Abstract
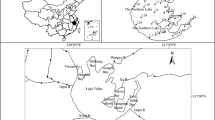
Cyanobacterial blooms occur in eutrophic lakes worldwide, and greatly impair these ecosystems. To explore influences of cyanobacterial blooms on dynamics of both particulate organic matter (POM) and dissolved organic matter (DOM), which are at the base of the food chain, an investigation was conducted from December 2014 to November 2015 that included various stages of the seasonal cyanobacterial blooms (dominated by Microcystis ) in a large-shallow eutrophic Chinese lake (Taihu Lake). Data from eight sites of the lake are compiled into a representative seasonal cycle to assess general patterns of POM and DOM dynamics. Compared to December, 5-fold and 3.5-fold increases were observed in July for particulate organic carbon (POC, 3.05–15.37 mg/L) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC, 5.48–19.25 mg/L), respectively, with chlorophyll a (Chl a ) concentrations varying from 8.2 to 97.7 μg/L. Approximately 40% to 76% of total organic carbon was partitioned into DOC. All C, N, and P in POM and DOC were significantly correlated with Chl a. POC:Chl a ratios were low, whereas proportions of the estimated phytoplankton-derived organic matter in total POM were high during bloom seasons. These results suggested that contributions of cyanobacterial blooms to POM and DOC varied seasonally. Seasonal average C:P ratios in POM and DOM varied from 79 to 187 and 299 to 2 175, respectively. Both peaked in July and then sharply decreased. Redundancy analysis revealed that Chl a explained most of the variations of C:N:P ratios in POM, whereas temperature was the most explanatory factor for DOM. These findings suggest that dense cyanobacterial blooms caused both C-rich POM and DOM, thereby providing clues for understanding their influence on ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrigo K R, Robinson D H, Worthen D L, Dunbar R B, DiTullio G R, VanWoert M, Lizotte M P. 1999. Phytoplankton community structure and the drawdown of nutrients and CO 2 in the Southern Ocean. Science, 283 (5400): 365–367.
Arrigo K R. 2005. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature, 437 (7057): 349–355.
Berman T, Bronk D A. 2003. Dissolved organic nitrogen: a dynamic participant in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Microb. Ecol., 31 (3): 279–305.
Berman T, Pollingher U. 1974. Annual and seasonal variations of phytoplankton, chlorophyll, and photosynthesis in Lake Kinncret. Limnol. Oceanogr., 19 (1): 31–55.
Bertilsson S, Berglund O, Karl D M, Chisholm S W. 2003. Elemental composition of marine Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus: implications for the ecological stoichiometry of the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr., 48 (5): 1 721–1 731.
Carlson C A, Hansell D A, Peltzer E T, Smith W O Jr. 2000. Stocks and dynamics of dissolved and particulate organic matter in the southern Ross Sea, Antarctica. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 47 (15-16): 3 201–3 225.
Chen Y W, Qin B Q, Teubner K, Dokulil M T. 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Taihu Lake, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res., 25 (4): 445–453.
Cifuentes L A, Sharp J H, Fogel M L. 1988. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry in the Delaware estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr., 33 (5): 1 102–1 115.
Cross W F, Wallace J B, Rosemond A D. 2007. Nutrient enrichment reduces constraints on material flows in a detritus-based food web. Ecology, 88 (10): 2 563–2 575.
Davis T W, Harke M J, Marcoval M A, Goleski J, Orano-Dawson C, Berry D L, Gobler C J. 2010. Effects of nitrogenous compounds and phosphorus on the growth of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacterial blooms. Aquat. Microb. Ecol., 61 (2): 149–162.
Ebina J, Tsutsui T, Shirai T. 1983. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Water Res., 17 (12): 1 721–1 726.
Elser J J, Chrzanowski T H, Sterner R W, Mills K H. 1998. Stoichiometric constraints on food-web dynamics: a whole-lake experiment on the Canadian Shield. Ecosystems, 1 (1): 120–136.
Elser J J, Hayakawa K, Urabe J. 2001. Nutrient limitation reduces food quality for zooplankton: Daphnia response to seston phosphorus enrichment. Ecology, 82 (3): 898–903.
Elser J J, Sterner R W, Gorokhova E, Fagan W F, Markow T A, Cotner J B, Harrison J F, Hobbie S E, Odell G M, Weider L W. 2000. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol. Lett., 3 (6): 540–550.
Elser J, Acharya K, Kyle M, Cotner J, Makino W, Markow T, Watts T, Hobbie S, Fagan W, Schade J, Hood J, Sterner R W. 2003. Growth rate-stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota. Ecol. Lett., 6 (10): 936–943.
Fukushima T, Park J C, Imai A, Matsushige K. 1996. Dissolved organic carbon in a eutrophic lake; dynamics, biodegradability and origin. Aquat. Sci., 58 (2): 139–157.
Geider R, La Roche J. 2002. Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis. Eur. J. Phycol., 37 (1): 1–17.
Glibert P M, Heil C A, Hollander D, Revilla M, Hoare A, Alexander J, Murasko S. 2004. Evidence for dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake during a cyanobacterial bloom in Florida Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 280: 73–83.
Hama T, Handa N. 1983. The seasonal variation of organic constituents in a eutrophic lake, Lake Suwa, Japan. Part II. Dissolved organic matter. Arch. Hydrobiol., 98 (4): 443–462.
Hecky R E, Campbell P, Hendzel L L. 1993. The stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in particulate matter of lakes and oceans. Limnol. Oceanogr., 38 (4): 709–724.
Hecky R E, Kilham P. 1988. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnol. Oceanogr., 33 (4 Part 2): 796–822.
Hessen D O, Andersen T, Brettum P, Faafeng B A. 2003. Phytoplankton contribution to sestonic mass and elemental ratios in lakes: implications for zooplankton nutrition. Limnol. Oceanogr., 48 (3): 1 289–1 296.
Hessen D O, Van Donk E, Gulati R. 2005. Seasonal seston stoichiometry: effects on zooplankton in cyanobacteriadominated lakes. J. Plankton Res., 27 (5): 449–460.
Hillebrand H, Steinert G, Boersma M, Malzahn A, Meunier C L, Plum C, Ptacnik R. 2013. Goldman revisited: fastergrowing phytoplankton has lower N:P and lower stoichiometric flexibility. Limnol. Oceanogr., 58 (6): 2 076–2 088.
Hopkinson C S Jr, Vallino J J, Nolin A. 2002. Decomposition of dissolved organic matter from the continental margin. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 49 (20): 4 461–4 478.
Hopkinson C S, Fry B, Nolin A L. 1997. Stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter dynamics on the continental shelf of the northeastern U.S.A. Cont. Shelf Res., 17 (5): 473–489.
Huang W J, Lai C H, Cheng Y L. 2007. Evaluation of extracellular products and mutagenicity in cyanobacteria cultures separated from a eutrophic reservoir. Sci. Total Environ., 377 (2–3): 214–223.
Kim B, Choi K, Kim C, Lee U H, Kim Y H. 2000. Effects of the summer monsoon on the distribution and loading of organic carbon in a deep reservoir, Lake Soyang, Korea. Water Res., 34 (14): 3 495–3 504.
Kim C, Nishimura Y, Nagata T. 2006. Role of dissolved organic matter in hypolimnetic mineralization of carbon and nitrogen in a large, monomictic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr., 51 (1): 70–78.
Kim T H, Kim G. 2013. Factors controlling the C:N:P stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter in the N-limited, cyanobacteria-dominated East/Japan Sea. J. Mar. Syst., 115-116: 1–9.
Klausmeier C A, Litchman E, Daufresne T, Levin S A. 2004. Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature, 429 (6988): 171–174.
Kong F X, Gao G. 2005. Hypothesis on cyanobacteria bloomforming mechanism in large shallow eutrophic lakes. Acta Ecol. Sin., 25 (3): 589–595.
Lü S G, Wang X C, Han B P. 2009. A field study on the conversion ratio of phytoplankton biomass carbon to chlorophyll-a in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 27 (4): 793–805.
Ma J R, Qin B Q, Paerl H W, Brookes J D, Hall N S, Shi K, Zhou Y Q, Guo J S, Li Z, Xu H, Wu T F, Long S X. 2016. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Taihu Lake, China. Limnol. Oceanogr., 61 (2): 711–722.
Martiny A C, Pham C T A, Primeau F W, Vrugt J A, Moore J K, Levin S A, Lomas M W. 2013. Strong latitudinal patterns in the elemental ratios of marine plankton and organic matter. Nat. Geosci., 6 (4): 279–283.
McCarthy M J, Lavrentyev P J, Yang L Y, Zhang L, Chen Y W, Qin B Q, Gardner W S. 2007. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, wellmixed, eutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China). Hydrobiologia, 581 (1): 195–207.
Mei Z P, Legendre L, Tremblay J É, Miller L A, Gratton Y, Lovejoy C, Yager P L, Gosselin M. 2005. Carbon to nitrogen (C:N) stoichiometry of the spring–summer phytoplankton bloom in the North Water Polynya (NOW). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap., 52 (12): 2 301–2 314.
Meyers P A. 1994. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem. Geol., 114 (3–4): 289–302.
Mitamura O, Seike Y, Kondo K, Goto N, Anbutsu K, Akatsuka T, Kihira M, Tsering T Q, Nishimura T M. 2003. First investigation of ultraoligotrophic alpine Lake Puma Yumco in the pre-Himalayas, China. Limnology, 4 (3): 167–175.
Nagata T. 2000. Production mechanisms of dissolved organic matter. In: Kirchman D L ed. Microbial Ecology of the Oceans. Wiley-Liss, New York.
Norrman B, Zwelfel U L, Hopkinson C S Jr, Brian F. 1995. Production and utilization of dissolved organic carbon during an experimental diatom bloom. Limnol. Oceanogr., 40 (5): 898–907.
Parsons T R, Takahashi M, Hargrave B. 1977. Biological Oceanographic Processes. 2 nd edn. Pergamon Press, New York. p.332.
Qin B Q, Li W, Zhu G W, Zhang Y L, Wu T F, Gao G. 2015. Cyanobacterial bloom management through integrated monitoring and forecasting in large shallow eutrophic Taihu Lake (China). J. Hazard. Mater., 287: 287–356.
Qin B Q, Xu P Z, Wu Q L, Luo L C, Zhang Y L. 2007. Environmental issues of lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia, 581 (1): 3–14.
Roth V N, Dittmar T, Gaupp R, Gleixner G. 2013. Latitude and pH driven trends in the molecular composition of DOM across a north south transect along the Yenisei River. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 123: 123–93.
Shi X L, Qian S Q, Kong F X, Zhang M, Yu Y. 2011. Differences in growth and alkaline phosphatase activity between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to media with different organic phosphorus. J. Limnol., 70 (1): 21–25.
Søndergaard M, Williams P J L B, Cauwet G, Riemann B, Robinson C, Terzic S, Woodward E M S, Worm J. 2000. Net accumulation and flux of dissolved organic carbon and dissolved organic nitrogen in marine plankton communities. Limnol. Oceanogr., 45 (5): 1 097–1 111.
Sterner R W, Elser J J. 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Sterner R W, Hagemeier D D, Smith W L, Smith R F. 1993. Phytoplankton nutrient limitation and food quality for Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr., 38 (4): 857–871.
Thurman E M. 1985. Organic Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Springer, Netherlands.
Wetz M S, Wheeler P A. 2003. Production and partitioning of organic matter during simulated phytoplankton blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr., 48 (5): 1 808–1 817.
Williams P J L B. 1995. Evidence for the seasonal accumulation of carbon-rich dissolved organic material, its scale in comparison with changes in particulate material and the consequential effect on net C /N assimilation ratios. Mar. Chem., 51 (1): 17–29.
Ye L L, Wu X D, Liu B, Yan D Z, Kong F X. 2015. Dynamics and sources of dissolved organic carbon during phytoplankton bloom in hypereutrophic Taihu Lake (China). Limnologica, 54: 54–5.
Yoshimura T, Ogawa H, Imai K, Aramaki T, Nojiri Y, Nishioka J, Tsuda A. 2009. Dynamics and elemental stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in particulate and dissolved organic pools during a phytoplankton bloom induced by in situ iron enrichment in the western subarctic Pacific (SEEDS-II). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 56 (26): 2 863–2 874.
Zhang Y L, Gao G, Shi K, Niu C, Zhou Y Q, Qin B Q, Liu X H. 2014. Absorption and fluorescence characteristics of rainwater CDOM and contribution to Taihu Lake, China. Atmos. Environ., 98: 98–483.
Zhang Y L, van Dijk M A, Liu M L, Zhu G W, Qin B Q. 2009. The contribution of phytoplankton degradation to chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in eutrophic shallow lakes: field and experimental evidence. Water Res., 43 (18): 4 685–4 697.
Zhang Y L, Yin Y, Liu X H, Shi Z Q, Feng L Q, Liu M L, Zhu G W, Gong Z J, Qin B Q. 2011a. Spatial-seasonal dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Taihu Lake, a large eutrophic, shallow lake in China. Org. Geochem., 42 (5): 510–519.
Zhang Y L, Yin Y, Zhang E L, Zhu G W, Liu M L, Feng L Q, Qin B Q, Liu X H. 2011b. Spectral attenuation of ultraviolet and visible radiation in lakes in the Yunnan Plateau, and the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 10 (4): 469–482.
Zlotnik I, Dubinsky Z. 1989. The effect of light and temperature on doc excretion by phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr., 34 (5): 831–839.
Acknowledgement
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments in the previous version of this manuscript. We thank Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research (TLLER) for providing the monitoring data of phytoplankton. We appreciate CHEN Chao for his help for sample collection in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (No. BK20131466), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31370509, 31100363), the Start-up Funds from Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. NIGLAS2011QD05)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Huang, Y., Lu, Y. et al. Stocks and dynamics of particulate and dissolved organic matter in a large, shallow eutrophic lake (Taihu, China) with dense cyanobacterial blooms. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 738–749 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7031-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7031-y