Abstract
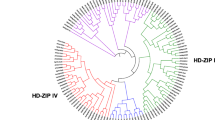
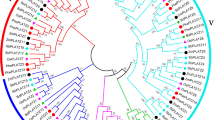
Homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) transcription factors are unique to plants and play important roles in plant growth and development. Although the HD-Zip gene family has been studied in many plant species, no comprehensive analysis of gene expression patterns under stress conditions has been reported in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). In this study, 48 putative HD-Zip genes were identified in the moso bamboo genome, and the predicted proteins clustered into four subfamilies (HD-Zip I–IV) based on phylogenetic analysis. Members of each subfamily shared similar conserved motifs, implying that they may perform similar functions. Our evolutionary analyses revealed that HD-Zip genes underwent a large-scale duplication event approximately 15 million years ago, the duplicated HD-Zip genes in moso bamboo are basically under purifying selection, and that the divergence time of HD-Zip genes between rice and moso bamboo was 15–23 million years ago. Analyses of expression in response to drought and salinity showed that some genes display stress-inducible expression patterns. Our study provides a systematic analysis of the HD-Zip gene family in moso bamboo. Analysis of gene expression patterns under abiotic stress may help in understanding the role of HD-Zip genes in moso bamboo and in overcoming challenges in moso bamboo growth and development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agalou A et al (2008) A genome-wide survey of HD-Zip genes in rice and analysis of drought-responsive family members. Plant Mol Biol 66(1–2):87–103. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9255-7
Altschul SF et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Ariel FD et al (2007) The true story of the HD-Zip family. Trends Plant Sci 12:419–426. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.08.003
Aso K et al (1999) Characterization of homeodomain-leucine zipper genes in the fern Ceratopteris richardii and the evolution of the homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in vascular plants. Mol Biol Evol 16(4):544–552
Bailey TL, Elkan C (1995) The value of prior knowledge in discovering motifs with MEME. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 3:21–29
Baima S et al (1996) The expression of the ATHB-8 homeobox gene is restricted to provascular cells in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 121(12):4171–4182
Baima S et al (2001) The arabidopsis ATHB-8 HD-zip protein acts as a differentiation-promoting transcription factor of the vascular meristems. Plant Physiol 126(2):643–655. doi:10.1104/pp.126.2.643
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004) Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16(7):1667–1678. doi:10.1105/tpc.021345
Bray EA (2004) Genes commonly regulated by water-deficit stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 55(407):2331–2341. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh270
Bryfczynski SP, Pargas RP (2009) GraphPad: a graph creation tool for CS2/CS7. Joint Conference Integrating Technology Into Computer Science Education, vol 41, no. 3, pp 389. doi:10.1145/1562877.1563031
Cao J et al (2011) Analyses of the oligopeptide transporter gene family in poplar and grape. BMC Genom 12(5):459–464. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-465
Carlos FM et al (2012) Identification of cis-acting promoter elements in cold- and dehydration-induced transcriptional pathways in arabidopsis, rice, and soybean. DNA Res 19(1):37–49. doi:10.1093/dnares/dsr040
Chan RL et al (1998) Homeoboxes in plant development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1442(1):1–19. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(98)00119-5
Cheng WH et al (2002) A unique short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase in Arabidopsis glucose signaling and abscisic acid biosynthesis and functions. Plant Cell 14:2723–2743. doi:10.1105/tpc.006494
Chunjie F et al (2013) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time pcr in bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 8(2):396. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056573
Cristina MD et al (1996) The Arabidopsis ATHB-10 (GLABRA2) is an HD-ZIP protein required for regulation of root hair development. Plant J 10(3):393–402. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.10030393.x
Depège-Fargeix N et al (2011) Functional characterization of the HD-ZIP IV transcription factor OCL1 from maize. J Exp Bot 62(1):293–305. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq267
Dezar CA et al (2010) HAHB10, a sunflower HD-Zip II transcription factor, participates in the induction of flowering and in the control of phytohormone-mediated responses to biotic stress. J Exp Bot 62:1061–1076. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq339
Eva H et al (2005) Homeodomain leucine zipper class I genes in Arabidopsis. Expression patterns and phylogenetic relationships. Plant Physiol 139(1):509–518. doi:10.1104/pp.105.063461
Finn RD et al (2006) Pfam: clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res 34:247–251. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj149
Frank W et al (1998) Two dehydration-inducible transcripts from the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum encode interacting homeodomain-leucine zipper proteins. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 15(3):413–421. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00222.x
Gasteiger E et al (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3784–3788. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg563
Guo AY et al (2007) [GSDS: a gene structure display server]. Yi chuan = Hereditas/Zhongguo yi chuan xue hui bian ji29:1023-1026
Guo L et al (2014) Differential retention and expansion of the ancestral genes associated with the paleopolyploidies in modern rosid plants, as revealed by analysis of the extensins super-gene family. BMC Genom 15(1):1–13. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-612
Harris JC et al (2011) Modulation of plant growth by HD-Zip class I and II transcription factors in response to environmental stimuli. New Phytol 190(4):823–837. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03733.x
Ivica L et al (2009) SMART 6: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D229–D232. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn808
Jim M et al (2003) Auxin signaling in Arabidopsis leaf vascular development. Plant Physiol 131(3):1327–1339. doi:10.1104/pp.013623
Johannesson H et al (2003) The Arabidopsis thaliana homeobox gene ATHB5 is a potential regulator of abscisic acid responsiveness in developing seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 51(5):719–729. doi:10.1023/A:1022567625228
Joonki K et al (2005) microRNA-directed cleavage of ATHB15 mRNA regulates vascular development in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant J 42(1):84–94. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02354.x
Juretic N et al (2005) The evolutionary fate of MULE-mediated duplications of host gene fragments in rice. Genome Res 15(9):1292–1297. doi:10.1101/gr.4064205
Krishanu M, Bürglin TR (2006) MEKHLA, a novel domain with similarity to PAS domains, is fused to plant homeodomain-leucine zipper III proteins. Plant Physiol 140(4):1142–1150. doi:10.1104/pp.105.073833
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2 method. Methods 25:402–408
Lynch M, Conery JS (2000) The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Sci 290(5494):1151–1155. doi:10.1126/science.290.5494.1151
Marie J et al (2011) Genome-wide characterization of the HD-ZIP IV transcription factor family in maize: preferential expression in the epidermis. Plant Physiol 157:790–803. doi:10.1104/pp.111.182147
Mayet A et al (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4(1):10. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Meijer AH et al (1997) Transcriptional repression by Oshox1, a novel homeodomain leucine zipper protein from rice. Plant J 11(2):263–276. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11020263.x
Miyuki N et al (2006) Characterization of the class IV homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141(4):1363–1375. doi:10.1104/pp.106.077388
Morelli G, Ruberti I (2002) Light and shade in the photocontrol of Arabidopsis growth. Trends Plant Sci 7(9):399–404
Mukesh J et al (2008) Genome-wide identification, classification, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses of homeobox genes in rice. FEBS J 275(275):2845–2861. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06424.x
Nakashima K et al (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149(1):88–95. doi:10.1104/pp.108.129791
Olsson ASB et al (2004) The homeobox genes ATHB12 and ATHB7 encode potential regulators of growth in response to water deficit in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 55(5):663–677. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-1581-4
Peng Z et al (2013a) The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat Genet 45(4):456–461. doi:10.1038/ng.2569
Peng Z et al (2013b) Transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the fast growing shoots of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 8(11):e78944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078944
Ponting CP, Aravind L (1999) START: a lipid-binding domain in StAR, HD-ZIP and signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24(4):130–132
Prigge M, Clark S (2006) Evolution of the class III HD-Zip gene family in land plants. Evol Dev 8(4):350–361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2006.00107.x
Prigge MJ et al (2005) Class III homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family members have overlapping, antagonistic, and distinct roles in arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 17(1):61–76. doi:10.1105/tpc.104.026161
Rabbani MA et al (2004) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133(4):1755–1767. doi:10.1104/pp.103.025742
Rozas J (2009) DNA sequence polymorphism analysis using DnaSP. Methods Mol Biol 537(537):337–350. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-251-9_17
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(6):406–425
Schena M, Davis RW (1992) HD-Zip proteins: members of an Arabidopsis homeodomain protein superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89(9):3894–3898. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.9.3894
Schrick K et al (2004) START lipid/sterol-binding domains are amplified in plants and are predominantly associated with homeodomain transcription factors. Genome Biol 5(6):50–67. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-6-r41
Seki M et al (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 31(3):279–292. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01359.x
Sessa G et al (1993) The Athb-1 and-2 HD-Zip domains homodimerize forming complexes of different DNA binding specificities. EMBO J 12(9):3507–3517
Sessa G et al (2005) A dynamic balance between gene activation and repression regulates the shade avoidance response in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 19(23):2811–2815. doi:10.1101/gad.364005
Skinner DJ, Gasser CS (2009) Expression-based discovery of candidate ovule development regulators through transcriptional profiling of ovule mutants. BMC Plant Biol 9(2):410–415. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-29
Steindler C et al (1999) Shade avoidance responses are mediated by the ATHB-2 HD-zip protein, a negative regulator of gene expression. Development 126(19):4235–4245
Sultan SE (2009) Plant developmental responses to the environment: eco-devo insights. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13(1):96–101. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2009.09.021
Toshitsugu N et al (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140(2):411–432. doi:10.1104/pp.105.073783
Vanessa V et al (2009) The HD-ZIP IV transcription factor OCL4 is necessary for trichome patterning and anther development in maize. Plant J 59(6):883–894. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03916.x
Wu H et al (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factors family and the expression patterns of DREB genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 10(5):e0126657. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126657
Xue C et al (2014) Genome-wide analysis of soybean HD-Zip gene family and expression profiling under salinity and drought treatments. PLoS ONE 9(2):e87156. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087156
Yang Z et al (2011) Systematic analysis of sequences and expression patterns of drought-responsive members of the HD-Zip gene family in maize. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28488. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028488
Zhang YJ et al (2011) High-throughput sequencing of six bamboo chloroplast genomes: phylogenetic implications for temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 6(5):e20596. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020596
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Laboratory of Modern Biotechnology for their assistance in this study. This work was supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Forestry Public Welfare Industry (201404601) and Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (31670672). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author’s contribution
Conceived and designed the experiments: DMC, ZC, HWY, YX. Performed the experiments: DMC, ZC, MW. Analyzed the data: DMC, ZC, HWY. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: DMC, ZC, MW, YW, YJW. Wrote the paper: DMC, ZC, YX.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material S1 Table
Oligonucleotide primer sequences used in qRT-PCR analysis of the 17 moso bamboo HD-ZIP I genes (XLSX 13 kb)
Supplementary material S2 Table
Genomic location and predicted characteristics of the putative HD-Zip proteins in moso bamboo (DOC 95 kb)
Supplementary material S3 Figure
Amino acid sequence motifs present in 48 moso bamboo HD-Zip proteins. Twenty-five motifs were identified by MEME (http://meme.nbcr.net/meme/) (PNG 51 kb)
Supplementary material S4 Table
Detailed information on conserved amino acid sequences and motif lengths (XLSX 10 kb)
Supplementary material S5 Table
Annotation of putative motifs based on Pfam searches (XLSX 10 kb)
Supplementary material S6 Text
Amino acid sequences of moso bamboo, rice, maize and sorghum HD-Zip proteins used for phylogenetic analysis. (TXT 92 kb)
Supplementary material S7 Table
Paralogous HD-Zip gene pairs identified in the moso bamboo genome (DOC 44 kb)
Supplementary material S8 Table
Orthologous HD-Zip gene pairs between moso bamboo and rice (DOC 75 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Chen, Z., Wu, M. et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the HD-Zip Gene Family in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). J Plant Growth Regul 36, 323–337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9642-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9642-x