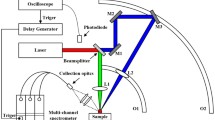
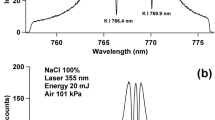
Abstract
Dual-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) provides improved sensitivity compared to conventional single-pulse LIBS. We used a combination of Nd: yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) and CO2 lasers to improve the sensitivity of LIBS. Significant emission intensity enhancement is noticed for both excited neutral lines and ionic lines for dual-pulse LIBS compared to single-pulse LIBS. However, the enhancement factor is found to be dependend on the energy levels of the lines, and resonance lines provided maximum enhancement. Our results indicate that IR reheating will cause significant improvement in sensitivity, regardless of the conditions, even with an unfocused reheating beam. The improved sensitivity with a YAG-CO2 laser combination is caused by the effective reheating of the pre-plume with a longer wavelength laser is due to efficient inverse Bremsstrahlung absorption. The role of the spot sizes, inter-pulse delay times, energies of the preheating and reheating pulses on the LIBS sensitivity improvements are discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Singh, S. Thakur, Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2007)
A. Ford, R. Waterbury, J. Rose, K. Pohl, M. Eisterhold, T. Thorn, K. Lee, E. Dottery, Proc. SPIE 7665, 76650Y (2010)
A. Bol’shakov, J. Yoo, C. Liu, J. Plumer, R. Russo, Appl. Opt. 49, C132 (2009)
D. Killinger, S. Allen, R. Waterbury, C. Stefano, E.L. Dottery, Opt. Express 15, 12905 (2007)
B. Rashind, R. Ahmed, R. Ali, M.A. Baig, Phys. Plasmas 18, 073301 (2011)
P. Benedetti, G. Cristoforetti, S. Legnaioli, V. Palleschi, L. Pardini, A. Salvetti, E. Tognoni, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 60, 1392 (2005)
G. Cristoforetti, S. Legnaioli, V. Palleschi, A. Salvetti, E. Tognoni, Appl. Phys. B 80, 559 (2005)
R. Noll, R. Sattmann, V. Sturm, S. Winkelmarm, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 19, 419 (2004)
L. St-Onge, V. Detalle, M. Sabsabi, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 57, 121 (2002)
J. Uebbing, J. Brust, W. Sdorra, F. Leis, K. Niemax, Appl. Spectrosc. 45, 1419 (1991)
A. Bogaerts, Z.Y. Chen, R. Gijbels, A. Vertes, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 58, 1867 (2003)
X. Pu, N. Cheung, Appl. Spectrosc. 57, 588 (2003)
X. Pu, W. Ma, N. Cheung, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 3416 (2003)
S. Lui, N. Cheung, Anal. Chem. 77, 2617 (2005)
M. Corsi, G. Cristoforetti, M. Giuffrida, M. Hidalgo, S. Legnaioli, V. Palleschi, A. Salvetti, E. Tognoni, C. Vallebona, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 59, 723 (2004)
L. Cabalin, J. Laserna, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 53, 723 (1998)
R. Russo, X. Mao, O. Borisov, H. Liu, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 15, 1115 (2000)
X. Mao, W. Chan, M. Shannon, R. Russo, J. Appl. Phys. 74, 4915 (1993)
X. Mao, W. Chan, M. Caetano, M. Shannon, R. Russo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 96, 126 (1996)
J. Aguilera, C. Aragon, F. Penalba, Appl. Surf. Sci. 127, 309 (1998)
K. Eland, D. Stratis, J. Carter, S. Angel, Proc. SPIE 3853, 288 (1999)
S. Harilal, B. O’Shay, M. Tillack, M. Mathew, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 013306 (2005)
H. Griem, Spectral Line Broadening by Plasmas (Academic Press, New York, 1974)
N. Konjevic, A. Lesage, J.R. Fuhr, W.L. Wiese, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 31, 819 (2002)
J. Chang, B. Warner, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 473 (1996)
R. Waterbury, A. Pal, D. Killinger, J. Rose, E. Dottery, G. Ontai, Proc. SPIE 6954, 95409 (2008)
Y. Ralchenko, A. Kramida, J. Reader, NIST ASD Team, NIST atomic spectra database (ver. 4.0.1) (Online). National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD (2010)
M. Asgill, M. Brown, K. Frische, W. Roquemore, D. Hahn, Appl. Opt. 49, C110 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Energy National Nuclear Security Administration under Award number DE-NA0001174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coons, R.W., Harilal, S.S., Hassan, S.M. et al. The importance of longer wavelength reheating in dual-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B 107, 873–880 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-4997-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-4997-6