Abstract
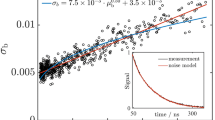
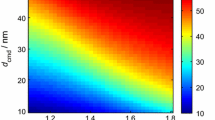
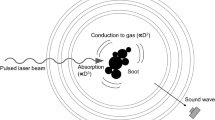
Laser-induced incandescence (LII) is a versatile technique for quantitative soot measurements in flames and exhausts. When used for particle sizing, the time-resolved signals are analysed as these will show a decay rate dependent on the soot particle size. Such an analysis has traditionally been based on the assumption of isolated primary particles. However, soot particles in flames and exhausts are usually aggregated, which implies loss of surface area, less heat conduction and hence errors in estimated particle sizes. In this work we present an experimental investigation aiming to quantify this effect. A soot generator, based on a propane diffusion flame, was used to produce a stable soot stream and the soot was characterised by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), a scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) and an aerosol particle mass analyzer coupled in series after a differential mobility analyzer (DMA-APM). Despite nearly identical primary particle size distributions for three selected operating conditions, LII measurements resulted in signal decays with significant differences in decay rate. However, the three cases were found to have quite different levels of aggregation as shown both in TEM images and mobility size distributions, and the results agree qualitatively with the expected effect of diminished heat conduction from aggregated particles resulting in longer LII signal decays. In an attempt to explain the differences quantitatively, the LII signal dependence on aggregation was modelled using a heat and mass transfer model for LII given the primary particle and aggregate size distribution data as input. Quantitative agreement was not reached and reasons for this discrepancy are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Santoro, C.R. Shaddix, in Applied Combustion Diagnostics (Taylor and Francis, New York, 2002), p. 252
C. Schulz, B.F. Kock, M. Hofmann, H. Michelsen, S. Will, B. Bougie, R. Suntz, G. Smallwood, Appl. Phys. B 83, 333 (2006)
P.-E. Bengtsson, M. Aldén, Appl. Phys. B 60, 51 (1995)
S. De Iuliis, F. Cignoli, G. Zizak, Appl. Opt. 44, 7414 (2005)
T. Lehre, B. Jungfleisch, R. Suntz, H. Bockhorn, Appl. Opt. 42, 2021 (2003)
D.R. Snelling, F.S. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, Ö.L. Gülder, Combust. Flame 136, 180 (2004)
S. Will, S. Schraml, K. Bader, A. Leipertz, Appl. Opt. 37, 5647 (1998)
Z.H. Lim, A. Lee, K.Y.Y. Lim, Z. Yanwu, S. Chorng-Haur, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 064319 (2010), 7 pp.
B.F. Kock, C. Kayan, J. Knipping, H.R. Orthner, P. Roth, Proc. Combust. Inst. 30, 1689 (2005)
R. Starke, B. Kock, P. Roth, Shock Waves 12, 351 (2003)
J. Delhay, P. Desgroux, E. Therssen, H. Bladh, P.-E. Bengtsson, H. Hönen, J. Black, I. Vallet, Appl. Phys. B 95, 825 (2009)
J.D. Black, M.P. Johnson, Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 14, 329 (2010)
H. Bladh, J. Johnsson, P.-E. Bengtsson, Appl. Phys. B 90, 109 (2008)
L.A. Melton, Appl. Opt. 23, 2201 (1984)
R.W. Weeks, W.W. Duley, J. Appl. Phys. 45, 4661 (1974)
H.A. Michelsen, J. Chem. Phys. 118, 7012 (2003)
F. Goulay, P.E. Schrader, L. Nemes, M.A. Dansson, H.A. Michelsen, Proc. Combust. Inst. 32, 963 (2009)
S. Will, S. Schraml, A. Leipertz, Opt. Lett. 20, 2342 (1995)
P. Roth, A.V. Filippov, J. Aerosol Sci. 27, 95 (1996)
A.V. Filippov, M. Zurita, D.E. Rosner, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 229, 261 (2000)
F. Liu, M. Yang, F.A. Hill, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, Appl. Phys. B 83, 383 (2006)
F. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, in 40th Thermophysics Conference (Seattle, Washington, 2008)
Ü.Ö. Köylü, G.M. Faeth, T.L. Farias, M.G. Carvalho, Combust. Flame 100, 621 (1995)
S.-A. Kuhlmann, J. Reimann, S. Will, J. Aerosol Sci. 37, 1696 (2006)
A.V. Filippov, D.E. Rosner, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 43, 127 (2000)
K.J. Daun, G.J. Smallwood, F. Liu, J. Heat Transf. 130, 121201 (2008), 9 pp.
H. Bladh, J. Johnsson, P.-E. Bengtsson, Appl. Phys. B 96, 645 (2009)
E.O. Knutson, K.T. Whitby, J. Aerosol. Sci. 6, 443 (1975)
K. Park, D. Dutcher, M. Emery, J. Pagels, H. Sakurai, J. Scheckman, S. Qian, M.R. Stolzenburg, X. Wang, J. Yang, P.H. McMurry, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 42, 801 (2008)
K. Park, F. Cao, D.B. Kittelson, P.H. McMurry, Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 577 (2003)
J. Pagels, A.F. Khalizov, P.H. McMurry, R.Y. Zhang, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 43, 629 (2009)
K. Park, D.B. Kittelson, M.R. Zachariah, P.H. McMurry, J. Nanopart. Res. 6, 267 (2004)
A. Malik, H. Abdulhamid, J. Pagels, J. Rissler, M. Lindskog, R. Bjorklund, P. Jozsa, J. Visser, A. Spetz, M. Sanati, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 45, 1 (2011)
CAST, Combustion Aerosol Standard (Jing Ltd., Im Park 4, CH-3052 Zollikofen BE, Switzerland). http://www.sootgenerator.com. Available September 2010
W.S. Rasband, ImageJ (U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007). http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/. Available September 2010
K. Tian, F.S. Liu, K.A. Thomson, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, D.S. Wang, Combust. Flame 138, 195 (2004)
F. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 111, 302 (2010)
H. Bladh, J. Johnsson, N.E. Olofsson, A. Bohlin, P.E. Bengtsson, Proc. Combust. Inst. 33, 641 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bladh, H., Johnsson, J., Rissler, J. et al. Influence of soot particle aggregation on time-resolved laser-induced incandescence signals. Appl. Phys. B 104, 331–341 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4470-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4470-y