Abstract
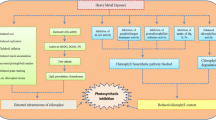
Ornamental pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is an important economic decorative plant well known for its abundant genetic diversity. However, high-temperature (HT) stress seriously affects its aesthetic and commercial value. In this work, we analyzed the effects of exogenous salicylic acid (SA) on seed germination and seedling growth of ornamental pepper under HT stress. The inherent physiological and biochemical basis of the alleviating effect of salicylic acid was further analyzed. The findings revealed SA with 0.01 mM and 0.1 mM was most effective in enhancing thermotolerance in seeds and seedlings, respectively. SA treatment increased the germination rate and germination potential, and reduced the oxidative damage of seeds under HT stress. For seedlings, spraying SA with 0.1 mM significantly alleviated yellow leaves and dwarfing under HT stress. SA could maintain high root vigor, inhibit water loss, and maintain the integrity of cell structure by regulating osmotic substance content under HT. SA-induced thermotolerance development involved in the activation of antioxidant defense system. SA decreased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), increased the activity of protective enzymes, and the content of non-enzymatic ROS scavengers in plants under HT. The changes of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters showed that SA was beneficial to maintain a high level of photosynthetic capacity of ornamental pepper seedlings under HT stress. Moreover, recovery also showed a mitigatory effect on injuries induced by HT stress. Taken together, this study provided evidence for the ability of exogenous SA application to moderate the detrimental effects by HT stress.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman M, Sawada Y, Nakabayashi R, Sato S, Hirakawa H, El-Sayed M, Hirai MY, Saito K, Yamauchi N, Shigyo M (2015) Integrating transcriptome and target metabolome variability in doubled haploids of Allium cepa for abiotic stress protection. Mol Breed 35(10):195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0378-2
Abdelrahman M, Burritt DJ, Lam-Son PT (2018) The use of metabolomic quantitative trait locus mapping and osmotic adjustment traits for the improvement of crop yields under environmental stresses. Semin Cell Dev Biol 83:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.06.020
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalase and peroxidases. Method Enzymol 2:764–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(55)02300-8
Chen LS, Cheng L (2009) Photosystem 2 is more tolerant to high temperature in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) leaves than in fruit peel. Photosynthetica 47(1):112–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-009-0017-4
Chen S, Yang J, Zhang M, Strasser RJ, Qiang S (2016) Classification and characteristics of heat tolerance in Ageratina adenophora populations using fast chlorophyll a fluorescence rise O-J-I-P. Environ Exp Bot 122:126–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.09.011
Cingoz GS, Gurel E (2016) Effects of salicylic acid on thermotolerance and cardenolide accumulation under high temperature stress in Digitalis trojana Ivanina. Plant Physiol Bioch 105:145–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.023
Comas LH, Eissenstat DM, Lakso AN (2000) Assessing root death and root system dynamics in a study of grape canopy pruning. New Phytol 147(1):171–178. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00679.x
Costa H, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2002) Effect of UV-B radiation on antioxidant defense system in sunflower cotyledons. Plant Sci 162(6):939–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00051-1
Fan MH, Sun X, Xu NJ, Liao Z, Li YH, Wang JX, Fan YP, Cui DL, Li P, Miao ZL (2017) Integration of deep transcriptome and proteome analyses of salicylic acid regulation high temperature stress in Ulva prolifera. Sci Rep 7:11052. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11449-w
Foyer CH, Rowell J, Walker D (1983) Measurements of the ascorbate content of spinach leaf protoplasts and chloroplasts during illumination. Planta 157(3):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405188
Gajanayake B, Trader BW, Reddy KR, Harkess RL (2011) Screening ornamental pepper cultivars for temperature tolerance using pollen and physiological parameters. Hortscience 46(6):878–884. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.46.6.878
He Y, Liu Y, Cao W, Huai M, Xu B, Huang B (2005) Effects of salicylic acid on heat tolerance associated with antioxidant metabolism in kentucky bluegrass. Crop Sci 45(3):988–995. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2003.0678
Horváth E, Szalai G, Janda T (2007) Induction of abiotic stress tolerance by salicylic acid signaling. J Plant Growth Regul 26(3):290–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-007-9017-4
Jedmowski C, Brüggemann W (2015) Imaging of fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction curve (OJIP) parameters, applied in a screening study with wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) genotypes under heat stress. J Photochem Photobiol B 151:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.07.020
Jespersen D, Yu J, Huang B (2017) Metabolic effects of acibenzolar-S-methyl for improving heat or drought stress in creeping bentgrass. Front Plant Sci 8:1224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01224
Jiang Y, Huang B (2001) Effects of calcium on antioxidant activities and water relations associated with heat tolerance in two cool-season grasses. J Exp Bot 52(355):341–349. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.355.341
Kalaji HM, Jajoo A, Oukarroum A, Brestic M, Zivcak M, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Łukasik I, Goltsev V, Ladle RJ (2016) Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 38(4):102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2113-y
Kampfenkel K, Van Montagu M, Inze D (1995) Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. Anal Biochem 225(1):165–167. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1995.1127
Kawano T, Bouteau F (2013) Crosstalk between intracellular and extracellular salicylic acid signaling events leading to long-distance spread of signals. Plant Cell Rep 32(7):1125–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1451-0
Khan MIR, Iqbal N, Masood A, Per TS, Khan NA (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates adverse effects of heat stress on photosynthesis through changes in proline production and ethylene formation. Plant Signal Behav 8(11):e26374. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.26374
Khan MIR, Khan NA, Masood A, Per TS, Asgher M (2016) Hydrogen peroxide alleviates nickel-inhibited photosynthetic responses through increase in use-efficiency of nitrogen and sulfur, and glutathione production in mustard. Front Plant Sci 7:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00044
Korkmaz A (2005) Inclusion of acetyl salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate into the priming solution improves low-temperature germination and emergence of sweet pepper. Hortic Sci 40(1):197–200. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.40.1.197
Larkindale J, Huang B (2005) Effects of abscisic acid, salicylic acid, ethylene and hydrogen peroxide in thermotolerance and recovery for creeping bentgrass. Plant Growth Regul 47(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-1536-z
Lee S, Kim SG, Park CM (2010) Salicylic acid promotes seed germination under high salinity by modulating antioxidant activity in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 188(2):626–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03378.x
Lee S, Lee HJ, Jung JH, Park CM (2015) The Arabidopsis thaliana RNA-binding protein FCA regulates thermotolerance by modulating the detoxification of reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 205(2):555–569. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13079
Li Z (2015) Synergistic effect of antioxidant system and osmolyte in hydrogen sulfide and salicylic acid crosstalk-induced heat tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Signal Behav 10(9):e1051278. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1051278
Li T, Hu Y, Du X, Tang H, Shen C, Wu J (2014) Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress in Torreya grandis cv. merrillii seedlings by activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant systems. PLoS One 9(10):e109492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109492
Li X, Lawas LMF, Malo R, Glaubitz U, Erban A, Mauleon R, Heuer S, Zuther E, Kopka J, Hincha DK, Jagadish KSV (2015a) Metabolic and transcriptomic signatures of rice floral organs reveal sugar starvation as a factor in reproductive failure under heat and drought stress. Plant Cell Environ 38(10):2171–2192. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12545
Li Z, Xie L, Li X (2015b) Hydrogen sulfide acts as a downstream signal molecule in salicylic acid-induced heat tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. J Plant Physiol 177:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.12.018
Liu Z, Yue M, Yang D, Zhu S, Ma N, Meng Q (2017) Over-expression of SlJA2 decreased heat tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants via salicylic acid pathway. Plant Cell Rep 36(4):529–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2100-9
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signaling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33(4):453–467. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02041.x
Misra N, Saxena P (2009) Effect of salicylic acid on proline metabolism in lentil grown under salinity stress. Plant Sci 177(3):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.05.007
Mittler R (2006) Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci 11(1):15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.002
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Breusegem FV (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plant. Trends Plant Sci 9(10):490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Oracz K, Bouteau HEM, Farrant JM, Cooper K, Belghazi M, Job C, Job D, Corbineau F, Bailly C (2007) ROS production and protein oxidation as a novel mechanism for seed dormancy alleviation. Plant J 50(3):452–465. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03063.x
Qin S, Sun X, Hu C, Tan Q, Zhao X, Xin J, Wen X (2017) Effect of NO3−: NH4+ ratios on growth, root morphology and leaf metabolism of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 39(9):198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2491-9
Quint M, Delker C, Franklin KA, Wigge PA, Halliday KJ, van Zanten M (2016) Molecular and genetic control of plant thermomorphogenesis. Nat Plants 2(1):15190. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.190
Sairam RK, Tyagi A (2004) Physiology and molecular biology of salinity stress tolerance in plants. Curr Sci India 86:407–421
Sgobba A, Paradiso A, Dipierro S, De Gara L, de Pinto MC (2015) Changes in antioxidants are critical in determining cell responses to short-and long-term heat stress. Physiol Plant 153(1):68–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12220
Shan D, Huang J, Yang Y, Guo Y, Wu C, Yang G, Gao Z, Zheng C (2007) Cotton GhDREB1 increases plant tolerance to low temperature and is negatively regulated by gibberellic acid. New Phytol 176(1):70–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02160.x
Sharma DK, Andersen SB, Ottosen CO, Rosenqvist E (2012) Phenotyping of wheat cultivars for heat tolerance using chlorophyll a fluorescence. Funct Plant Biol 39(11):936–947. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP12100
Shi Q, Bao Z, Zhu Z, Ying Q, Qian Q (2006) Effects of different treatments of salicylic acid on heat tolerance, chlorophyll fluorescence, and antioxidant enzyme activity in seedlings of Cucumis sativa L. Plant Growth Regul 48(2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-5482-6
Shin H, Oh S, Kim K, Kim D (2016) Proline accumulates in response to higher temperatures during dehardening in peach shoot tissues. Hortic J 85(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.2503/hortj.MI-088
Stefanov D, Petkova V, Denev ID (2011) Screening for heat tolerance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) lines and cultivars using JIP-test. Sci Hortic 128(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2010.12.003
Strasser RJ, Srivastava A, Tsimilli-Michael M (2000) The fluorescence transient as a tool to characterize and screen photosynthetic samples. In: Yunus M, Pathre U, Mohanty P (eds) Probing photosynthesis: mechanisms, regulation and adaptation. Taylor & Francis Publishers, London, pp 445–483
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Michael M, Srivastava A (2004) Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. In: Papageorgiou E, Govindjee GC (eds) Chlorophyll a fluorescence. Advances in photosynthesis and respiration, vol 19. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 321–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-3218-9_12
Stummel JR, Bosland P (2007) Ornamental pepper Capsicum annuum. In: Anderson NO (ed) Flower breeding and genetics. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 561–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4428-1_21
Tozzi ES, Easlon HM, Richards JH (2013) Interactive effects of water, light and heat stress on photosynthesis in Fremont cottonwood. Plant Cell Environ 36(8):1423–1434. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12070
Triantaphylides C, Krischke M, Hoeberichts FA, Ksas B, Gresser G, Havaux M, Van Breusegem F, Mueller MJ (2008) Singlet oxygen is the major reactive oxygen species involved in photooxidative damage to plants. Plant Physiol 148(2):960–968. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.125690
Wang L, Li S (2006) Salicylic acid-induced heat or cold tolerance in relation to Ca2+ homeostasis and antioxidant systems in young grape plants. Plant Sci 170(4):685–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.09.005
Wang L, Fan L, Loescher W, Duan W, Liu G, Cheng J, Luo H, Li S (2010) Salicylic acid alleviates decreases in photosynthesis under heat stress and accelerates recovery in grapevine leaves. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-34
Xie Z, Zhang Z, Hanzlik S, Cook E, Shen Q (2007) Salicylic acid inhibits gibberellin-induced alpha-amylase expression and seed germination via a pathway involving an abscisic-acid-inducible WRKY gene. Plant Mol Biol 64(3):293–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9152-0
Xu S, Li J, Zhang X, Wei H, Cui L (2006) Effects of heat acclimation pretreatment on changes of membrane lipid peroxidation, antioxidant metabolites, and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in two cool-season turfgrass species under heat stress. Environ Exp Bot 56(3):274–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.03.002
Xu Y, Du H, Huang B (2013) Identification of metabolites associated with superior heat tolerance in thermal bentgrass through metabolic profiling. Crop Sci 53(4):1626–1635. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2013.01.0045
You J, Chan Z (2015) ROS regulation during abiotic stress responses in crop plants. Front Plant Sci 6:1092. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01092
Zheng Y, Jia A, Ning T, Xu J, Li Z, Jiang G (2008) Potassium nitrate application alleviates sodium chloride stress in winter wheat cultivars differing in salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 165(14):1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2008.01.001
Zong X, Li D, Gu L, Li D, Liu L, Hu X (2009) Abscisic acid and hydrogen peroxide induce a novel maize group C MAP kinase gene, ZmMPK7, which is responsible for the removal of reactive oxygen species. Planta 229(3):485–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0848-4
Zushi K, Kajiwara S, Matsuzoe N (2012) Chlorophyll a fluorescence OJIP transient as a tool to characterize and evaluate response to heat and chilling stress in tomato leaf and fruit. Sci Hortic 148:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.022
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Ming Jiang Scholar fund from Fujian Province and FAFU (116-114120019); Special Innovation Foundation from FAFU (CXZX2016108, CXZX2017168); Foundation for Fostering Young Talents and Scientific Research Starting Foundation for Mingjiang Scholars from College of Horticulture, FAFU, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Lan, M., Han, X. et al. Response of Ornamental Pepper to High-Temperature Stress and Role of Exogenous Salicylic Acid in Mitigating High Temperature. J Plant Growth Regul 39, 133–146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09969-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09969-y