Abstract
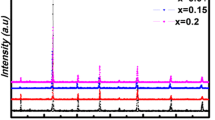
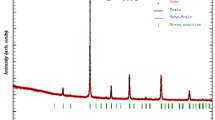
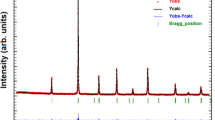
The thermal, structural and magnetocaloric properties of La1−xLixMn1−yFeyO3 (x = 0.1, 0.2 and y = 0, 0.1) powders were investigated in this study for application in magnetic refrigeration systems, using thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis and superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer. All samples were synthesized by flash combustion method using glycine as fuels and nitrates as precursors. The Li and Fe doped samples exhibited a rhombohedral structure and an R\(\overline{3}\)c space group. The increase of Li concentration to 20%, leads to the formation of LiMn2O4 spinel phase as a secondary phase. The ferromagnetic–paramagnetic transition was inferred from the temperature dependence of the magnetization. The magnetic entropy change (−ΔSM) has been calculated using the magnetization isotherms data. However, the increase of La substitution by Li from 10 to 20% leads to a decrease of the Curie temperature TC from 215 to 75 K accompanied with a maximum magnetic entropy change \(/ - \Delta {\text{S}}_{{\text{M}}}^{{{\text{max}}}} /\) from 3.63 to 1.52 J.Kg−1 K−1 under a magnetic field change of 5 T. Moreover, by the 10% Fe doping, there is a clear trend of decreasing the Curie temperature, the magnetic entropy change and the relative cooling efficiency. Therefore, in the vicinity of TC, (−ΔSM) reached a maximum value of 1.54 J.Kg−1 K−1 for La0.9Li0.1Mn0.9Fe0.1O3 and 0.96 J.Kg−1 K−1 for La0.8Li0.2Mn0.9Fe0.1O3. According to the Arrott plots results, a second-order ferromagnetic–paramagnetic transition was found for all the doped samples.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.A. Gschneidner Jr., V.K. Pecharsky, Magnetocaloric materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 387–429 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.matsci.30.1.387
B.F. Yu, Q. Gao, B. Zhang, X.Z. Meng, Z. Chen, Review on research of room temperature magnetic refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 26, 622–636 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-7007(03)00048-3
T. Tang, K.M. Gu, Q.Q. Cao, D.H. Wang, S.Y. Zhang, Y.W. Du, Magnetocaloric properties of Ag-substituted perovskite-type manganites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 222, 110–114 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)00544-8
K.A. Gschneidner Jr., V.K. Pecharsky, A.O. Tsokol, Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 1479 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/68/6/R04
V.K. Pecharsky, K.A. Gschneidner Jr., Some common misconceptions concerning magnetic refrigerant materials. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4614–4622 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1405836
V.K. Pecharsky, K.A. Gschneidner Jr., Y. Mudryk, D. Paudyal, Making the most of the magnetic and lattice entropy changes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3541–3547 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.03.013
S.A. Ahmed, Structural and electrical properties in La1−xLixMnO3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 340, 131–139 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.11.021
F.Y. Shih, K.Z. Fung, Effect of Li addition on structural, electrical and electrochemical properties on lanthanum manganite. J. Alloys Compd. 391, 95–103 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.06.046
S.L. Ye, W.H. Song, J.M. Dai, S.G. Wang, K.Y. Wang, C.L. Yuan, Y.P. Sun, Effect of Li substitution on the crystal structure and magnetoresistance of LaMnO3. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 5915–5919 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1319971
S. Roy, Y.Q. Guo, S. Venkatesh, N. Ali, Interplay of structure and transport properties of sodium-doped lanthanum manganite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 13, 9547 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/13/42/314
S. Bhattacharya, R.K. Mukherjee, B.K. Chaudhuri, H.D. Yang, Effect of Li doping on the magnetotransport properties of La0.7Ca0.3−yLiyMnO3 system: decrease of metal–insulator transition temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4101 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1580650
S.K. Barik, C. Krishnamoorthi, R. Mahendiran, Effect of Fe substitution on magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Sr0.3Mn1−xFexO3 (0.05≤ x≤ 0.20). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1015–1021 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.12.007
L.K. Leung, A.H. Morrish, B.J. Evans, Magnetic properties of iron-doped manganites. Phys. Rev. B 13, 4069 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.13.4069
K.H. Ahn, X.W. Wu, K. Liu, C.L. Chien, Magnetic properties and colossal magnetoresistance of La(Ca)MnO3 materials doped with Fe. Phys. Rev. B 54, 15299 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.54.15299
S. Hcini, M. Boudard, S. Zemni, M. Oumezzine, Effect of Fe-doping on structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Nd0.67Ba0.33Mn1−xFexO3 manganites. Ceram. Int. 40, 16041–16050 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.140
X.L. Wang, S.J. Kennedy, P. Gehringer, W. Lang, H.K. Liu, S.X. Dou, Colossal magnetoresistance in La1−xLixMnO3. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 7177 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.367793
S. Ait Bouzid, A.C. Galca, M. Sajieddine, V. Kuncser, A.M. Rostas, N. Iacob, M. Enculescu, L. Amarande, I. Pasuk, A. Essoumhi, Magneto-functionalities of La1-xAxMnO3 (A= K; Ba) synthesized by flash combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 839, 155546 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155546
K.V. Manukyan, A. Cross, S. Roslyakov, S. Rouvimov, A.S. Rogachev, E.E. Wolf, A.S. Mukasyan, Solution combustion synthesis of nano-crystalline metallic materials: mechanistic studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 24417–24427 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp408260m
E.A.C. Miranda, J.F.M. Carvajal, O.J.R. Baena, Effect of the fuels glycine, urea and citric acid on synthesis of the ceramic pigment ZnCr2O4 by solution combustion. Mater. Res. 18, 1038–1043 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.019915
C.B. Larsen, S. Samothrakitis, A.D. Fortes, A.O. Ayaş, M. Akyol, A. Ekicibil, M. Laver, Basal plane ferromagnetism in the rhombohedral manganite La0.85Ag0.15MnO3+δ. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 498, 166192 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166192
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
M. Gowrishankar, D. Babu, R.P. Saravanan, Room temperature multiferroism in La and Ti co-substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 171, 34–37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.044
A.K. Zak, W.A. Majid, M.E. Abrishami, R. Yousefi, X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13, 251–256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.11.024
G. Shabbir, A.H. Qureshi, K. Saeed, Nano-crystalline LaFeO3 powders synthesized by the citrate-gel method. Mater. Lett. 60, 3706–3709 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.093
J.I. Langford, Some applications of pattern fitting to powder diffraction data. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. 14, 185 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-3535(87)90018-9
O. AitMellal, L. Oufni, M.Y. Messous, F. Neatu, M. Florea, S. Neatu, A.M. Rostas, M. Secu, Structural and optical investigations of Ce3+/Mn2+-doped LaPO4 phosphors. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 2137–2147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08678-7
A.M. Ahmed, G. Papavassiliou, H.F. Mohamed, E.M.M. Ibrahim, Structural, magnetic and electronic properties on the Li-doped manganites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 392, 27–41 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.05.004
S. Jin, S. Zhang, H. Li, K. Chu, X. Yu, X. Guan, X. Pu, X. Liu, A-site Na-doping to enhance room-temperature TCR of La1-xNaxMnO3 polycrystalline ceramics. Mater. Today Commun. 28, 102496 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102496
Y.S. Chou, J.W. Stevenson, T.R. Armstrong, L.R. Pederson, Mechanical properties of La1-xSrxCo0.2Fe0.8O3 mixed-conducting perovskites made by the combustion synthesis technique. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 1457–1464 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2000.tb01410.x
Y.C. Liou, Y.R. Chen, Synthesis and microstructure of (LaSr)MnO3 and (LaSr)FeO3 ceramics by a reaction-sintering process. Ceram. Int. 34, 273–278 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.09.015
H. Li, K. Chu, X. Pu, X. Yu, X. Guan, S. Jin, X. Liu, Optimization of room-temperature TCR of polycrystalline La0.9-xSrxK0.1MnO3 ceramics by Sr adjustment. Ceram. Int. 47, 94–101 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.111
K.L. Yanapu, S.S. Samatham, D. Kumar, V. Ganesan, P.V. Reddy, Effect of bismuth doping on the physical properties of La–Li–Mn–O manganite. Appl. Phys. A 122, 199 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9731-5
K. De, R. Ray, R.N. Panda, S. Giri, H. Nakamura, T. Kohara, The effect of Fe substitution on magnetic and transport properties of LaMnO3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 339–346 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.09.118
S. Ait Bouzid, M. Sajieddine, O. Mounkachi, M. Mansori, A. Essoumhi, Influence of iron substitution on the ferromagnetic ordering and magnetic entropy variation in La1-xNaxMn1-yFeyO3 (x= 0.1, 0.2 and y= 0, 0.1). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537, 168194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168194
A. Ammar, S. Zouari, A. Cheikh-Rouhou, Fe doping effects on the structural and magnetic properties in Pr0.5Sr0.5Mn1−xFexO3 with 0≤ x≤ 0.3. Phys. Status Solidi C 1, 1645–1648 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssc.200304441
A.S. Wills, N.P. Raju, J.E. Greedan, Low-temperature structure and magnetic properties of the spinel LiMn2O4: a frustrated antiferromagnet and cathode material. Chem. Mater. 11, 1510–1518 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm981041
R. M’nassri, Magnetocaloric effect and its implementation in critical behaviour study of La0.67Ca0.33Mn0.9Fe0.1O3. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 551–557 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1153-7
L. Li, K. Nishimura, W.D. Hutchison, K. Mori, Large magnetocaloric effect in La2/3Ca1/3Mn1−xSixO3 (x= 0.05–0.20) manganites. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 175002 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/17/175002
T.L. Phan, P.Q. Thanh, P.D.H. Yen, P. Zhang, T.D. Thanh, S.C. Yu, Ferromagnetic short-range order and magnetocaloric effect in Fe-doped LaMnO3. Solid State Commun. 167, 49–53 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2013.06.009
J. Yang, W.H. Song, Y.Q. Ma, R.L. Zhang, B.C. Zhao, Z.G. Sheng, G.H. Zheng, J.M. Dai, Y.P. Sun, Structural, magnetic, and transport properties of the Cu-doped manganite La0.85Te0.15Mn1−xCuxO3 (0 ≤x≤ 0.20). Phys. Rev. B 70, 092504 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.70.092504
L. Li, K. Nishimura, M. Fujii, K. Mori, Effect of Mn-site Si substitution on magnetic, transport properties and colossal magnetoresistance in La2/3Ca1/3Mn1−xSixO3 (x= 0.05–0.25) system. Solid State Commun. 144, 10–14 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2007.07.033
M.S. Anwar, F. Ahmed, B.H. Koo, Structural distortion effect on the magnetization and magnetocaloric effect in Pr modified La0.65Sr0.35MnO3 manganite. J. Alloys Compd. 617, 893–898 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.105
A. Guedri, S. Mnefgui, S. Hcini, E.K. Hlil, A. Dhahri, B-site substitution impact on structural and magnetocaloric behavior of La0.55Pr0.1Sr0.35Mn1-xTixO3 manganites. J. Solid State Chem. 297, 122046 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122046
S. Hcini, F. Hcini, M.L. Bouazizi, S. Zemni, Correlation between magnetic and electrical properties of La0.7Ba0.15Ag0.15MnO3 manganite prepared by sol gel method. Appl. Phys. A 126, 498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03694-0
B.K. Banerjee, On a generalised approach to first and second order magnetic transitions. Phys. Lett. 12, 16–17 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9163(64)91158-8
R. M’nassri, M.M. Nofal, P. de Rango, N. Chniba-Boudjada, Magnetic entropy table-like shape and enhancement of refrigerant capacity in La1.4Ca1.6Mn2O7–La1.3Eu0.1Ca1.6Mn2O7 composite. RSC Adv. 9, 14916–14927 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00984A
A.H. El-Sayed, M.A. Hamad, Magnetocaloric effect in La1−xLixMnO3. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31, 4167–4171 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4699-3
X. Bohigas, J. Tejada, E. Del Barco, X.X. Zhang, M. Sales, Tunable magnetocaloric effect in ceramic pe rovskites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 390–392 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.121844
Z.M. Wang, G. Ni, Q.Y. Xu, H. Sang, Y.W. Du, Magnetic entropy change in perovskite manganites La0.65Nd0.05Ca0.3Mn0.9B0.1O3 (B= Mn, Cr, Fe). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 234, 371–374 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00424-3
Z. Liu, W.G. Lin, K.W. Zhou, J.L. Yan, Effect of Cu doping on the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of La0.7Sr0.25Na0.05Mn1−xCuxO3 manganites. Ceram. Int. 44, 2797–2802 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.021
A.E. Elyacoubi, R. Masrour, A. Jabar, Magnetocaloric effect and magnetic properties in SmFe1-xMnxO3 perovskite: monte carlo simulations. Solid State Commun. 271, 39–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2017.12.015
Z. Wang, Q. Xu, H. Zhang, Magnetocaloric effect at room temperature in manganese perovskite La0.65Nd0.05Pb0.3MnO3 with double resistivity peaks. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 3229–3233 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.07.013
M.C. Silva-Santana, P. Barrozo, E.J.R. Plaza, L. de los Santos Valladares, N.O. Moreno, Magnetocaloric and magnetic properties of SmFe0.5Mn0.5O3 complex perovskite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 612–617 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.076
K. Laajimi, M. Khlifi, E.K. Hlil, M.H. Gazzah, J. Dhahri, Enhancement of magnetocaloric effect by Nickel substitution in La0.67Ca0.33Mn0.98Ni0.02O3 manganite oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 491, 165625 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165625
M. Baazaoui, M. Boudard, S. Zemni, Magnetocaloric properties in Ln0.67Ba0.33Mn1−xFexO3 (Ln= La or Pr) manganites. Mater. Lett. 65, 2093–2095 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.04.051
Y. Sun, W. Tong, Y. Zhang, Large magnetic entropy change above 300 K in La0.67Sr0.33Mn0.9Cr0.1O3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 232, 205–208 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00263-3
M.R. Laouyenne, M. Baazaoui, K. Farah, E.K. Hlil, M. Oumezzine, A large magnetocaloric effect of La0.8Na0.2Mn0.97Bi0.03O3 manganite synthesized by pechini Sol-Gel method and compared to the sample synthesized by solid-state route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 474, 393–399 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.11.070
S.E. Kossi, S. Ghodhbane, S. Mnefgui, J. Dhahri, E.K. Hlil, The impact of disorder on magnetocaloric properties in Ti-doped manganites of La0.7Sr0.25Na0.05Mn (1–x) TixO3 (0≤ x≤ 0.2). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 395, 134–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.07.050
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Moroccan National Center for Scientific and Technical Research in the framework of excellence scholarship number 17USMS2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ait Bouzid, S., Sajieddine, M., Hlil, E.K. et al. Structural, magnetic transition and magnetocolaric properties of La1−xLixMn1−yFeyO3 (x = 0.1, 0.2 and y = 0, 0.1) manganites. Appl. Phys. A 128, 121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05254-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05254-6