Abstract
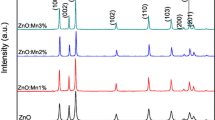
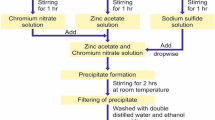
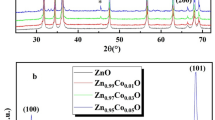
In this report, the real part of ac conductance (Σ(T, f)) of pure ZnO nanoparticle, manganese-doped ZnO nanocapsules and nanoplates was estimated as a component of frequency (f) by shifting zero-frequency Ohmic conductance (Σ0) with the tuning of the temperature (T) to understand the nonlinear AC conduction mechanism in semiconductor. The UV–VIS absorption spectrum showed a change in band gap from 3.67 eV for pure ZnO NPs to 3.31 eV for Mn-doped ZnO NPs with the change in excitonic peak from 372.5 nm for ZnO NPs to 375 nm for Mn-ZnO NPs. The HRTEM and SAED analysis along with XRD showed formation of nanocapsules and nanoplates with hexagonal wurtzite crystal phase. The doped semiconductor nanocrystals showed a ‘T’ dependent transition nature. Scaling speculations from theoretical models are used to dissect the effects of ac conduction and the nonlinearity exponent (xf) of the onset frequency \({{f}_{\mathrm{c}}\sim\Sigma }_{0}^{{x}_{f}}\). The overall scaling formalism for the ac conductance Σ0 was properly scaled with a universal curve as per the information for Σ(T,f) under different T. The metallic and semiconductor contribution in the dc conductivity of the doped nanosystems is highlighted. The normalized conductance (Σ/Σ0) as a function of normalized frequency curves was depicted by a single power law for Mn-ZnO nanocapsules and nanoplates. The AC conduction process showed that xf is a lot of phase delicate and can be utilized to describe the phase changes in these doped nanosystems originated due to change in Mn2+ doping concentration.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
H.M. Xiong, Y. Xu, Q.-G. Ren, Y.-Y. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 7522 (2008)
F. Bagheri, H. Haratizadeh, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 141, 106422 (2022)
M. Belhaj, C. Dridi, H. Elhouichet, J.C. Valmalette, J. Appl. Phys. 119, 095501 (2016)
F. Abrinaei, N. Molahasani, J. Optical Soc. Am. B 35(8), 2015 (2018)
M. Nirmala, A. Anukaliani, Mater. Lett. 65, 2645 (2011)
J. Zhong, S. Muthukumar, Y. Chen, Y. Lu, H.M. Ng, W. Jiang, E.L. Garfunkel, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 3401 (2003)
C. Belkhaoui, R. Lefi, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 7020 (2018)
D. Sharma, R. Jha, J. Alloy. Compd. 698, 532 (2017)
M.H. Zulfiqar, M. Zubair, A. Khan, T. Hua, N. Ilyas, S. Fashu, A.M. Afzal, M.A. Safeen, R. Khan, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 9463–9474 (2021)
H. Saadi, Z. Benzarti, P. Sanguino, Y. Hadouch, D. Mezzane, K. Khirouni, N. Abdelmoula, H. Khemakhem, Appl. Phys. A 128, 691 (2022)
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Mater. Des. 96, 99 (2016)
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, Mater. Res. Bull. 111, 70 (2019)
D. Zhang, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 86(1), 93 (2012)
A.K. Bhunia, S. Saha, Luminescence 36, 149 (2021)
A.K. Bhunia, P.K. Jha, S. Saha, Luminescence 37, 892 (2022)
S. Benramache, B. Benhaoua, H. Bentrah, J. Nanostr. Chem. 3, 1 (2013)
Z.R. Tian, J.A. Voigt, J. Liu, B. Mckenzie, M.J. Mcdermott, M.A. Rodriguez, H. Konishi, H. Xu, Nat. Mater. 2, 821 (2003)
R. Karmakar, S.K. Neogi, A. Banerjee, S. Bandyopadhyay, Appl. Surf. Sci. 263, 671 (2012)
A.K. Bhunia, T. Kamilya, S. Saha, Chem. Select 1, 2872–2882 (2016)
A.K. Bhunia, T.N. Ghosh, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 17963 (2022)
J.C. Dyre, T.B. Schroder, Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 873 (2000)
W.K. Lee, J.F. Liu, A.S. Nowich, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 1559 (1991)
A.S. Nowick, A.V. Vaysleyb, B.S. Lim, J. Appl. Phys. 76, 4429 (1994)
K.K. Bardhan, R.K. Chakrabarty, Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 1068 (1994)
T.N. Ghosh, U.N. Nandi, S. Chattopadhyay, D. Jana, S.C. Saha, Solid State Commun. 152, 1595 (2012)
U.N. Nandi, S. Sircar, A. Karmakar, S. Giri, J. Phys Condens. Matter 24, 265601 (2012)
D. Chakraborty, U.N. Nandi, D. Jana, Md.G. Masud, S. Giri, J. Appl. Phys. 118, 035103 (2015)
U.N. Nandi, Y.Z. Long, D. Chakraborty, Results Phys. 3, 84 (2013)
D. Talukdar, U.N. Nandi, K.K. Bardhan, C.C. Bufon, T. Heinzel, A. De, C.D. Mukherjee, Phys. Rev. B 84, 054205 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Physics of Vidyasagar University. The author AKB is thankful to the Department of Physics, Government General Degree College at Gopiballavpur-II. The author AKB is thankful to the CRF, IIT Kharagpur.
Funding
Author AKB is thankful to Dept. of Higher Education, Science and Technology and Biotechnology, Government of West Bengal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AKB and SS assisted the problem of the research, carried out the measurement and manuscript writing. AKB and TNG, KB assisted the measurement, discussed and helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhunia, A.K., Ghosh, T.N., Bhunia, K. et al. Nonlinear alternating current conduction study in manganese-doped zinc oxide nanocapsules and nanoplates. Appl. Phys. A 129, 81 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06373-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06373-4