Abstract
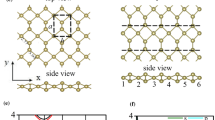
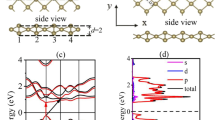
The size- and diameter-dependent structural, electronic and dielectric properties of tellurium 1-D nanowire (Te-NW) and tellurium nanotubes (Te-NTs) with trigonal and hexagonal cross sections have been calculated using density functional theory . The nanostructures having trigonal cross sections are progressively more stable than hexagonal Te-NTs with decreasing binding energy. We further find that bandgap of trigonal cross section is larger as compare to the hexagonal one. Dielectric properties of these materials are strongly dependent on the direction of polarization of the incident light. The peaks in absorption spectrum come from the transition between the conduction and valence band states. The real part of dielectric function reveals the existence of plasma frequency which indicates that the materials are behaving like dielectric ones in the parallel polarization direction. It is anticipated that these results may point towards new possibilities in the development of optoelectronic devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Grosshans, G.V. Assche, J. Wenger, R. Brouri, N.J. Cerf, P. Grangier, Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238–241 (2003)
Z.L. Wang, Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312, 242–246 (2006)
M. Law, L.E. Greene, J.C. Johnson, R. Saykally, P. Yang, Nanowire dye-sensitized solar cells. Nature Mater. 4, 455–459 (2005)
Y. Wu, R. Fan, P. Yang, Block-by-block growth of single-crystalline si/SiGe superlattice nanowires. Nano Lett. 2, 83–86 (2002)
Y. Guo, S. Wang, Y. Jia, W.-S. Su, Structural, electronic, and optical properties of \(\alpha\)-te tubular nanostructures: A first-principles study. APL Mater. 7, 031105 (2019)
Z. Liu, Z. Hu, J. Liang, S. Li, Y. Yang, S. Peng, Y. Qian, Size-controlled synthesis and growth mechanism of monodisperse tellurium nanorods by a surfactant-assisted method. Langmuir 20, 214–218 (2004)
P.K. Balguri, D.G.H. Samuel, D.B. Aditya, S.V. Bhaskar, U. Thumu, Enhanced flexural strength of tellurium nanowires/epoxy composites with the reinforcement effect of nanowires. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 310, 012157 (2018)
P. Mohanty, T. Kang, B. Kim, J. Park, Synthesis of single crystalline tellurium nanotubes with triangular and hexagonal cross sections. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 791–795 (2006)
P. Ghosh, M. U. Kahaly, and U. V. Waghmare, “Atomic and electronic structures, elastic properties, and optical conductivity of bulk te and te nanowires: A first-principles study,” Physical Review B, vol. 75, June 2007
G.D. Moon, S. Ko, Y. Xia, U. Jeong, Chemical transformations in ultrathin chalcogenide nanowires. ACS Nano 4, 2307–2319 (2010)
Y. Wang, Z. Tang, P. Podsiadlo, Y. Elkasabi, J. Lahann, N. Kotov, Mirror-like photoconductive layer-by-layer thin films of te nanowires: The fusion of semiconductor, metal, and insulator properties. Adv. Mater. 18, 518–522 (2006)
H.-W. Liang, J.-W. Liu, H.-S. Qian, S.-H. Yu, Multiplex templating process in one-dimensional nanoscale: Controllable synthesis, macroscopic assemblies, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1450–1461 (2013)
J.-W. Liu, J.-H. Zhu, C.-L. Zhang, H.-W. Liang, S.-H. Yu, Mesostructured assemblies of ultrathin superlong tellurium nanowires and their photoconductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 8945–8952 (2010)
J.-W. Liu, J. Xu, H.-W. Liang, K. Wang, S.-H. Yu, Macroscale ordered ultrathin telluride nanowire films, and tellurium/telluride hetero-nanowire films. Angewandte Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 7420–7425 (2012)
D. Tsiulyanu, A. Tsiulyanu, H.-D. Liess, I. Eisele, Characterization of tellurium-based films for NO2 detection. Thin Solid Films 485, 252–256 (2005)
Z.-H. Lin, Z. Yang, H.-T. Chang, Preparation of fluorescent tellurium nanowires at room temperature. Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 351–357 (2008)
T.S. Sreeprasad, A.K. Samal, T. Pradeep, Bending and shell formation of tellurium nanowires induced by thiols. Chem. Mater. 21, 4527–4540 (2009)
Y.-J. Zhu, W.-W. Wang, R.-J. Qi, X.-L. Hu, Microwave-assisted synthesis of single-crystalline tellurium nanorods and nanowires in ionic liquids. Angewandte Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 1410–1414 (2004)
B. Mayers, Y. Xia, Formation of tellurium nanotubes through concentration depletion at the surfaces of seeds. Adv. Mater. 14, 279–282 (2002)
B. Geng, Y. Lin, X. Peng, G. Meng, L. Zhang, Large-scale synthesis of single-crystalline te nanobelts by a low-temperature chemical vapour deposition route. Nanotechnology 14, 983–986 (2003)
M. Mo, J. Zeng, X. Liu, W. Yu, S. Zhang, Y. Qian, Controlled hydrothermal synthesis of thin single-crystal tellurium nanobelts and nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 14, 1658–1662 (2002)
Q. Wang, G.-D. Li, Y.-L. Liu, S. Xu, K.-J. Wang, J.-S. Chen, Fabrication and growth mechanism of selenium and tellurium nanobelts through a vacuum vapor deposition route. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 12926–12932 (2007)
Q. Lu, F. Gao, S. Komarneni, Biomolecule-assisted reduction in the synthesis of single-crystalline tellurium nanowires. Adv. Mater. 16, 1629–1632 (2004)
C.J. Hawley, B.R. Beatty, G. Chen, J.E. Spanier, Shape-controlled vapor-transport growth of tellurium nanowires. Cryst. Growth Des. 12, 2789–2793 (2012)
J.-W. Liu, J. Xu, W. Hu, J.-L. Yang, S.-H. Yu, Systematic synthesis of tellurium nanostructures and their optical properties: From nanoparticles to nanorods, nanowires, and nanotubes. ChemNanoMat 2, 167–170 (2015)
A. Kramer, M. L. V. de Put, C. L. Hinkle, and W. G. Vandenberghe, “Tellurium as a successor of silicon for extremely scaled nanowires: a first-principles study,” npj 2D Materials and Applications, vol. 4, May 2020
W. Huang, Y. Zhang, Q. You, P. Huang, Y. Wang, Z. N. Huang, Y. Ge, L. Wu, Z. Dong, X. Dai, Y. Xiang, J. Li, X. Zhang, and H. Zhang, “Enhanced photodetection properties of tellurium@selenium roll-to-roll nanotube heterojunctions,” Small, p. 1900902, Apr. 2019
G. Kresse, J. Hafner, Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 47, 558–561 (1993)
G. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996)
G. Kresse, D. Joubert, From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple [phys. rev. lett. 77, 3865 (1996)]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1396–1396 (1997)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996)
H.J. Monkhorst, J.D. Pack, Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188–5192 (1976)
S. Yi, Z. Zhu, X.-L. Cai, J. Cho, The nature of bonding in bulk tellurium composed of one-dimensional helical chains. Inorgan. Chem. 57, 12 (2017)
V.B. Anzin, M.I. Eremets, Y.V. Kosichkin, A.I. Nadezhdinskii, A.M. Shirokov, Measurement of the energy gap in tellurium under pressure. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 42, 385–390 (1977)
M. Gajdoš, K. Hummer, G. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, F. Bechstedt, Linear optical properties in the projector-augmented wave methodology. Phys. Rev. B 73, 045112 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge UGC for providing the computational HPC facility in the Department of Physics, HPU Summer Hill shimla through FIST grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, T., Thakur, R. & Sharma, R. Structural, electronic and dielectric properties of Tellurium 1-D nanostructures : a DFT study. Appl. Phys. A 128, 41 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05183-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05183-4