examine the chlorophyll content, photosynthetic parameters, proline, reactive oxygen species (ROS) concentrations, antioxidant activities, and relative expression of the chlorophyll a/b response protein, CAT1, POD, MnSODM, P5CS, BADH genes and bZIP, DREB transcription factors in G. gandavensis seedlings under 0.3%, 0.6%, and 0.9% NaCl conditions, with and without 0.1 mmol·L−1 Spd. G. gandavensis seedlings exhibited reduced chlorophyll content; a decreased net photosynthetic rate (Pn); and increased relative electric conductivity (REC), malondialdehyde (MDA), proline and soluble protein contents, antioxidant activities, and relative expression of the CAT1, POD, MnSODM, P5CS, and BADH genes under 0.3%, 0.6%, and 0.9% NaCl conditions. And Spd spraying under 0.3% and 0.6% salt treatment reduced the decrease in chla content by approximately 55.2% and 23.4%, while increased Pn, proline content and the expression of CAT1, POD, MnSODM, P5CS, and BADH genes. Exogenously applied Spd effectively alleviated the damage caused by salt stress (0.3% and 0.6%) by upregulating the REC, proline content, gas exchange, antioxidant enzyme activity, and expression of CAT1, POD, MnSODM, P5CS, and BADH genes in G. gandavensis seedlings. However, when the seedlings were grown under 0.9% NaCl, no significant differences were found in the physiological and molecular responses between Spd-treated and non-Spd-treated plants. Therefore, the present study suggests that exogenous Spd can efficiently counteract the adverse effect of low (0.3%) and moderate (0.6%) salt stress on G. gandavensis seedlings.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in the NCBI BankIt repository under ID PRJNA523989. (Note: The database has been uploaded, and the content will be made available at the time of publication of this manuscript.)
Abbreviations
- PAs:
-
Polyamines
- Spm:
-
Spermine
- Spd:
-
Spermidine
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- REC:
-
Relative electric conductivity
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Put:
-
Putrescine
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- PPFD:
-
Photosynthetic photon flux density
- RH:
-
Relative humidity
- H2O2 :
-
Peroxide
- O2 − :
-
Superoxide anion
- PVP:
-
Polyethylene pyrrole
- Pn:
-
Net photosynthetic rate
- Tr:
-
Transpiration rate
- Gs:
-
Stomatal conductance
- Ci:
-
Intercellular CO2 concentration
- P5CS:
-
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase
- BADH:
-
Betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase
- DREB:
-
Dehydration-responsive element binding
- bZIP:
-
Basic leucine zipper
References
Abd El Wahed MA, Gamal El Din KM (2004) Stimulation effect of spermidine and stigmasterol on growth, lowering, biochemical constituents and essential oil of chamomile plant (Chamomilla recutita L., Rausch). Bulg J Plant Physiol 30:48–60
Ahmad P, Sarwat M, Sharma S (2008) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants and signaling in plants. J Plant Biol 51(3):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030694
Ahmad P, Jeleel CA, Azooz MM, Nabi G (2009) Generation of ROS and non-enzymatic antioxidants during abiotic stress in Plants. Bot Res Int 2(1):11–20
Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 53:1331–1341. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1331
Ashraf M, Harris P (2004) Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci Plant Sci 166(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.10.024
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680590910410
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Causin HF, Bordón DAE, Burrieza H (2020) Salinity tolerance mechanisms during germination and early seedling growth in Chenopodium quinoa Wild. Genotypes with different sensitivity to saline stress. Environ Exp Bot 172:103995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.103995
Chen THH, Murata N (2011) Glycinebetaine protects plants against abiotic stress: mechanisms and biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Environ 34:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02232.x
Chen LF, Lu W, Sun J, Guo SR, Zhang ZX, Yang YJ (2011) Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis and carbohydrate accumulation in roots and leaves of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings under salt stress. J Nanjing Agric Univ 34(3):31–36
Chunthaburee S, Sanitchon J, Pattanagul W, Theerakulpisut P (2015) (2015) Application of exogenous spermidine (Spd) improved salt tolerance of rice at the seedling and reproductive stages. Proc Environ Sci 29:134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2015.07.224
Cui JQ, Hua YP, Zhou T, Liu Y, Huang JY, Yue CP (2020) Global landscapes of the Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX) family members uncover their potential roles in regulating the rapeseed resistance to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103429
Deshmukh PS, Sairam RK, Shukla DS (1991) Measurement of ion leakage as a screening technique for drought resistance in wheat genotypes. Indian J Plant Physiol 35:89–911
Díaz-Vivancos P, Clemente-Moreno MJ, Rubio M, Olmos E, García JA, Martínez-Gómez P et al (2008) Alteration in the chloroplastic metabolism leads to ROS accumulation in pea plants in response to plum pox virus. J Exp Bot 59:2147–2160. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern082
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra SMA (2009) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2666-8_12
Gao L, Ma Y, Wang P et al (2017) Transcriptome profiling of Clematis apiifolia: insights into heat-stress responses. DNA Cell Biol 36(11):938. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.3850
Giannopotitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gorham EJ, McDonnel E, Budrewicz RG (1985) Wyn Jones, Salt tolerance in the Triticeae: growth and solute accumulation in leaves of Thinopyrum bessarabicum. J Exp Bot 36:1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/36.7.1021
Grumet R, Hanson AD (1986) Genetic evidence for an osmoregulatory function of glycinebetaine accumulation in barley. Funct Plant Biol 13(3):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9860353
Guidi L, Tonini M, Soldatini GF (2000) Effects of high light and ozone fumigation on photosynthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 38:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0981-9428(00)01172-4
Hajiboland R, Ebrahimi N (2011) Effect of exposure to UV radiation on growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant defense system in tobacco (Nicotiana rustica L. cv. Basmas) plants treated with exogenous polyamines. Genet Plant Physiol 1:76–90
Handa AK, Mattoo AK (2010) Differential and functional interactions emphasize the multiple roles of polyamines in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.02.009
Hasegawa PM (2013) Sodium (Na+) homeostasis and salt tolerance of plants. Environ Exp Bot 92(8):19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.03.001
Hmida-Sayari A, Gargouri-Bouzid R, Bidani A, Jaoua L, Savoure A, Jaoua S (2005) Overexpression of delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers salt tolerance in transgenic potato plants. Plant Sci 169:746–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.05.025
Hossain Z, Mandal AK, Kumar DS et al (2006) Decline in ascorbate peroxidase activity—a prerequisite factor for tepal senescence in gladiolus. J Plant Physiol 163(2):186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2005.03.004
Hurkman WJ, Fornari CS, Tanaka CK (1989) A comparison of the effect of salt on polypeptide and translatable mRNA in roots of a salt tolerant and salt sensitive cultivar of barley. Plant Physiol 90:1444–1456. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.90.4.1444
Hussain SS, Ali M, Ahmad M, Siddique KHM (2011) Polyamines: natural and engineered abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Biotechnol Adv 29:300–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.01.003
Khan MIR, Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan NA (2012) Variation in salt tolerance of wheat cultivars: role of glycinebetaine and ethylene. Pedosphere 22:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(12)60060-5
Khavarinejad RA, Chaparzadeh N (1998) The effects of NaCl and CaCl2 on photosynthesis and growth of alfalfa plants. Photosynthetica 35:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:100692872
Kishore B, Hong Z, Miao G, Hu C, Verma D (1995) Over expression of delta-pyrroline-5-carboxylatesynthetase increase proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 108:1387–1394
Koval VS, Koval SF (1996) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in barley-identification of number of genes. Genetica 32:1098–1103
Legocka J, Zajchert I (1999) Role of spermidine in the stabilization of the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-protein complex of photo-system II during leaf senescence process. Acta Physiol Plant 21:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-999-0066-0
Levitt J (1980) Responses of plants to environmental stresses, water, radiation, salt and other stresses, vol 2. Academic Press, New York
Li T, Hu YY, Du XH, Tang H, Shen CH, Wu JS (2014) Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress in Torreya grandis cv. Merrillii seedlings by activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant systems. PLoS ONE 9(10):e109492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109492
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) [34] Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Ma XL, Wang YJ, Xie SL, Wang C, Wang W (2007) Glycine-betaine application ameliorates negative effects of drought stress in tobacco. Russ J Plant Physiol 54:472–479. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707040061
Ma X, Song L, Yu W et al (2015) Growth, physiological, and biochemical responses of Camptotheca acuminata seedlings to different light environments. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00321
Ma X, Zheng J, Zhang X et al (2017) Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress on Dianthus superbus (Caryophyllaceae) by activating photosynthesis, protecting morphological structure, and enhancing the antioxidant system. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00600
Mansour MMF (2000) Nitrogen containing compounds and adaptation of plants to salinity stress. Biol Plant 43:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:100287353
Minocha R, Majumdar R, Minocha SC (2014) Polyamines and abioti stress in plants: a complex relationship. Front Plant Sci 5:175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00175
Misra N, Saxena P (2009) Effect of salicylic acid on proline metabolism in lentil grown under salinity stress. Plant Sci 177(3):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.05.007
Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M, Tal M (2000) Activities of SOD and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle enzymes in sub-cellular compartments in leaves and roots of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii. Physiol Plant 110:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2000.110106.x
Montero E, Cabot C, Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C (1997) Endogenous abscisic acid levels are linked to decreased growth of bush bean plants treated with NaCl. Physiol Plant 101:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01814.x
Munns R (2010) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant, Cell Environ 25(2):239–250. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0016-8025.2001.00808.x
Mustafavi SH, Badi HN, Sękara A et al (2018) Polyamines and their possible mechanisms involved in plant physiological processes and elicitation of secondary metabolites. Acta Physiol Plant 40(6):102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2671-2
Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Rahman A, Alam Md. M, Mahmud J-A, Suzuki T, Fujita M (2016) Polyamines confer salt tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) by reducing sodium uptake, improving nutrient homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Front Plant Sci 7:1104. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01104
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Syeed S, Khan NA (2011) Salicylic acid alleviates decreases in photosynthesis under salt stress by enhancing nitrogen and sulfur assimilation and antioxidant metabolism differentially in two mungbean cultivars. J Plant Physiol 168:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.11.001
Orabi SA, Talaat IM, Balbaa LK, Abdalla AE (2015) Inluence of pyridoxine and spermine on lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) plants. Nusantara Biosci 7:139–143. https://doi.org/10.13057/nusbiosci/n070213
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60:324–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Ecoenv.2004.06.010
Parvin S, Lee OR, Sathiyaraj G, Khorolragchaa A, Kim YJ, Yang DC (2014) Spermidine alleviates the growth of saline-stressed ginseng seedlings through antioxidative defense system. Genetics 53:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.021
Patra SK, Mohanty CR (2015) Genetic divergence study in gladiolus. Int J Agric Sci Res 3(2):356.
Patterson BD, MacRae EA, Ferguson IB (1984) Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium (IV). Anal Biochem 139:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(84)90039-3
Qasim M, Ashraf M, Jamil MA, Ashraf MY, Ur-Rehman S, Rha ES (2003) Water relations and leaf gas exchange properties in some elite canola (Brassica napus) lines under salt stress. Ann Appl Biol 142:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00255.x
Rao KVM, Raghavendra AS, Janardhan Reddy K (eds) (2006) Physiology and molecular biology of stress tolerance in plants. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Rasool S, Hameed A, Azooz MM et al (2013) Salt stress: causes, types and responses of plants[M]//ecophysiology and responses of plants under salt stress. Springer, New York, pp 1–24
Rhodes D, Rich PJ, Brunk DG, Ju GC, Rhodes JC, Pauly MH, Hansen LA (1989) Development of two isogenic sweet corn hybrids differing for glycinebetaine content. Plant Physiol 91:1112–1121. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.91.3.1112
Roussos P, Gasparatos D, Kyriakou C, Tsichli K, Tsantili E, Haidouti C (2013) Growth, nutrient status and biochemical changes in sour orange (Citrus aurantium L.) plants subjected to sodium chloride stress. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 44:805–816
Savouré A, Thorin D, Davey M, Hua XJ, Mauro S, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Verbruggen N (1999) NaCl and CuSO4 treatments trigger distinct oxidative defense mechanism in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia L. Plant Cell Environ 22:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00404.x
Seraini-Fracasini D, Di Sandro A, Del Duca S (2010) Spermine delays leaf senescence in Lactuca sativa and prevents the decay of chloroplast photosystems. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.03.005
Shen C, Hu Y, Du X et al (2014) Salicylic acid induces physiological and biochemical changes in Torreya grandis, cv. Merrillii, seedlings under drought stress. Trees 28(4):961–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1009-y
Shi H, Chan Z (2014) Improvement of plant abiotic stress tolerance through modulation of the polyamine pathway. J Integr Plant Biol 40:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12128
Shi R, Cao Y, Guo P, et al (2008) Effect of salt stress on the photosynthetic properties and osmotic adjustment ability in Vicia faba L rain fed crops, 2008(005):312–315. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-0896.2008.05.013(in Chinese)
Shu S, Guo SR, Yuan LY (2012) A review: polyamines and photosynthesis. In: Advances in photosynthesis—fundamental aspects. InTech, Rijeka, edited by Mohammad Najafpour, ISBN: 978-953-307-928-8, pp. 439–464. https://doi.org/10.5772/1385
Silva-Ortega CO, Ochoa-Alfaro AE, Reyes-Agüero JA, Aguado-Santacruz GA, Jiménez-Bremont JF (2008) Salt stress increases the expression of p5cs gene and induces proline accumulation in cactus pear. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2007.10.011
Singh NK, Bracken CA, Hasegawa PM, Handa AK, Buckel S, Hermodson MA, Pfankoch F, Regnier FE, Bressan RA (1987) Characterization of osmotin. A thaumatin-like protein associ-ated with osmotic adjustment in plant cells. Plant Physiol 85:529–536. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.85.2.529
Takahashi T, Kakehi J (2010) Polyamines: ubiquitous polycations with unique roles in growth and stress responses. Ann Bot 105:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp259
Tang H, Hu YY, Yu WW, Song LL, Wu JS (2015) Growth, photosynthetic and physiological responses of Torreya grandis seedlings to varied light environments. Trees 29(4):1011–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1180-9
Tavladoraki P, Cona A, Federico R, Tempera G, Viceconte N, Saccoccio S, Battaglia V, Toninello A, Agostinelli E (2012) Polyamine catabolism: target for antiproliferative therapies in animals and stress tolerance strategies in plants. Amino Acids 42:411–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1012-1
Thomas RL, Jen JJ, Morr CV (1982) Changes in soluble and bound peroxidase-IAA oxidase during tomato fruit development. J Food Sci 47:158–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1982.tb11048.x
Uma S, Prasad TG, Kumar MU (1995) Genetic variability in recovery growth and synthesis of stress proteins in response to polyethylene glycol and salt stress in finger millet. Ann Bot 76:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1995.1076
van Doorn WG, Stead AD (1994) The physiology of petal senescence which is not initiated by ethylene. In: Scott RJ, Stead AD (eds) Molecular and cellular aspects of plant reproduction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 239–254
Viu AFM, Viu MAO, Tavares AR, Vianello F, Lima GPP (2009) Endogenous and exogenous polyamines in the organogenesis in Curcuma longa L. Sci Hortic 121:501–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.03.003
Wang AG, Luo GH (1990) Quantitative relation between the reaction of hydroxylamine and superoxide anion radicals in plants. Plant Physiol Commun. 6:55–57 (in Chinese)
Winicov I (1998) New molecular approaches to improving salt tolerance in crop plants. Ann Bot 82:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1998.0731
Xie SS, Wu HJ, Zang HY, Wu LM, Zhu QQ, Gao XW (2014) Plant growth promotion by spermidine-producing Bacillus subtilis OKB105. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27(7):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-01-14-0010-R
Yang YK, Lee SY, Park WT, Park NI, Park SU (2010) Exogenous auxins and polyamines enhance growth and rosmarinic acid production in hairy root cultures of Nepeta cataria L. Plant Omics 3(6):190–193
Zheng J, Ma X, Zhang X et al (2018) Salicylic acid promotes plant growth and salt-related gene expression in Dianthus superbus, L. (Caryophyllaceae) grown under different salt stress conditions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24(2):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0496-x
Zhou J, Fu L, Zeng K et al (2010) Study on osmotic adjustment on inorganic ions of cucumber seedling under NaCl stress. J Henan Agric Sci. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2010.02.023
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Miss Qi Shi for assistance with plant growth and observation in the greenhouse.
Funding
This study was financially supported by grants from the project of Wenzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau, Zhejiang Province-Study on the collection, conservation and utilization of germplasm resources of G. gandavensis (N20150014) and the project of Agricultural Department of Zhejiang Province-Collection, Reproduction, and Conservation of Germplasm Resources of G. gandavensis. These fundings did not play any role in the design of the study; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; or writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RQ and XM conceived and designed the experiments. XM, RQ, and XZ performed the experiments. RQ and XM wrote the manuscript. QH and HL revised the manuscript. JZ performed the data analysis and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, R., Ma, X., Zhang, X. et al. Effect of Exogenous Spermidine on Osmotic Adjustment, Antioxidant Enzymes Activity, and Gene Expression of Gladiolus gandavensis Seedlings Under Salt Stress. J Plant Growth Regul 40, 1353–1367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10198-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10198-x